Echinax clara, Haddad, Charles R., 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.209739 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6174682 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CF0B6C69-FFA0-023F-FF21-F94BFA9EAFF8 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Echinax clara |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Echinax clara View in CoL sp. nov.
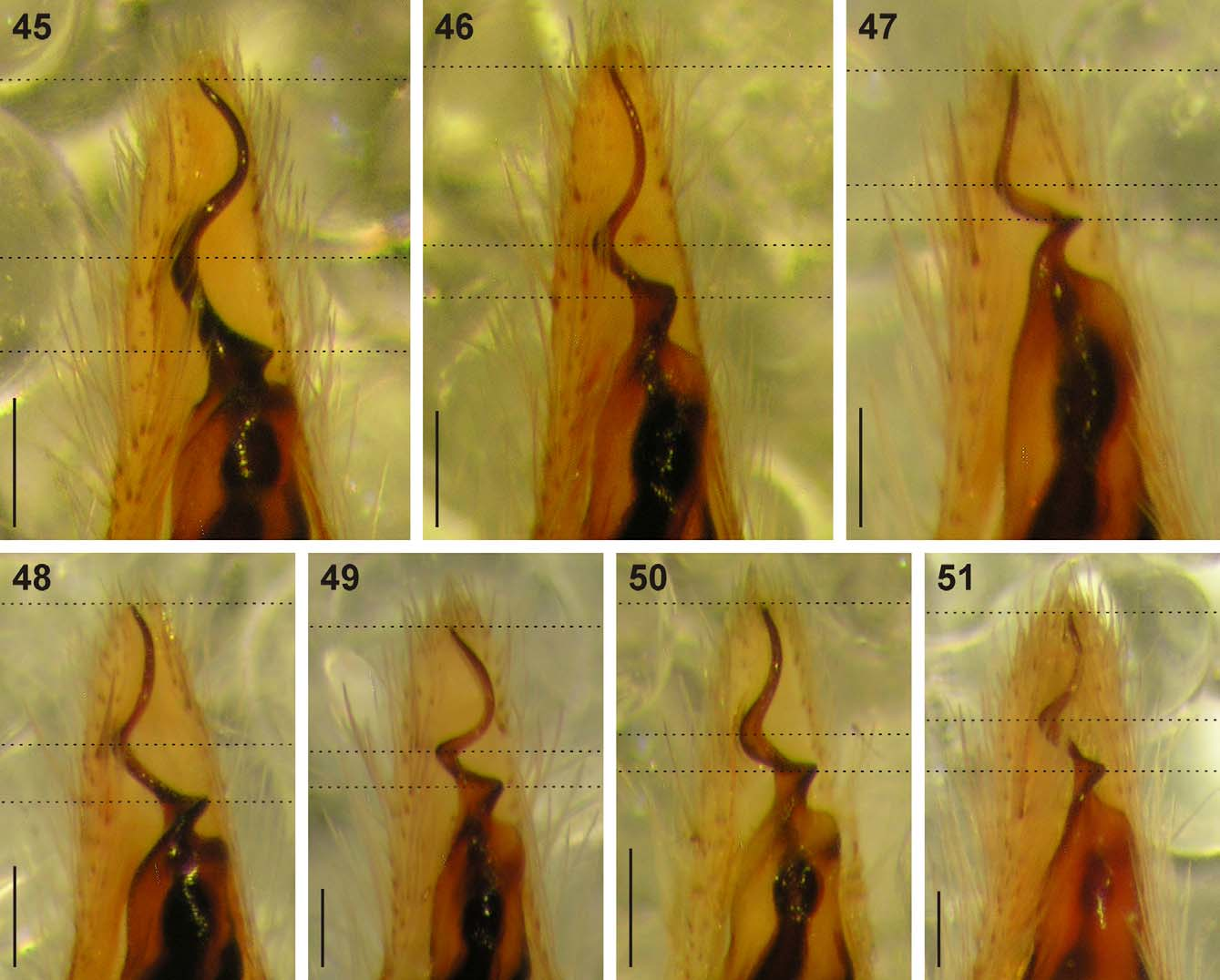
Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1 – 16 , 45 View FIGURES 45 – 51 , 52–55 View FIGURES 52 – 55
Etymology. The species name is Latin for “clear, distinct”, referring to the distinct shape of the male embolus.
Diagnosis. Females can be easily recognised by the very small epigynal ridges ( Fig. 52 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ) and the nearly transverse copulatory ducts bent at a right angle medially ( Fig. 53 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ). The male is unique amongst the African species in having a prolateral and retrolateral spine in the proximal third of the cymbium dorsally ( Fig. 55 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ), as well as by the relatively short and strongly curved distal coil of the embolus ( Fig. 54 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ).
Female (holotype, Luki, MRAC 236910). Measurements: CL 1.85, CW 1.53, AL 2.35, AW 1.64, TL 4.18 (3.95–4.60), FL 0.19, SL 0.90, SW 0.90, AME–AME 0.06, AME–ALE 0.02, ALE–ALE 0.32, PME–PME 0.11, PME–PLE 0.07, PLE–PLE 0.39, PERW 0.54, MOQAW 0.30, MOQPW 0.33, MOQL 0.37.
Length of leg segments: I 1.65 + 0.63 + 1.33 + 1.30 + 0.65 = 5.56; II 1.61 + 0.63 + 1.28 + 1.30 + 0.65 = 5.47; III 1.52 + 0.60 + 1.25 + 1.38 + 0.65 = 5.40; IV 1.87 + 0.65 + 1.55 + 2.00 + 0.74 = 6.81.
General appearance as in Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1 – 16 . Carapace cream, eye region black except between PME; broad median band of black feathery setae from PER to posterior slope, with fine black stripe from posterior of fovea to posterior margin of carapace; lateral margins with broad stripe of black feathery setae from palpal coxa to posterior margin. All eyes with black rings; AER procurved, medians much larger than laterals; AME separated by distance slightly less than ½ their diameter; AME separated from ALE by distance approximately 1⁄10 AME diameter; clypeus height equal to 1½ AME diameter; PER strongly procurved, medians slightly larger than laterals; PME separated by distance equal to their diameter; PME separated from PLE by distance approximately equal to ½ PME diameter; CW: PERW = 2.83: 1. Chelicerae cream, with pectinate curved setae on promargin; two closely spaced teeth on promargin, distal tooth much larger than proximal; retromargin with two adjacent subequal teeth, distal tooth very slightly larger than proximal tooth, close to fang base. Endites and sternum cream, without markings; labium cream, with black transverse marking along proximal margin. Legs cream, spine bases with faint black spot; femora all with incomplete black ventral ring distally; remaining leg segments uniform in colour. Leg spination: femora: I pl 2 do 3 rl 2, II pl 2 do 3 rl 2, III pl 2 do 3 rl 2, IV pl 2 do 3 rl 1; all femora with plv and rlv rows of erect setae; patellae: all with do 1 terminal spine; tibiae: I pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 3 rlv 2, II pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 3 rlv 2, III pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 2 rlv 2, IV pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 2 rlv 2 vt 2; metatarsi: I pl 1 rl 1 plv 2 rlv 2, II pl 1 rl 1 plv 2 rlv 2, III pl 3 rl 3 plv 1 rlv 1 vt 3, IV pl 3 rl 3 plv 1 rlv 1 vt 3. Palpal spination: femora: pl 1 do 2 rl 1, with plv and rlv erect setae; patellae: pl 1 do 2; tibiae: pl 1 do 2 plv 1; tarsi: pl 1 rl 1 plv 3 rlv 1. Abdomen with small dorsal scutum extending ¼ abdomen length; dorsum pale grey, with narrow black oval marking anteriorly, black X-shaped marking at ½ abdomen length, and lateral margins with irregular black marking; black feathery setae on markings, white feathery setae surrounding them; venter creamy-grey, covered in short straight setae with scattered longer setae, with dark grey subrectangular marking medially. Epigyne with short curved lateral ridges at midpoint of epigyne, separated by at least their width, with copulatory openings situated laterally in ridges ( Fig. 52 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ); copulatory ducts initially straight, nearly transverse, curving anteriorly at right angle medially, entering oval anterior ST II; broad ducts connecting ST II to broad, kidney-shaped posterior ST I; ST I nearly as broad as ST II ( Fig. 53 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ).
Male (paratype, Luki, MRAC 236912). Measurements: CL 1.80, CW 1.47, AL 2.15, AW 1.10, TL 3.80 (3.80–3.90), FL 0.23, SL 0.77, SW 0.77, AME–AME 0.05, AME–ALE 0.01, ALE–ALE 0.29, PME–PME 0.08, PME–PLE 0.06, PLE–PLE 0.32, PERW 0.48, MOQAW 0.30, MOQPW 0.29, MOQL 0.35.
Length of leg segments: I 1.85 + 0.60 + 1.50 + 1.43 + 0.73 = 6.11; II 1.78 + 0.57 + 1.40 + 1.38 + 0.70 = 5.83; III 1.65 + 0.55 + 1.38 + 1.50 + 0.68 = 5.76; IV 1.93 + 0.58 + 1.60 + 2.03 + 0.75 = 6.89.
General appearance as in Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1 – 16 , male more slender and smaller than female. Carapace cream, eye region black except between PME; broad median band of black feathery setae from PER to posterior slope, broken up by asetose striae directed between coxae, with fine black stripe from posterior of fovea to posterior margin of carapace; lateral margins black, markings expanded medially from coxae, with broad stripe of black feathery setae from palpal coxa to posterior margin. All eyes with black rings; AER procurved, medians much larger than laterals; AME separated by distance slightly less than ½ their diameter; AME separated from ALE by distance approximately 1⁄10 AME diameter; clypeus height equal to 1½ AME diameter; PER strongly procurved, medians slightly larger than laterals; PME separated by distance equal to ¾ their diameter; PME separated from PLE by distance approximately equal to ½ PME diameter; CW: PERW = 3.06: 1. Chelicerae cream, with pectinate curved setae on promargin; two closely spaced teeth on promargin, distal tooth larger than proximal; retromargin with two adjacent teeth, subequal in size, distal tooth close to fang base. Endites and sternum cream, without markings; labium cream, with black transverse marking along proximal margin. Legs cream, spine bases with distinct black spot; femora all with incomplete black markings proximally, at ½ and ½ femur length and distally, starting mediolaterally and curving laterally; patellae all black distally and laterally; tibiae all with broken black markings laterally; metatarsi with black rings proximally, medially and distally, corresponding to paired spines. Leg spination: femora: I pl 2 do 3 rl 2, II pl 2 do 3 rl 2, III pl 2 do 3 rl 2, IV pl 2 do 3 rl 2; all femora with plv and rlv rows of erect setae; patellae: all with do 1 terminal spine; tibiae: I pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 3 rlv 2, II pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 3 rlv 2, III pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 2 rlv 2, IV pl 2 do 1 rl 2 plv 2 rlv 2 vt 2; metatarsi: I pl 1 rl 1 plv 2 rlv 2, II pl 1 rl 1 plv 2 rlv 2, III pl 2 rl 2 plv 1 rlv 1 vt 3, IV pl 2 rl 2 plv 1 rlv 1 vt 3. Palpal spination: femora: pl 1 do 2 rl 1, with plv and rlv erect setae; patellae: pl 1 do 2; tibiae: pl 1 do 1 plv 1; tarsi: pl 1 rl 1 plv 2 rlv 1. Abdomen with scutum nearly covering entire dorsum; dorsum mottled black with two pairs of cream spots anteriorly and medially, with fine cream chevrons posteriorly; dorsum covered predominantly with brown feathery setae, with scattered black feathery setae; venter cream, with broad black stripe along midline from pedicel to spinnerets, covered in short straight setae with scattered long straight setae. Male palp cream, cymbium yellow-brown, with a few spatulate setae dorsally in distal ½ ( Fig. 55 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ); tegulum pear-shaped, yellow-brown with dark brown ducts; embolus with broad base and two ridges, first leading to prolateral and second to retrolateral basal loop of embolus; embolus long, with 1½ coils, distal section strongly curved; longitudinal distance from retrolateral bend to prolateral bend approximately ½ the distance from prolateral bend to embolus tip ( Figs 45 View FIGURES 45 – 51 , 54 View FIGURES 52 – 55 ).
Type material. Holotype Ƥ: D.R. CONGO: Bas-Congo: Mayombe, Luki Forest Reserve, 05°37'S, 13°05'E, 266 m a.s.l., leg. D. de Bakker & J.-P. Michiels, 14.IX.2007 (canopy fogging, secondary rainforest) ( MRAC 236910).
Paratypes: D.R. CONGO: Bas-Congo: Mayombe, Luki Forest Reserve, 05°37'S, 13°05'E, 266 m a.s.l., leg. D. de Bakker & J.-P. Michiels, 1.X.2007 (canopy fogging, primary rainforest), 13 ( MRAC 236903); same data, 26.IX.2007, 2Ƥ ( MRAC 236901); same data, 30.IX.2007, 1Ƥ ( MRAC 236913); same locality, leg. D. de Bakker & J.-P. Michiels, 17.IX.2007 (canopy fogging, secondary rainforest), 1Ƥ ( MRAC 236904); same data, 28.IX.2007, 23 ( MRAC 236912); same data, 20.IX.2007, 2Ƥ ( MRAC 236906); same data, 24.IX.2007, 3Ƥ ( MRAC 236908). GHANA: Kakum forest, 05°20'N, 01°23'W, leg. R. Jocqué, D. de Bakker & L. Baert, 21.XI.2005 (fogging, primary forest), 1Ƥ ( MRAC 236916); same data, 18.XI.2005, 3Ƥ ( MRAC 236918).
Additional material examined. None.
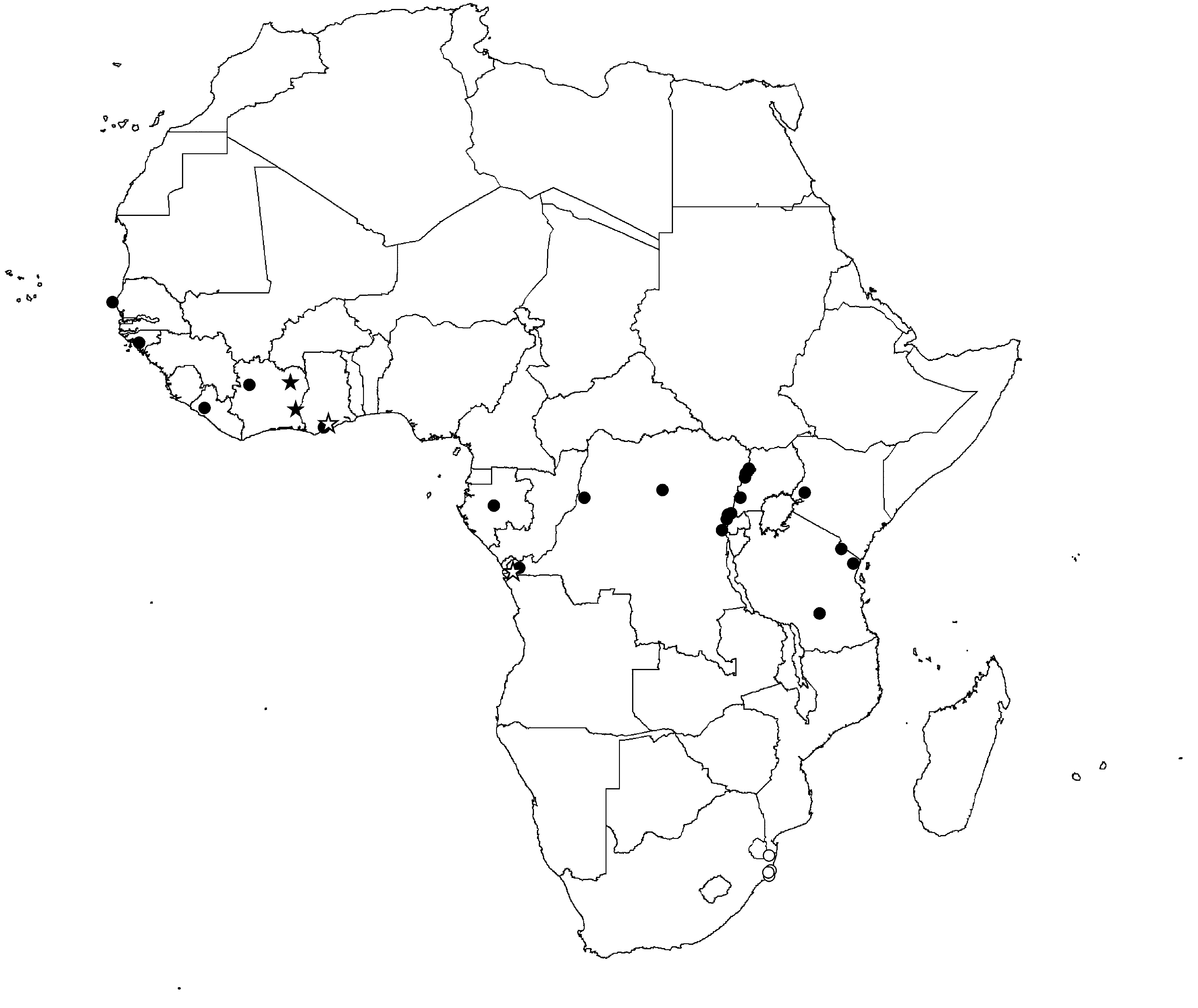
Distribution. Known only from two localities in Central and West Africa ( Fig. 68 View FIGURE 68 ).
Natural history. The species was only collected by canopy fogging in primary and secondary rainforest.
| MRAC |
Musée Royal de l’Afrique Centrale |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |