Hygrodromicus shaanxiensis Cheng, Li & Peng, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4963.1.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5AE81AAE-AF66-4973-B4E6-644134B7B67C |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4697018 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D13B87B7-FFC1-3649-A7FB-1C5EFF53A82A |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi (2021-04-16 08:59:31, last updated 2023-11-02 14:59:22) |
|
scientific name |
Hygrodromicus shaanxiensis Cheng, Li & Peng |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Hygrodromicus shaanxiensis Cheng, Li & Peng View in CoL , sp. n.
( Figs 5–7 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 )
Type material (1 ♂). Holotype: ♂ ‘ China: Shaanxi Prov., Ankang City, Ningshaan County, Pingheliang , 33°28′N, 108°29′E, alt. 2100 m, 13.vii.2012, Yu-Hong Pan leg. GoogleMaps / HOLOTYPE <red rectangular label, printed> ♂, H. shaanxiensis sp. n., det. Cheng, Li & Peng, 2021, SNUC’ ( SNUC) .
Description. Measurements (in mm) and ratios: BL 5.86, FL 3.22, HL 0.67, HW 0.95, PL 0.89, PWb 0.89, PWm 1.06, EL 1.67, EW 1.83, AnL 3.17, AeL 1.13; HL/HW 0.71, PL/PWm 0.84, EL/EW 0.91.
Body ( Fig. 5A View FIGURE 5 ) broad, dark brown, with paler mouthparts, antennae and tarsi, reddish-brown.
Head ( Fig. 5B View FIGURE 5 ) subtriangular and transverse, broadest at level of eyes; vertex strongly transverse, with deep Ushaped impression between eyes; frons between supra-anternnal tubercles slightly impressed; clypeus indistinctly convex; eyes moderately prominent, about 1.2 times as long as temples; ocelli moderately large, distinct and promi- nent, distance between ocelli 1.5 times as long as distance between ocellus and posterior margin of eye. Pubescence on head long, dense and decumbent in anterior portion. Labrum ( Fig. 5D View FIGURE 5 ) subrectangular, with nearly straight anterior margin. Mandibles as in Figs 5E–F View FIGURE 5 ; right mandible with small, distinct, subtriangular tooth on inner margins near middle. Maxillary palpus as in Fig. 5G View FIGURE 5 . Labium as in Fig. 5H View FIGURE 5 . Antennae as in Fig. 5C View FIGURE 5 ; length × width (in mmm) of antennomeres 1–11: 0.27 × 0.12: 0.21 × 0.10: 0.27 × 0.10: 0.25 × 0.10: 0.28 × 0.10: 0.27 × 0.10: 0.29 × 0.11: 0.27 × 0.11: 0.29 × 0.11: 0.29 × 0.11: 0.40 × 0.10.
Male. Apical margin of abdominal tergite VIII ( Fig. 5I View FIGURE 5 ) slightly emarginated; apical margin of sternite VIII ( Fig. 5J View FIGURE 5 ) broadly emarginated. Aedeagus ( Figs 6D–F View FIGURE 6 ) long, median lobe indistinctly narrowed toward moderately wide, rounded apex, curved ventrad (if see laterally, as in Fig. 6B View FIGURE 6 ); parameres symmetrical, slender, exceeding apex of median lobe, each bearing three apical setae; apical portion of internal sac with characteristic curved membranous structures, with very long flagellum between them.
Female. Unknown.
Comparative notes. Hygrodromicus shaanxiensis sp. n. differs from the remaining species of the genus by the shape of the median lobe and structure of the internal sac.
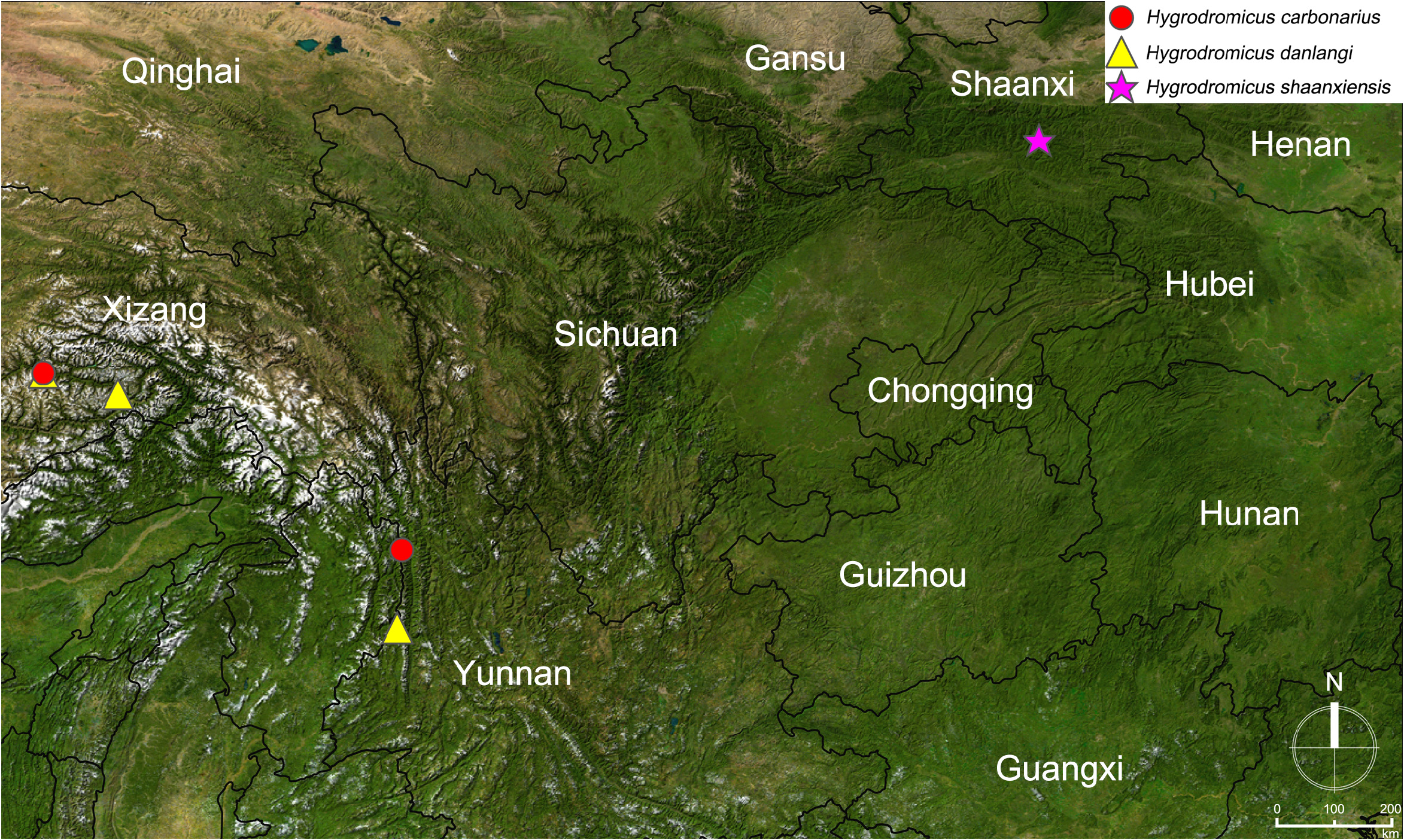
Distribution. Central China: Qinling Mountains, Shaanxi ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ).
Bionomics. The specimen was collected at elevation about 2100 m a.s.l. and was taken from mixed leaf litter near a stream.
Etymology. The specific epithet is the Latin adjective derived from the name of the type locality: Shaanxi Province.
FIGURE 5. Hygrodromicus shaanxiensis sp. n.. Habitus of male in dorsal view (A); head in dorsal view (B); left antenna (C); labrum in dorsal view (D); left maxilla in ventral view (G); right (E) and left (F) mandibles in dorsal view; labium in ventral view (H); abdominal sternite VIII (I) and tergite VIII (J). Scale bar: 2.0 mm in A; 1.0 mm in C; 0.30 mm in B; 0.10 mm in D–J.
FIGURE 6. Aedeagus features of Hygrodromicus shaanxiensis sp. n.: dorsal view (A), lateral view (B), and ventral view (C). Scale bar: 0.20 mm.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.