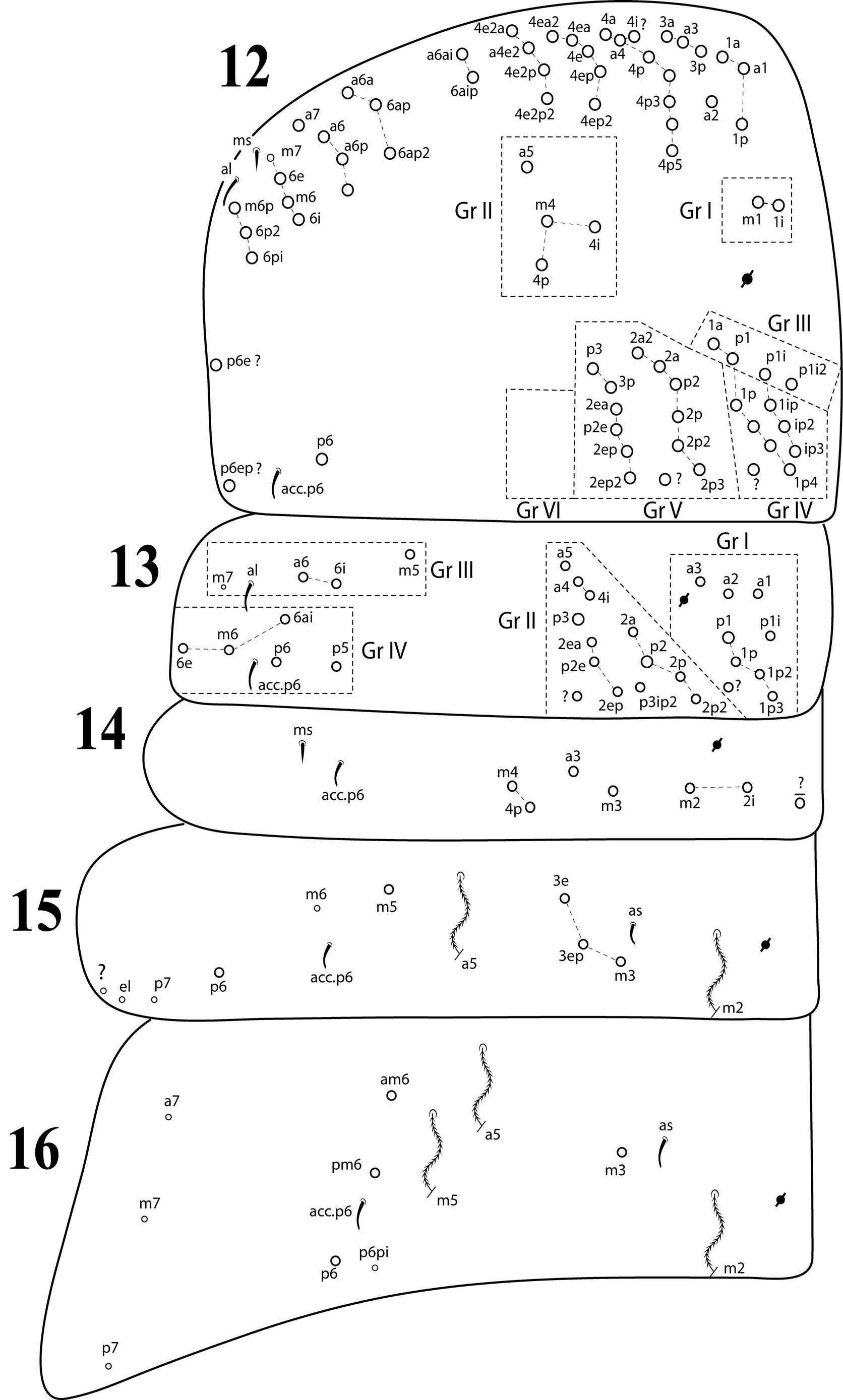
Coecobrya
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4200.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C53B1C14-27A9-481B-BF69-33BA9D82C422 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6075082 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D81187E6-FFA2-FFD6-FF7A-FF11FA04F9BC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Coecobrya |
| status |
|
Key to the world species of Coecobrya
* Cave-dwelling species
1 Eyes present ( boneti -group)............................................................................ 2
- Eyes absent ( tenebricosa -group)........................................................................ 9
2(1) Eyes 1+1 or 3+3...................................................................................... 3
- Eyes 2+2; Vietnam............................................................ C. tetrophthalma ( Denis, 1948)
3(2) Eyes 1+1............................................................................................ 4
- Eyes 3+3............................................................................................ 8
4(3) Abd I with 5+5 central mac or less.......................................................................5
- Abd I with 6+6 central mac............................................................................. 6
5(4) Th II with 2+2 mac ( p4 and p 4i) in Gr VI; Abd I with 4 + 4 central mac; Abd IV with 6+6 central mac; Cambodia......................................................................... C. tukmeas Zhang, Deharveng & Chen, 2009 *
- Th II without mac in Gr VI; Abd I with 5+5 central mac; Abd IV with 7+7 central mac ( Figs 12 View FIGURES 12 – 16 , 17 View FIGURES 17 – 20 ); China...................................................................................... C. sanmingensis Xu & Zhang, 2015
6(4) Abd IV with 6+6 central mac or less; dorsal manubrium without smooth chaetae.................................. 7
- Abd IV with 7+7 central mac; dorsal manubrium with smooth chaetae ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ); Indonesia............................................................................................ C. indonesiensis ( Chen & Deharveng, 1997) *
7(6) Abd IV with 6+6 central mac; Vietnam.................................................. C. boneti ( Denis, 1948)
- Abd IV with 4+4 central mac; China................................. C. oculata Zhang, Bedos & Deharveng, 2016 *
8(3) Labial chaeta r smooth ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ); Th II with 3+3 ( m1, m2 and m 2i) medio-median mac; unguiculus without external teeth ( Fig 38 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ); China........................................................... C. mulun Zhang, Qu & Deharveng, 2010
- Labial chaeta r ciliate ( Fig 37 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ); Th II with 1+1 ( m1) medio-median mac; unguiculus with one external tooth ( Fig 39 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ); China............................................................................... C. qin Zhang & Dong, 2014
9(1) Mucronal basal spine long reaching at least near apex of apical tooth ( Fig 44 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ).....................................10
- Mucronal basal spine very short, not reaching the apex of apical tooth ( Fig 45 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ); USA............. C. caeca ( Schött, 1896)
10(9) Unguis with 2 unpaired teeth, with one minute apical tooth ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36 – 45 )............................................ 11
- Unguis with at most 1 unpaired tooth ( Figs 38–39 View FIGURES 36 – 45 )..........................................................13
11(10) Tenent hairs spatulate.................................................................................12
- Tenent hairs pointed; India.......................................................... C. montana (Imms, 1912)
12(11) Tibiotarsus with rows of smooth inner differentiated chaetae; Afghanistan................. C. submontana (Stach, 1960)
- Tibiotarsus with rows of ciliate inner differentiated chaetae; New Caledonia.............................................................................. C. neocaledonica Zhang, Bedos & Deharveng, 2014 (in: Zhang et al. 2014 a)
13(10) Manubrium with dorsal smooth chaetae ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 36 – 45 )........................................................... 14
- Manubrium without dorsal smooth chaetae................................................................38
14(13) Unguis without unpaired inner teeth......................................................................15
- Unguis with unpaired inner tooth ( Figs 38–39 View FIGURES 36 – 45 )............................................................. 16
15(14) Dental smooth part about 0.7 times as long as mucro; Japan............................. C. ishikawai ( Yosii, 1956a) *
- Dental smooth part about 1.5 times as long as mucro; Korea................................. C. maritima Park, 2004
16(14) Outer tooth on unguiculus at most slightly broader than unguiculus itself.........................................17
- Outer tooth on unguiculus twice as broad as unguiculus itself; New Guinea................... C. papuana ( Yosii, 1971) *
17(16) Antennae less than three times as long as the cephalic diagonal................................................18
- Antennae more than five times as long as the cephalic diagonal; Hawaii ( USA)... C. nupa ( Christiansen & Bellinger, 1992) *
18(17) Tibiotarsus with rows of ciliate inner differentiated chaetae ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ), i.e. with ciliations closely appressed to axis........19
- Tibiotarsus without rows of ciliate inner differentiated chaetae ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 36 – 45 )........................................ 25
19(18) Abd IV with 4+4 central mac...........................................................................20
- Abd IV with more than 4+4 central mac.................................................................. 23
20(19) Abd III with 2 + 2 lateral mac...........................................................................21
- Abd III with 3 + 3 lateral mac...........................................................................22
21(20) Th II with 4+4 mac in Gr IV; Th III with 9+9 to 13+13 mac in Gr I; Northern Hemisphere.. C. tenebricosa ( Folsom, 1902) *
- Th II with 2+2 mac in Gr IV; Th III with 8+8 mac in Gr I; Rapa Nui ( Eastern Island , Chile)................................................................................... C. aitorererere Bernard, Soto-Adames & Wynne, 2015
22(20) Th II with 2+2 mac in Gr I; collophore anterior face with 2+2 long central mac; Japan......... C. tibiotarsalis ( Yosii, 1964)
- Th II with 1+1 mac in Gr I; collophore anterior face with 1+1 long central mac; China..... C. brevis Xu, Yu & Zhang, 2012
23(19) Abd III with 2+2 central mac...........................................................................24
- Abd III with 1+1 central mac; Germany............................................... C. hoefti ( Schäffer, 1896)
24(23) Th II with 3+3 ( m1, m2 and m 2i) medio-median and 2+2 ( m4 and m4p) medio-lateral mac; Hungary................................................................................... C. magyari Chen, Wang & Christiansen, 2002
- Th II with 2+2 ( m1 and m2) medio-median and 3+3 ( m4, m 4i and m4p) medio-lateral mac; Thailand...................................................................................... C. lanna Zhang, Deharveng & Chen, 2009
25(18) Unguis with unpaired inner distal tooth at more than 25% from the base of the claw ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36 – 45 )........................26
- Unguis elongate, with unpaired inner distal tooth basal, at less than 20% from the base of the claw; Japan............................................................................................ C. akiyoshiana ( Yosii, 1956a) *
26(25) Abd II with 2+2 central mac............................................................................27
- Abd II with 3+3 or 4+4 central mac......................................................................29
27(26) Th II with 4+4 mac in Gr I–II altogether..................................................................28
- Th II with 6+6 mac in Gr I –II altogether; Thailand...................................... C. similis Deharveng, 1990
28(27) Abd IV with 3+3 central mac and 3+3 lateral mac; Japan................................... C. arcuata (Yosii, 1955)
- Abd IV with 4+4 central mac and 6+6 lateral mac; Rapa Nui ( Easter Island , Chile)... C. kennethi Jordana & Baquero, 2008 *
29(26) Abd III with 1+1 central mac ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 12 – 16 )....................................................................30
- Abd III with 2+2 central mac; Hawaii (USA).............................. C. kukae Christiansen & Bellinger, 1992 *
30(29) Abd I with 4+4 central mac.............................................................................31
- Abd I with 5+5 central mac.............................................................................33
31(30) Abd IV with 4+4 central mac or more................................................................... 32
- Abd IV with 2+2 central mac; Hawaii ( USA)................................. C. lua Christiansen & Bellinger, 1992 *
32(31) Abd IV with 4+4 central mac; China............................................... C. islandica Shi & Pan, 2015
- Abd IV with 6+6 or 7+7 central mac; Republic of Vanuatu.................................. C. aokii ( Yoshii, 1995)
33(30) Unguis with paired teeth at more than 35% from the base of the unguis ( Figs 38–40 View FIGURES 36 – 45 ).............................. 34
- Unguis with paired teeth at less than 25% from the base of the unguis; Japan............... C. spinidentata ( Yosii, 1942) *
34(33) Abd IV with 3+3 central mac...........................................................................35
- Abd IV with 4+4 or 5+5 central mac.....................................................................36
35(34) Th II without medio-lateral mac; Hawaii ( USA)............................ C. borerae Christiansen & Bellinger, 1992
- Th II with 3+3 ( m4, m 4i and m4p) medio-lateral mac; China................... C. oligoseta Chen & Christiansen, 1997
36(34) Abd IV with 4+4 central mac...........................................................................37
- Abd IV with 5+5 central mac; Japan and Korea........................................ C. dubiosa ( Yosii, 1956a) *
37(36) Th II with p4 and p 4i mac; China................................................ C. pani Xu, Yu & Zhang, 2012
- Th II without mac p4 and p 4i; Thailand......................................... C. guanophila Deharveng, 1990 *
38(13) Abd III with 1+1 central mac ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 12 – 16 )....................................................................39
- Abd III with 2+2 central mac...........................................................................46
39(38) Abd IV with at least 6+6 central mac.....................................................................40
- Abd IV with 5+5 central mac or less......................................................................42
40(39) Abd IV with 7+7 central mac ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 17 – 20 )...................................................................41
- Abd IV with 6+6 central mac; China................................ C. annulata Zhang, Bedos & Deharveng, 2016 *
41(40) Collophore posterior face with 1+1 large apical smooth chaetae ( Fig 32 View FIGURES 31 – 35 ); Th II with 10+10 mac in Gr V; Th III with 11+11 or less mac in Gr II; China................................................ C. communis Chen & Christiansen, 1997
- Collophore posterior face with 2+2 large apical smooth chaetae; Th II with 13+13 mac in Gr V; Th III with 13+13 mac in Gr II ( Figs 12–13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ); South Africa............................................................ C. anaguilae sp. nov. *
42(39) Abd IV with 4+4 or 5+5 central mac.....................................................................44
- Abd IV with 3+3 central mac...........................................................................43
43(42) Abd I with 2+2 mac; Abd II with 2+2 central mac; Java........................... C. edenticulata ( Handschin, 1926) *
- Abd I with 6+6 mac; Abd II with 3+3 central mac ( Fig 15 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ); China.......... C. ciliata Zhang, Bedos & Deharveng, 2016 *
44(42) Abd IV with 5+5 central mac...........................................................................45
- Abd IV with 4+4 central mac, China.............................. C. gejianbangi Zhang, Bedos & Deharveng, 2016 *
45(44) Th II with 1+1 mac ( p4) in Gr VI; Abd II with 2+2 central mac; Australia...... C. tropicalis Qu, Chen & Greenslade, 2007
- Th II without mac in Gr VI; Abd II with 3+3 central mac ( Figs 12, 15 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ); China............... C. qinae Xu & Zhang, 2015
46(38) Abd IV with at least 7+7 central mac.....................................................................47
- Abd IV with 5+5 or less central mac..................................................................... 48
47(46) Abd IV with 7+7 central mac ( Fig 17 View FIGURES 17 – 20 ); China............................... C. liui Wang, Chen & Christiansen, 2002
- Abd IV with at least 8 + 8 central mac; Tibet................................ C. tibetensis Chen & Christiansen, 1997
48(46) Abd IV with 5+5 central mac.......................................................................... 49
- Abd IV with 4+4 central mac; China........................................... C. draconis Zhang & Dong, 2014 *
49(48) Th III with 8+8 lateral mac; Abd III with 3+3 lateral mac; Tibet................... C. huangi Chen & Christiansen, 1997
- Th III with 5+5 lateral mac; Abd III with 2+2 lateral mac; China.......................... C. xui Zhang & Dong, 2014
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |