Physoschistura harkishorei, Das & Darshan, 2017
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4337.3.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4A839CF4-EDF3-4E9C-A899-7F76F01D4E06 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5658731 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E248F371-0C7B-FF81-ABEB-FE06FA90FE35 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Physoschistura harkishorei |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Physoschistura harkishorei , new species
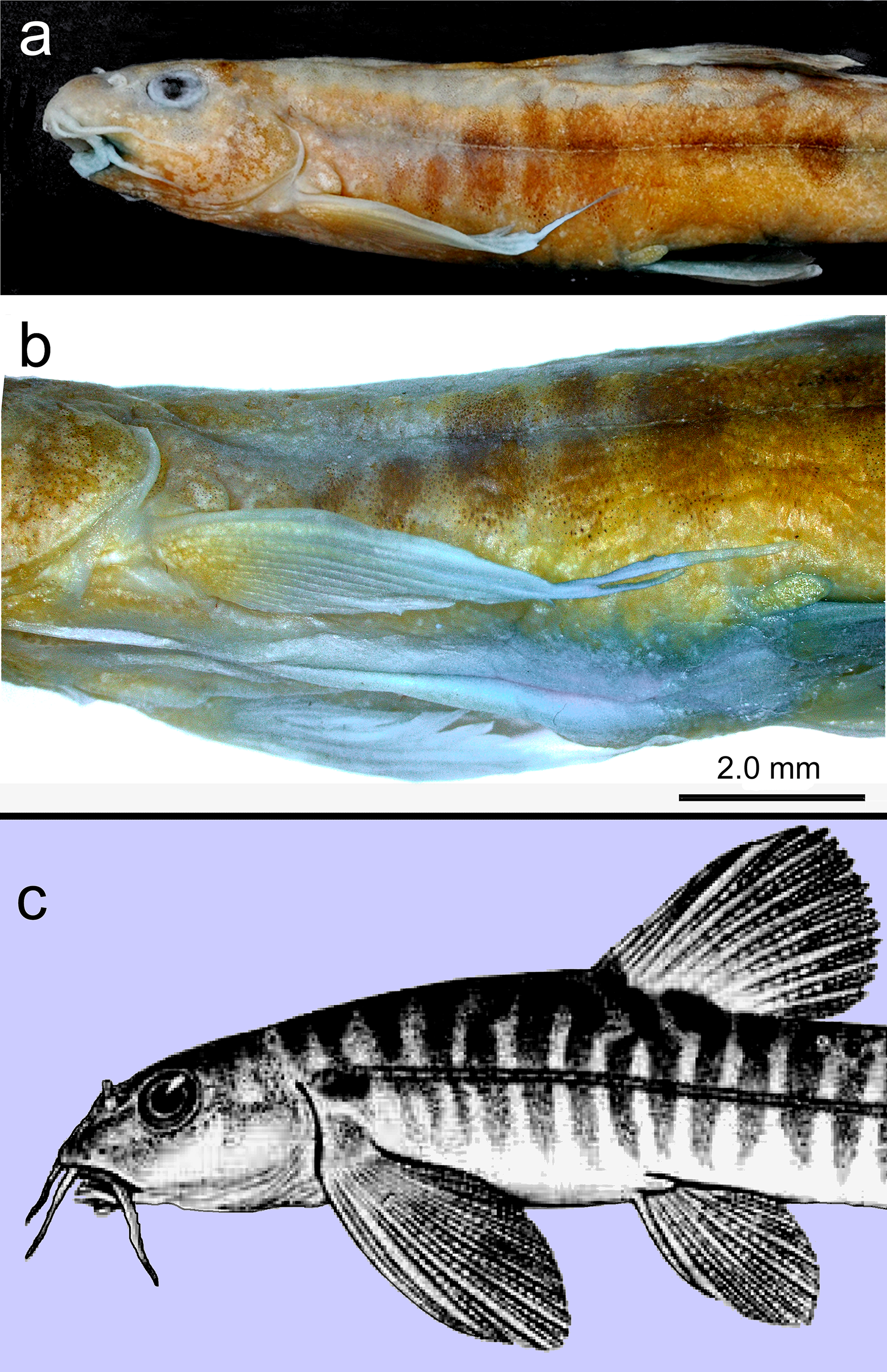
( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 )
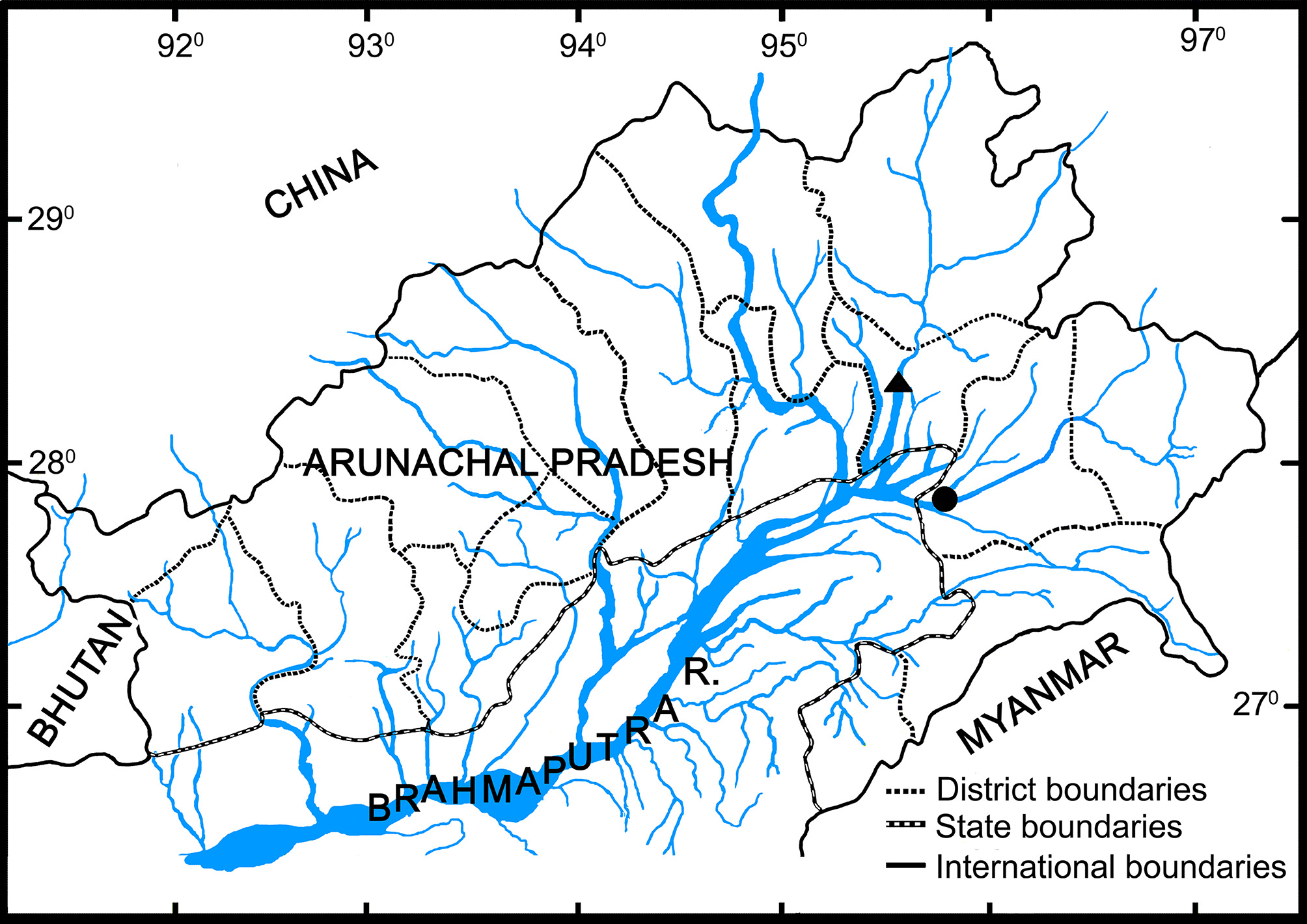
Holotype. RGUMF 290 , 41.3 mm SL; male, India: Arunachal Pradesh state, Lower Dibang Valley district, Dibang River (the Brahmaputra basin); 28°09´59˝ N 95°43´55˝E; Boni Amin Laskar , August 2004.
Paratypes. RGUMF 291–295, 5, 42.5–53.4 mm SL; same data as holotype. RGUMF 332 , 1 , 46.1 mm SL, male, India: Arunachal Pradesh state, Lohit district, Lohit River at Alubari Ghat , at the immediate side of Lohit bridge ( Alubari bridge), 27°51´29˝ N 96°01´36 ˝ E, elevation 159 msl; Achom Darshan and Santoshkumar Abujam , 29th August 2016 .
Diagnosis. Physoschistura harkishorei can be distinguished from all known congeners by the combination of the following characters: the second branched ray of the pectoral fin with a distal filamentous extension; body colour pattern consisting of 9–10 brownish vertically-elongated spots or blotches along the flank, 8–10 brownish saddles on back, saddles not contiguous with the lateral blotches; lateral line complete; a pelvic-fin lobe present; a well-developed free posterior chamber of the air-bladder; and caudal fin with 7+8 branched rays.
Description. Morphometric data of holotype and six paratypes are shown in Table 1 View TABLE 1 . Dorsal profile elevating abruptly in snout region, gently inclined to dorsal-fin origin, then sloping gently downwards towards caudal fin; ventral profile almost straight up to anal-fin origin, then inclined evenly towards caudal-fin base. Body crosssection sub-cylindrical anteriorly, laterally compressed from base of last pectoral-fin ray to base of caudal fin. Body covered with minute scales, absent between bases of pectoral fin and belly anterior to pelvic fin. Lateral line midlateral, complete, and straight. Cephalic lateral-line system with 7 supraorbital, 4 + 11 infraorbital, 9 preoperculo-mandibular, and 3 supratemporal pores.
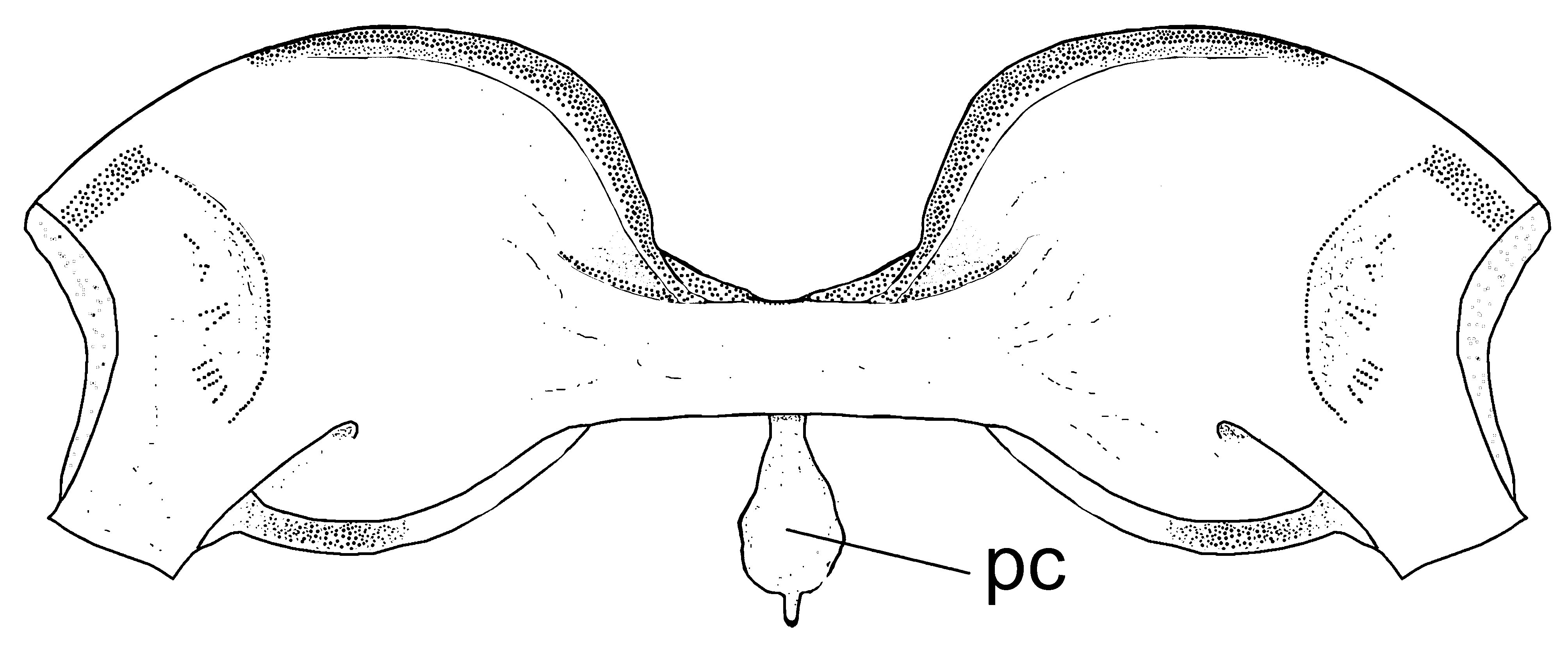
Head depressed. Eye oval, placed in upper and anterior half of head, not visible in ventral view. Interorbital space flat, wide. Mouth inferior, small, strongly curved backward, about twice as wide as long. Processus dentiformis present, no corresponding notch in lower jaw. Lower lip with prominent median notch, forming two triangular pads ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ). Three pairs of barbels, outer rostral barbel long, reaching posterior rim of eye; inner rostral barbel shorter, extending to middle of snout; maxillary barbel extending slightly beyond vertical through posterior rim of eye. Anterior and posterior nostrils adjacent. Anterior nostrils in a flap-like tube, its tip truncate.
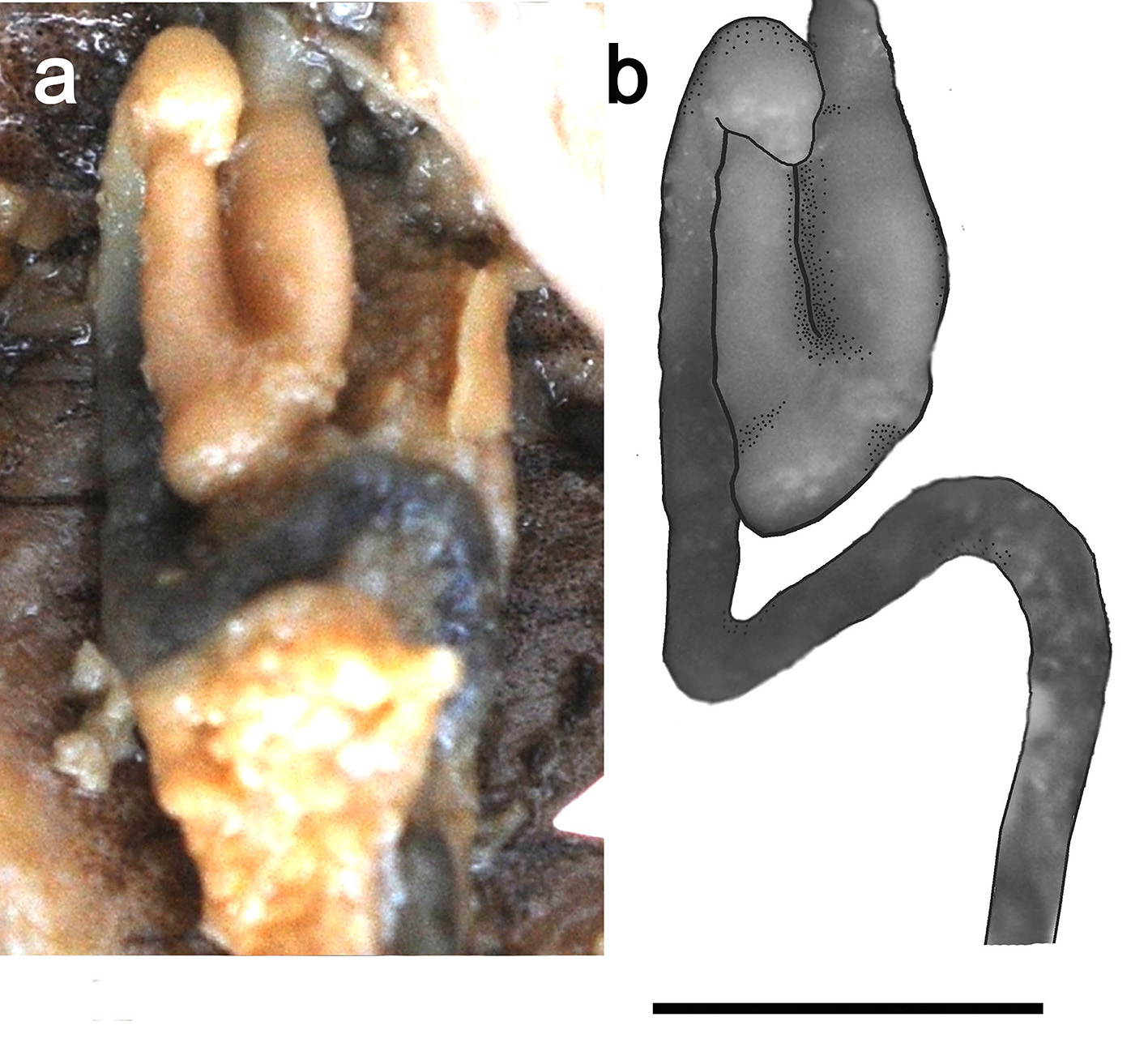
Dorsal fin with 2(2) or 3*(5) simple and 8(1) or 8½*(5) or 9(1) branched rays, its origin slightly anterior to vertical through pelvic-fin origin. Distal margin of dorsal fin slightly convex. Pelvic fin with 1(7) simple and 7(7) branched rays. Pelvic-fin lobe prominent and large. Pectoral fin with 1(7) simple and 9 (1) or 10 *(6) branched rays. Second branched ray of pectoral fin with distal filamentous extension, often extended far beyond pelvic-fin origin, reaching upto posterior margin of pelvic-fin lobe in larger specimens greater than 49.0 mm SL. Anal fin with 2(7) simple and 5 (1) or 5½* (6) branched rays. Adpressed pelvic fin not reaching vent. Caudal fin forked, lobes equal in length, with 7+8 branched rays. Free posterior chamber of air-bladder placed immediately behind air-bladder capsule, spherical in shape, not encapsulated ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ). Intestine with large loop extending forward towards left posterolateral side of stomach ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ).
Sexual dimorphism. Males possess a suborbital flap ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ) while females have a suborbital groove in place of male’s suborbital flap. The first branched pectoral-fin ray broadens in males by fusing together and separating at towards the tip ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ). No distinct sexual dichromaticism or dimorphism.
Colouration. In 70% alcohol, background body colour yellowish cream, ornamented dorsally with 8–10 brownish saddles and 9–10 vertically elongated spots or blotches along flank, saddles alternately placed with lateral blotches, not contiguous. In some paratypes, predorsal lateral blotches extend well below lateral line. Head and snout region scattered with brown spots. A conspicuous dark-brown spot at dorsal-fin origin, a transverse brownish streak at middle of dorsal fin due to heavy accumulations of melanophores in mid-region of fin rays. Mid-base of dorsal fin, from third to sixth branched rays, along with the adjoining basal membrane brownish, distal and sub-basal portion of dorsal fin hyaline. Basicaudal bar basally broad, narrower dorsally, incomplete, terminated at a point about half eye diameter above ventral margin of caudal-fin base.
Etymology. The new species is named in memory of Late Harkishore Das, the father of the first author, who inspired him (DND) to take up fisheries research as his academic career.
Distribution. Presently, known from the Dibang River, its type locality and the Lohit River (both Brahmaputra basin) in Arunachal Pradesh ( Figs. 7 View FIGURE 7 , 8 View FIGURE 8 ).
Discussion
Physoschistura harkishorei differs from P. dikrongensis , and P. elongata , its sympatric congeners in the Brahmaputra basin, in having a complete (vs. incomplete) lateral line, a filamentous extension (vs. lacking extension) in the second branched ray of the pectoral fin, and lateral body markings in the form of verticallyelongated blotches (vs. bars). Further, P. harkishorei differs from P. dikrongensis by its shorter snout (32.9–40.6% HL vs. 44.1–53.9), dorsal-fin (9.1–10.4% SL vs. 13.8–17.7), 8–10 blotches (vs. 11–15 bars) along the flank, fewer (2 vs. 4) simple anal-fin rays, and supraorbital canal pores (7 vs. 9); and from P. elongata in having a longer caudal peduncle (12.9–16.7% SL vs. 11.3) and a shorter prepelvic length (46.8–53.2% SL vs. 53.8).
The new species differs from P. chhimtuipuiensis in having a complete (vs. incomplete) lateral line, a filamentous extension (vs. lacking extension) of the second branched ray of the pectoral fin, a shorter head (lateral head length 19.4–22.8% SL vs. 23.0–25.9, dorsal head length 17.6–19.3% SL vs. 21.5–22.7), snout (32.9–40.6% HL vs. 42.0–45.0), a slender caudal peduncle (6.8–8.7% SL vs. 10.9–12.1), a narrower interorbital distance (21.2– 25.5% HL vs. 29.0–32.0) and absence (vs. presence) of scales between bases of pectoral-fin and on the belly.
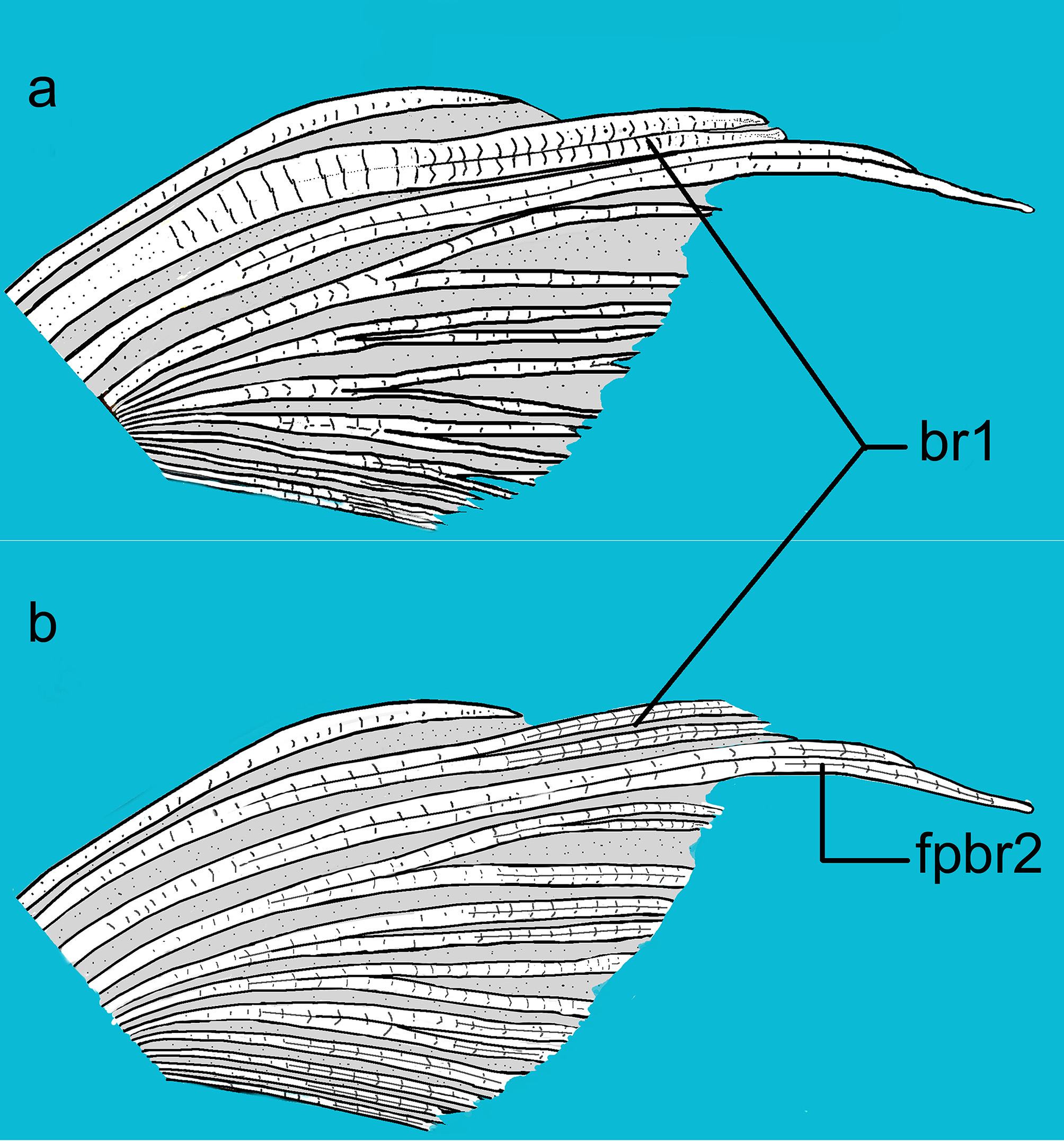
The new species and Physoschistura raoi are the only two members of the genus with a long pectoral fin extending up to the origin of the pelvic fin. In the new species, the pectoral fin is extended to the pelvic-fin origin or often beyond by means of a distal filamentous extension of the second branched ray ( Figs. 9a & b View FIGURE 9 ). In case of P. raoi , the pectoral fin is large and long but lacking any filamentous extension of the fin rays ( Fig. 9c View FIGURE 9 ). Further, the new species differs from P. raoi by its complete lateral line (vs. incomplete).
The new species can be easily distinguished from P. rivulicola , P. chulabhornae , P. pseudobrunneana , and P. brunneana in having a complete (vs. incomplete) lateral line and the second branched ray of the pectoral fin filamentously extended (vs. lacking filamentous extension). It further differs from P. chulabhornae , P. pseudobrunneana , and P. brunneana in having (vs. lacking) a pelvic-fin lobe.
Physoschistura harkishorei shares with P. tuivaiensis , P. chindwinensis , P. prashadi , P. tigrina , P. shanensis , P. shuangjiangensis and P. absumbra a complete lateral line; but is distinct from them by having (vs. lacking) a filamentous extension of the second branched ray of the pectoral fin. Further, P. harkishorei differs from P. tuivaiensis and P. chindwinensis in having a shorter snout (32.9–40.6% HL vs. 43.4–51.0) and head (lateral head length 19.4–22.8% SL vs. 23.1–27.3); from P. prashadi by its fewer (2–3 vs. 4) simple dorsal-fin rays, shorter snout (32.9–40.6% HL vs. 43.8–57.0), and narrower interorbital distance (21.2–25.5% HL vs. 28.2–40.1); from P. tigrina by its shorter snout (32.9–40.6% HL vs. 46.9–50.6), more slender body (13.3–15.9% SL vs. 17.0–19.0), caudal peduncle depth (6.8–8.7% SL vs. 9.8–11.0), and narrower interorbital distance (21.2–25.5% HL vs. 27.3– 29.2); from P. shanensis in having fewer branched pectoral-fin rays (9–10 vs. 12) and branched caudal-fin rays in the upper lobe (7vs. 8); from P. shuangjiangensis by its slender body (head depth at nape 11.3–13.4% SL vs. 13.9– 15.2, body depth 13.3–15.9% SL vs.17.9–20.5, caudal peduncle depth 6.8–8.7% SL vs. 11.0–13.1) and fewer branched caudal-fin rays in the upper lobe (7 vs. 9), and from P. absumbra in having an incomplete (vs. complete) basicaudal bar, a shorter head (dorsal head length17.6–19.3% SL vs. 23–25, lateral head length19.4–22.8% SL vs. 26–28), and a body colour pattern consisting of vertically elongated lateral spots or blotches (vs. regular bars).
TABLE 1. Morphometric data of Physoschistura harkishorei, new species (n = 7).
| Holotype | Range | Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total length (mm) | 51.7 | 51.7–63.2 | - |
| Standard length (mm) | 41.3 | 41.3–53.4 | - |
| In percent of standard length | |||
| Body depth | 13.4 | 13.3–15.9 | 14.7±1.23 |
| Head depth at nape | 12.3 | 11.3–13.4 | 12.3±0.75 |
| Head depth at eye | 10.4 | 8.5– 11.4 | 9.8±1.19 |
| Lateral head length | 22.8 | 19.4–22.8 | 21.4±1.27 |
| Dorsal head length | 19.2 | 17.6– 19.3 | 93.8±0.72 |
| Caudal peduncle length | 15.9 | 12.9–16.7 | 75.1±1.47 |
| Caudal peduncle depth | 7.7 | 6.8–8.7 | 38.6±0.88 |
| Pre-dorsal length | 50.8 | 44.2–50.8 | 236.7±2.41 |
| Pre-pelvic length | 49.2 | 46.8–53.2 | 251.7±2.44 |
| Pre-anus length | 68.8 | 66.7–71.7 | 342.9±1.91 |
| Pre-anal length | 75.5 | 73.2–76.7 | 377.6±1.41 |
| Pelvic fin length | 16.5 | 14.9–17.4 | 80.7±0.92 |
| Anal fin length | 17.7 | 15.1–17.8 | 81.4±1.34 |
| Pectoral fin length | 26.9 | 23.1–28.9 | 133.8±2.38 |
| Maximum head width at cheek | 9.9 | 9.9–12.2 | 56.8±0.89 |
| Head width at nares | 7.5 | 7.5–10.5 | 43.4±1.12 |
| Body width at anal-fin origin | 6.3 | 6.3–8.0 | 36.5±0.69 |
| Body width at dorsal-fin origin | 9.7 | 9.5–12.9 | 53.9±1.36 |
| In percent of lateral head length | |||
| Snout length | 32.9 | 32.9–40.6 | 188.3±3.13 |
| Interorbital distance | 25.5 | 21.2–25.5 | 121.4±1.79 |
| Eye diameter | 25.5 | 21.2–26.7 | 117.7±2.48 |
| Mouth gape width | 29.8 | 23–33.7 | 141.9±3.96 |
| Head depth at eye | 45.7 | 38.3–50.0 | 227.1±4.39 |
| Head depth at nape | 54.3 | 51.6–62.7 | 284.6±4.23 |
| Maximum head width | 43.6 | 5.6–59.3 | 213±6.11 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |