Alocobisium tibetense, Hu, Junfang & Zhang, Feng, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3641.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6A804C8E-47A4-4381-8363-5C9D7DF908E0 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6158871 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/739DCAF5-6947-4009-B158-B9909E8AF647 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:739DCAF5-6947-4009-B158-B9909E8AF647 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Alocobisium tibetense |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Alocobisium tibetense View in CoL sp. nov.
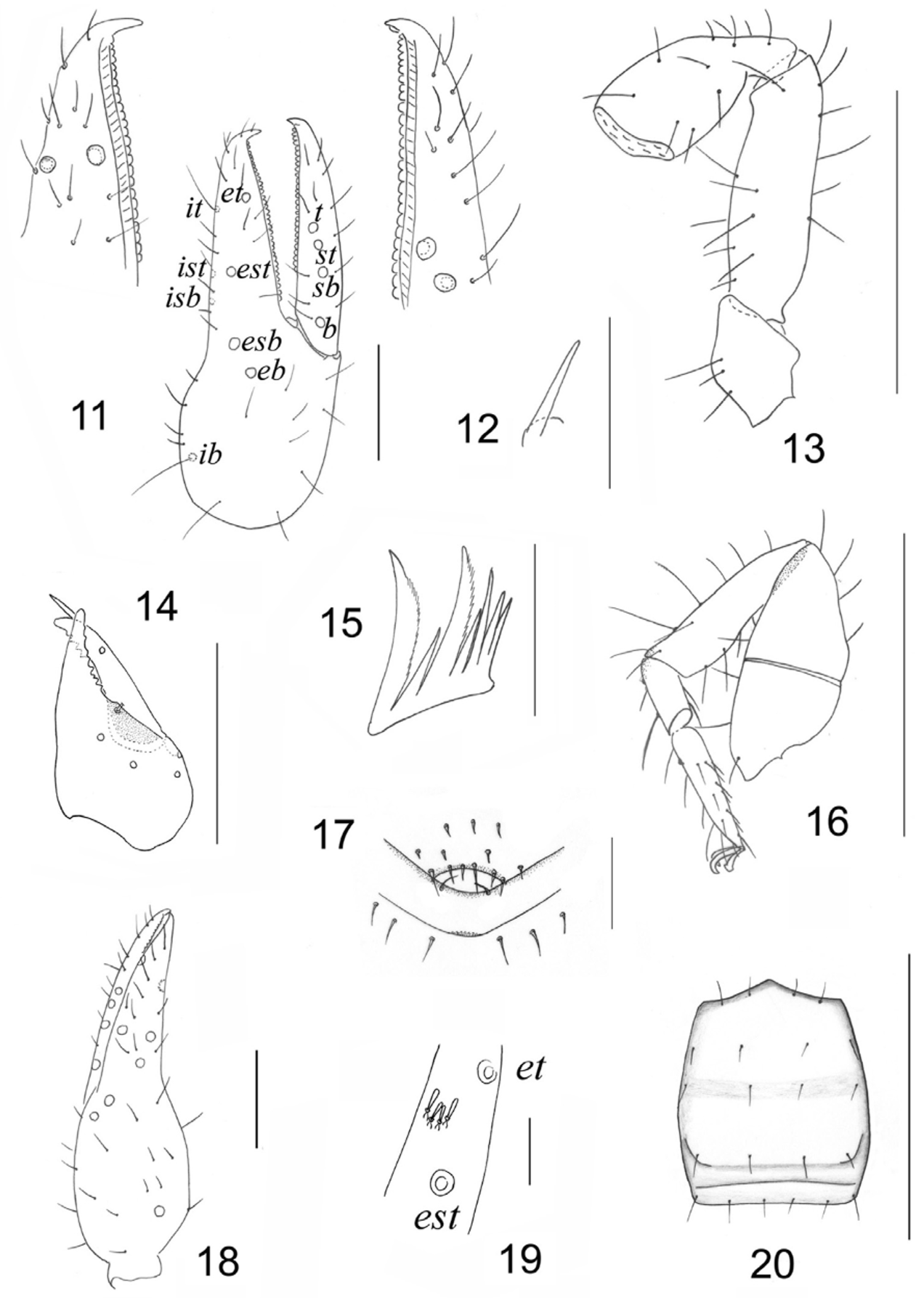
( Figs 10–20 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURES 11 – 20 )
Type material. Holotype male (Ps.-MHBU-XZ83010801), Medog County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China, 1100 m alt., 8 January 1983, Yinheng Han leg. Paratypes: 4 males and 2 females (Ps.-MHBU-XZ83010802- 83010807), same data as for holotype.
Diagnosis. Small species; carapace with a distinct furrow near posterior margin and a vestigial furrow near middle; eyeless; trichobothrium ib situated near base of hand, ist closer to est than to isb, st nearer to t than to sb.
Etymology. The specific name refers to the type locality.
Description. Carapace and pedipalps yellowish-brown, furrow darker; other parts yellow ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 ). Carapace. Smooth and longer than broad ( Fig. 20 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ), with a total of 22–24 setae, including 4 on anterior margin and 6 on posterior margin (6–8 on posterior margin in female); epistome rounded; eyeless; with a distinct furrow near posterior margin and a vestigial furrow near middle.
Abdomen elongate. Pleural membrane with longitudinal striate and medially weakly granulated. Male tergal chaetotaxy: 8: 8: 8: 8: 8: 8: 8: 8: 6: 4+4T: 4+4T; anterior genital operculum ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) with 12–14 setae; posterior genital operculum with 2 anterior setae and 6–8 marginal setae, genitalia with 3+3 internal setae; one microseta in front of each stigma of sternites III and IV; sternal chaetotaxy (IV–XI): 8: 12: 12: 12: 12: 12: 10: 6+4T; no gland openings on sternite VI. Female tergal chaetotaxy: 5–6: 7–8: 8: 8: 8: 8: 7: 7: 7: 6: 4+4T; anterior genital operculum with 4 setae and posterior genital operculum with 10 marginal setae; chaetotaxy of sternites IV–XI: 12: 14: 14: 14: 12: 10: 8–10: 6+4T; anal cone with 2 dorsal and 2 ventral setae.
Pedipalps smooth. Apex of coxa with 2 setae, setae P 8–9, I 7, II 7, III 5, IV 5. Trochanter ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) without tubercle. Male fixed chelal finger ( Figs 11, 18 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) with 33–35 teeth, movable finger with 28–30 teeth, all teeth contiguous (female fixed chelal finger with 39–43 contiguous teeth, movable finger with 30–35 teeth). Trichobothrium ib near base of hand, trichobothria eb and esb on distal portion of hand, ist closer to est than to isb; 4 antiaxial feather-shaped setae clustered between et and est ( Fig. 19 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ); trichobothrium st nearer to t than to sb, t short and acuminate, situated near middle of movable finger.
Cheliceral palm ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) with 5 setae, movable finger with 1 seta; fixed finger with 8–9 teeth; movable finger with 4–5 teeth; serrula exterior with 19–20 lamellae; serrula interior with 13–15 lamellae; galea ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) simple, without branchlets, longer in female than in male; rallum ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) of 7 blades, the proximal and antepenultimate blades larger than others and with denticles on anterior margin.
Junction between femur and patella of leg IV ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 11 – 20 ) perpendicular, leg IV basitarsus with one subbasal tactile seta (TS 0.30); telotarsus with one tactile seta (TS 0.26); subterminal seta bifurcate distally, arolium shorter than the thin and smooth claws.
Dimensions (in mm; length/breadth or depth ratio in parentheses). Male. Body length 1.16–1.30. Carapace 0.39–0.40/0.33–0.36 (1.11–1.18). Pedipalps: trochanter 0.18/0.11 (1.64), femur 0.35–0.37/0.11–0.12 (3.08–3.18), patella 0.28–0.29/0.14–0.15 (1.93–2.0 0), chela (with pedicel) 0.54–0.58/0.18–0.20 (2.90–3.00), chela (without pedicel) 0.50–0.53 (2.65–2.78), hand length (with pedicel) 0.27–0.28 (1.40–1.50), movable finger length 0.30–0.32 (1.11–1.14 times longer than hand with pedicel). Chelicera 0.18–0.19/0.11–0.13 (1.46–1.64), movable finger length 0.13–0.14. Leg I: femur 0.15–0.18/0.07–0.08 (2.14–2.25), patella 0.14–0.15/0.07–0.08 (1.88–2.0 0), tibia 0.15/0.04–0.05 (3.00–3.75), basitarsus 0.05–0.08/0.04 (1.25–2.00), telotarsus 0.13–0.14/0.03–0.04 (3.50– 4.33). Leg IV: femur + patella 0.33–0.35/0.13–0.15 (2.33–2.54), tibia 0.24–0.28/0.07 (3.43–4.00), basitarsus 0.10– 0.11/0.05 (2.00–2.20), telotarsus 0.18–0.19/0.04 (4.50–4.75).
Female. Body length 1.10–1.15. Carapace 0.40–0.41/0.35–0.36 (1.14). Pedipalps: trochanter 0.18–0.19/0.11–0.12 (1.58–1.64), femur 0.37–0.38/0.11–0.13 (2.92–3.36), patella 0.29–0.30/0.14–0.15 (2.00–2.07), chela (with pedicel) 0.59–0.63/0.20–0.21 (2.95–3.00), chela (without pedicel) 0.55–0.58 (2.75–2.76), hand length (with pedicel) 0.29– 0.30 (1.43–1.45), movable finger length 0.30–0.33 (1.03–1.11 times longer than hand with pedicel). Chelicera 0.22– 0.23/0.13 (1.69–1.77), movable finger length 0.14–0.15. Leg I: femur 0.17–0.18/0.06–0.07 (2.57–2.83), patella 0.15– 0.16/0.07–0.08 (2.00–2.14), tibia 0.16–0.18/0.05–0.06 (3.00–3.20), basitarsus 0.08–0.09/0.04 (2.00–2.25), telotarsus 0.14–0.15/0.04 (3.50–3.75). Leg IV: femur + patella 0.33–0.35/0.14–0.15 (2.33–2.34), tibia 0.25–0.28/0.07–0.08 (3.50–3.57), basitarsus 0.11–0.12/0.05–0.06 (2.00–2.20), telotarsus 0.17–0.18/0.04 (4.25–4.50).
Distribution. This species is known from China (Tibet).
Remarks. A. tibetense sp. nov. differs from A. rahmi in having the carapace thinner (1.21–1.25 times vs. 1.14 times as long as broad) in the female and bearing a distinct posterior furrow. A. tibetense sp. nov. resembles Alocobisium malaccense Beier, 1952 , from Malaysia, in having a distinct furrow on the carapace, but differs in the position of the trichobothrium st (nearer to sb than to t in A. malaccense ) and the larger size of the pedipalps ( A. malaccense femur length 0.23 mm, patella length 0.19 mm, hand length 0.20 mm and finger length 0.20 mm).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |