Delicatophycus porosus Mironov, Chudaev & Jüttner, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.548.1.2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6592503 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D50587E3-FFFB-BD3D-F494-BE4E6537FEDE |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Delicatophycus porosus Mironov, Chudaev & Jüttner |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Delicatophycus porosus Mironov, Chudaev & Jüttner , sp. nov.
LM description ( Figs 46–61 View FIGURES 46–61 ):— Valves dorsiventral, semi-lanceolate, with moderately arched dorsal margin and slightly convex to almost straight ventral margin. Ends obtusely rounded and barely protracted. Valve dimensions (n=65): length 16.0–29.5 μm, width 5.0–6.0 μm, maximum length/width ratio 5.0. Axial area narrow-lanceolate, becoming wider in center of valve. Central area absent on ventral side and only sometimes slightly widened dorsally, and irregular, bordered by shortened striae of different length. Raphe clearly lateral and bent to ventral side near proximal ends. Central raphe ends simple. Terminal raphe fissures curved towards dorsal side. Striae slightly radiate, 17.5–20.5 in 10 μm. Areolae not discernible in LM.
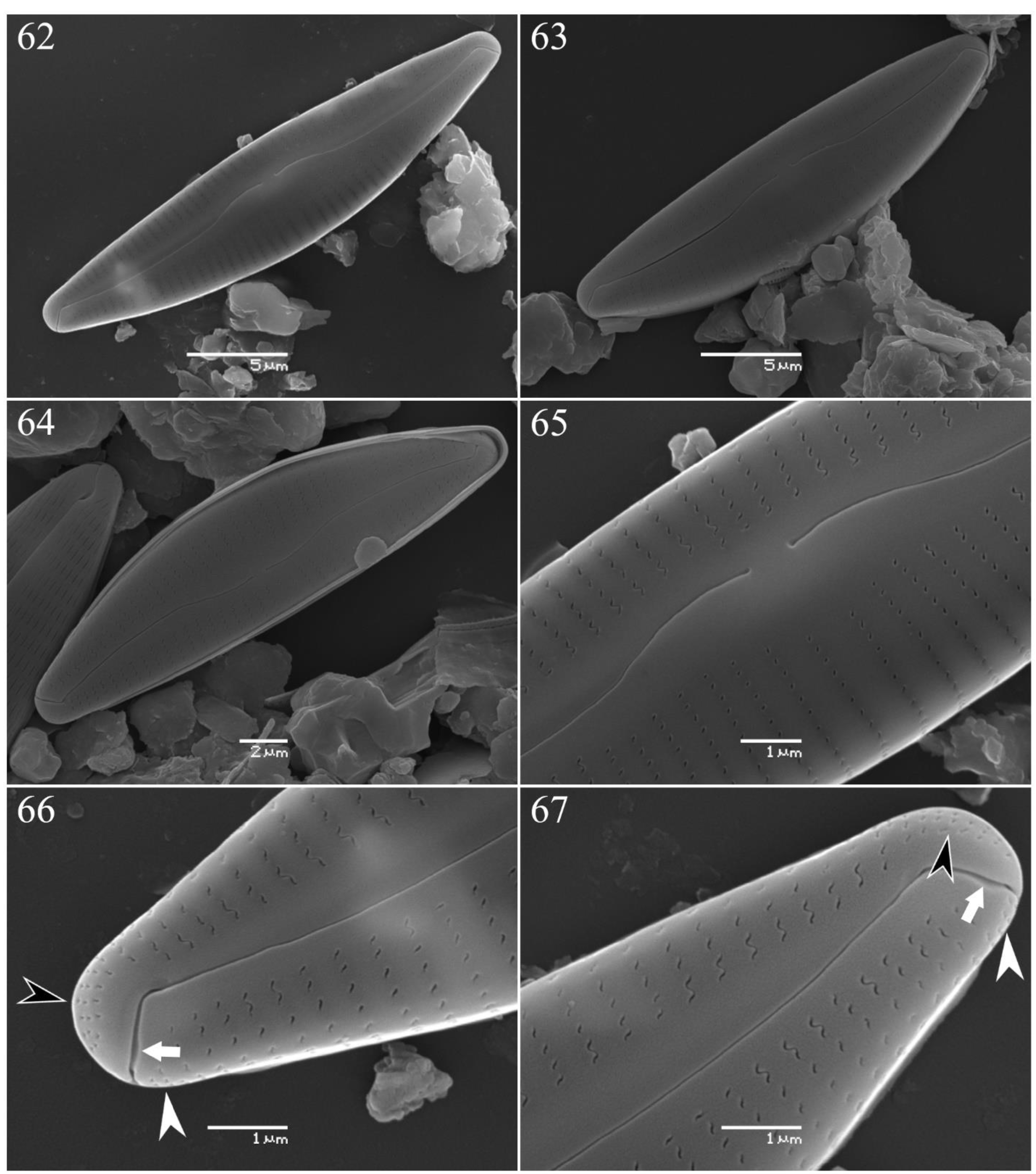
SEM external valve surface ( Figs 62–67 View FIGURES 62–67 ):— Terminal fissures deflected to dorsal side of the valve. Small notch present on dorsal side of each terminal fissure ( Figs 66–67 View FIGURES 62–67 , white arrows). Striae undulate, areolae appear to be tildeshaped. APFs present, pores small round to oval, hence differ from tilde-shaped areolae in external view. APF divided by distal raphe fissure into two unequal sections. Dorsal part of APF ( Figs 66–67 View FIGURES 62–67 , white arrowheads), composed of only two rows of pores, much smaller than ventral part ( Figs 66–67 View FIGURES 62–67 , black arrowheads). Thus, the new species appears to have Type II APFs ( Liu et al. 2022).
SEM internal valve surface ( Figure 68–77 View FIGURES 68–73 View FIGURES 74–77 ):— Proximal raphe ends covered by dorsally curved flap ( Figs 71– 73 View FIGURES 68–73 , white arrows). Central area irregular, with 1–2 shortened dorsal striae ( Figs 72–73 View FIGURES 68–73 , black arrowheads). Raphe terminates with helictoglossae adjacent to the last striae ( Figs 74–77 View FIGURES 74–77 , white arrows). Internal openings of areolae located in distinct transapical grooves with small stubs on margins ( Figs 71–73 View FIGURES 68–73 , white arrowheads). Areola density 40.0–44.0 in 10 µm. Virgae much broader than striae, becoming narrower towards valve ends. APFs composed of pores occluded by convex tubercle ( Figs 74–77 View FIGURES 74–77 ).
Type: — RUSSIA. Krasnodar Territory: Adegoy River, vicinity of Afonka Khutor , on mosses, 44.72580° N, 37.93992° E, 176 m asl, D. A GoogleMaps . Chudaev , 27th May 2016 (Holotype: MW-D! slide 501s1 = Fig. 54 View FIGURES 46–61 ; isotypes: slides LE A0000300 , LE A0000303 ) .
Etymology: —The specific epithet refers to the possession of apical pore fields.
Distribution and ecology: —The species is so far only known from the River Adegoy (samples 501, 502, 506, 507, 508, 509, 510). In the type material it is associated with several unidentified species in Achnanthidium Kützing (1844: 75) , Diatoma moniliformis ( Kützing 1834: 580) D.M. Williams (2012: 260) , Encyonopsis cesatii ( Rabenhorst 1853: 39) Krammer (1997b: 156) , Gomphonella olivacea ( Hornemann 1810: fasc. 24, pl. 1429) Rabenhorst (1853: 61), Gomphonema tergestinum (Grunow in Van Heurck 1880: pl. 25, fig. 40) Fricke in A. Schmidt (1902: pl. 234, figs 39–43), Navicula cryptotenella Lange-Bertalot in Krammer & Lange-Bertalot (1985: 62) and Nitzschia media Hantzsch (1860: 40) .
| A |
Harvard University - Arnold Arboretum |
| LE |
Servico de Microbiologia e Imunologia |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |