Rhagovelia rosensis Padilla-Gil, 2011
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4958.1.11 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:ADD5204B-A342-4A85-8F10-778241D70E9E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4691769 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/E7216366-DF24-5A7E-FF35-B81DFE2A6867 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhagovelia rosensis Padilla-Gil, 2011 |
| status |
|
Rhagovelia rosensis Padilla-Gil, 2011 View in CoL
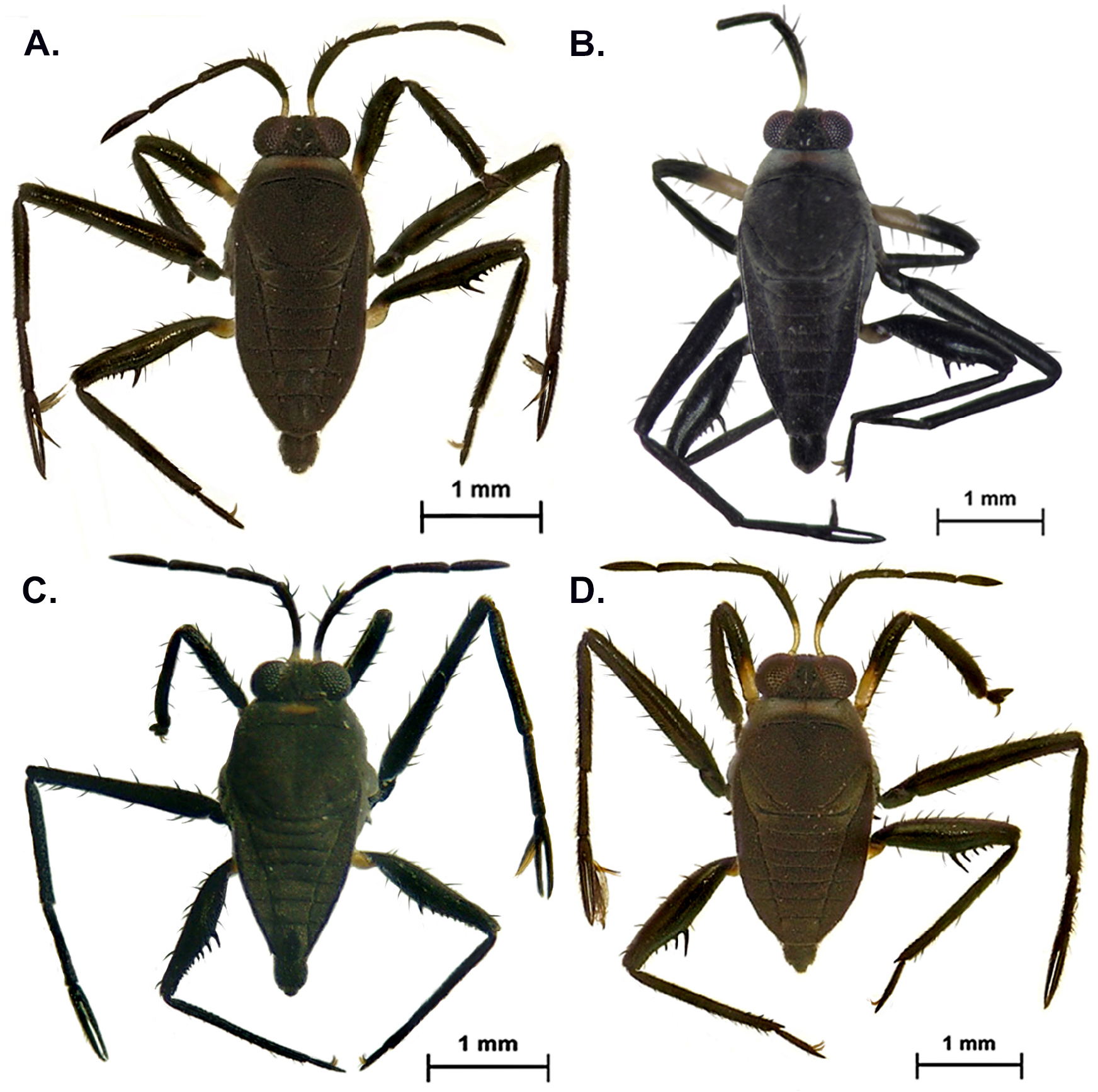
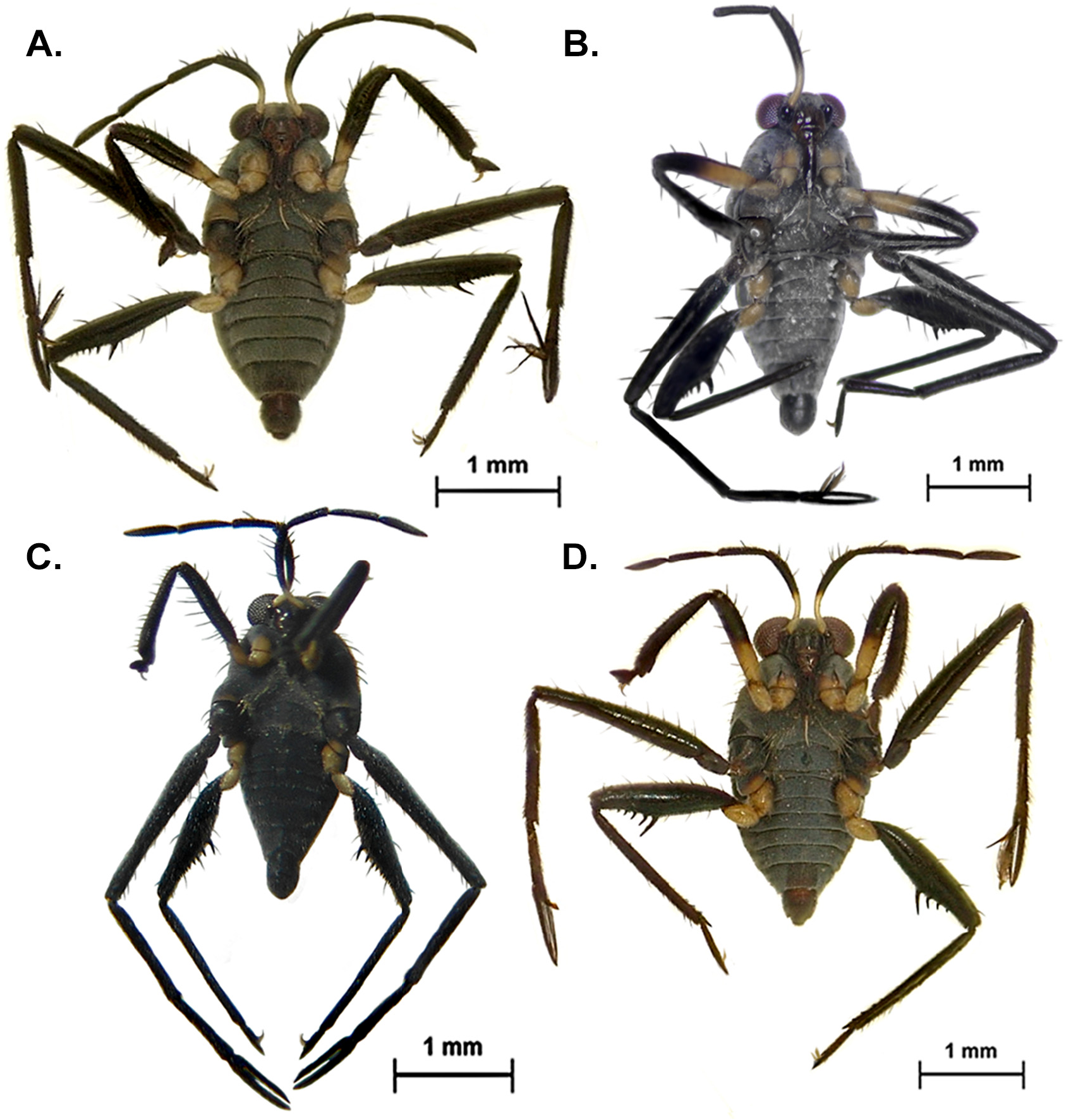
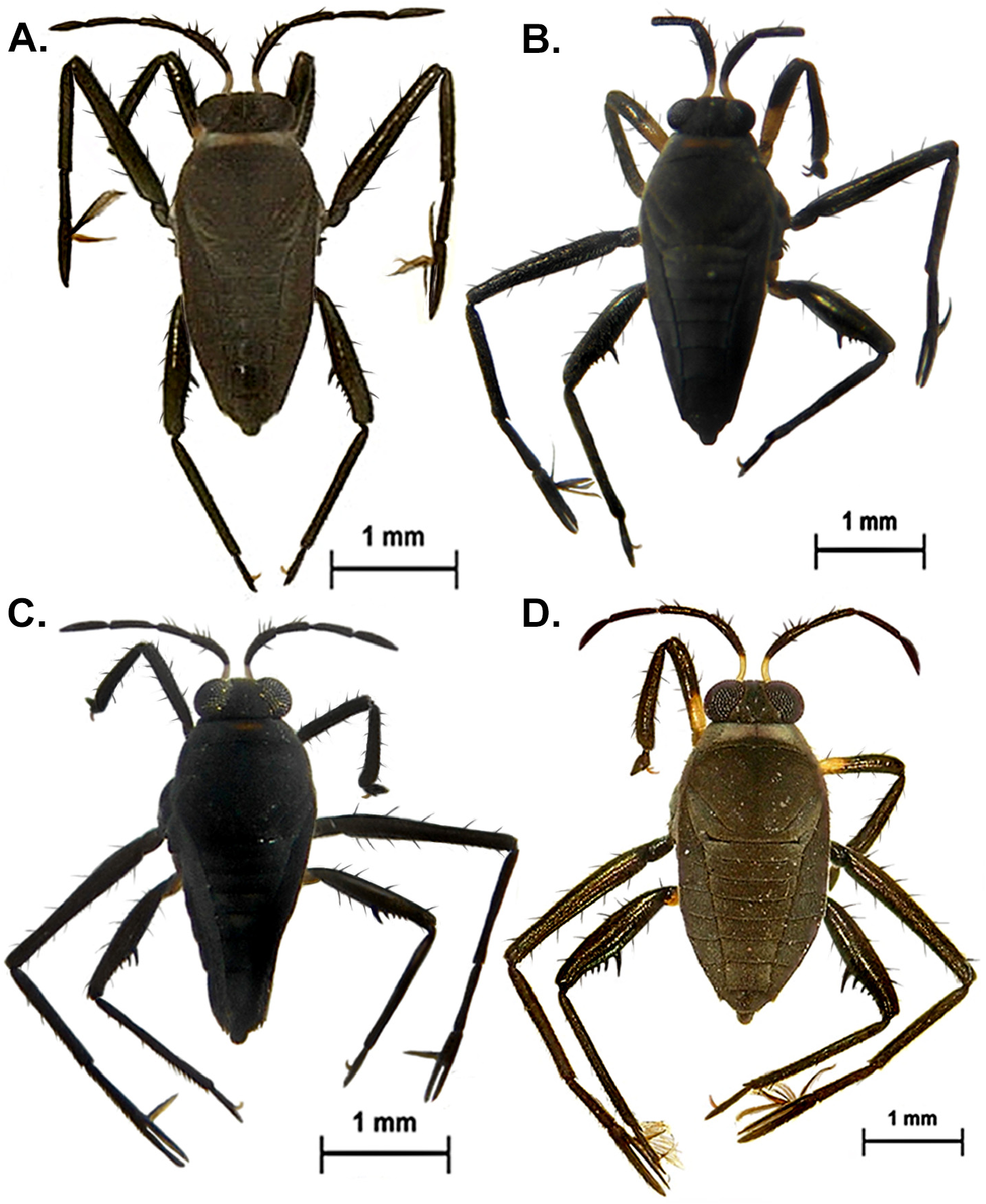
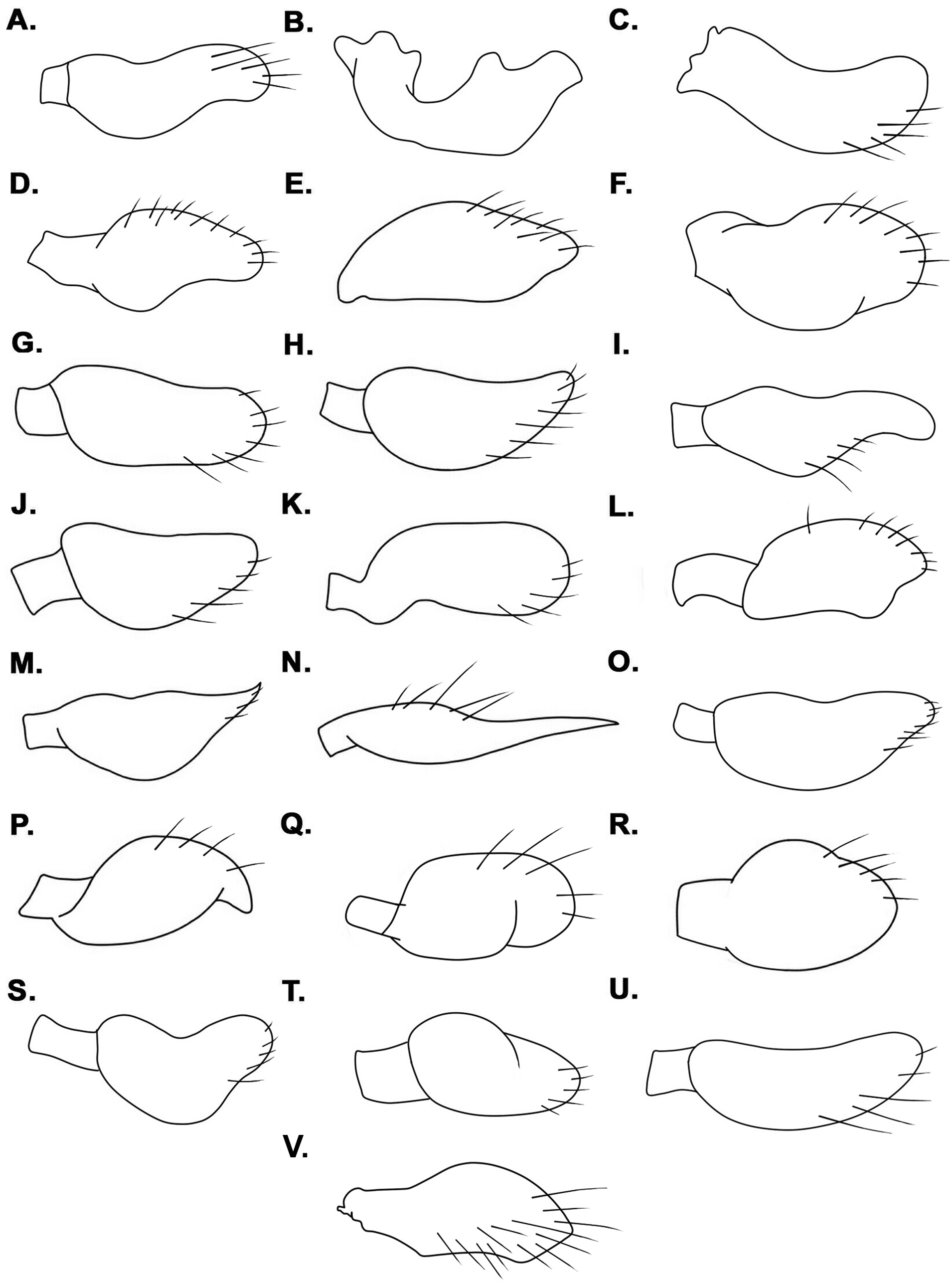
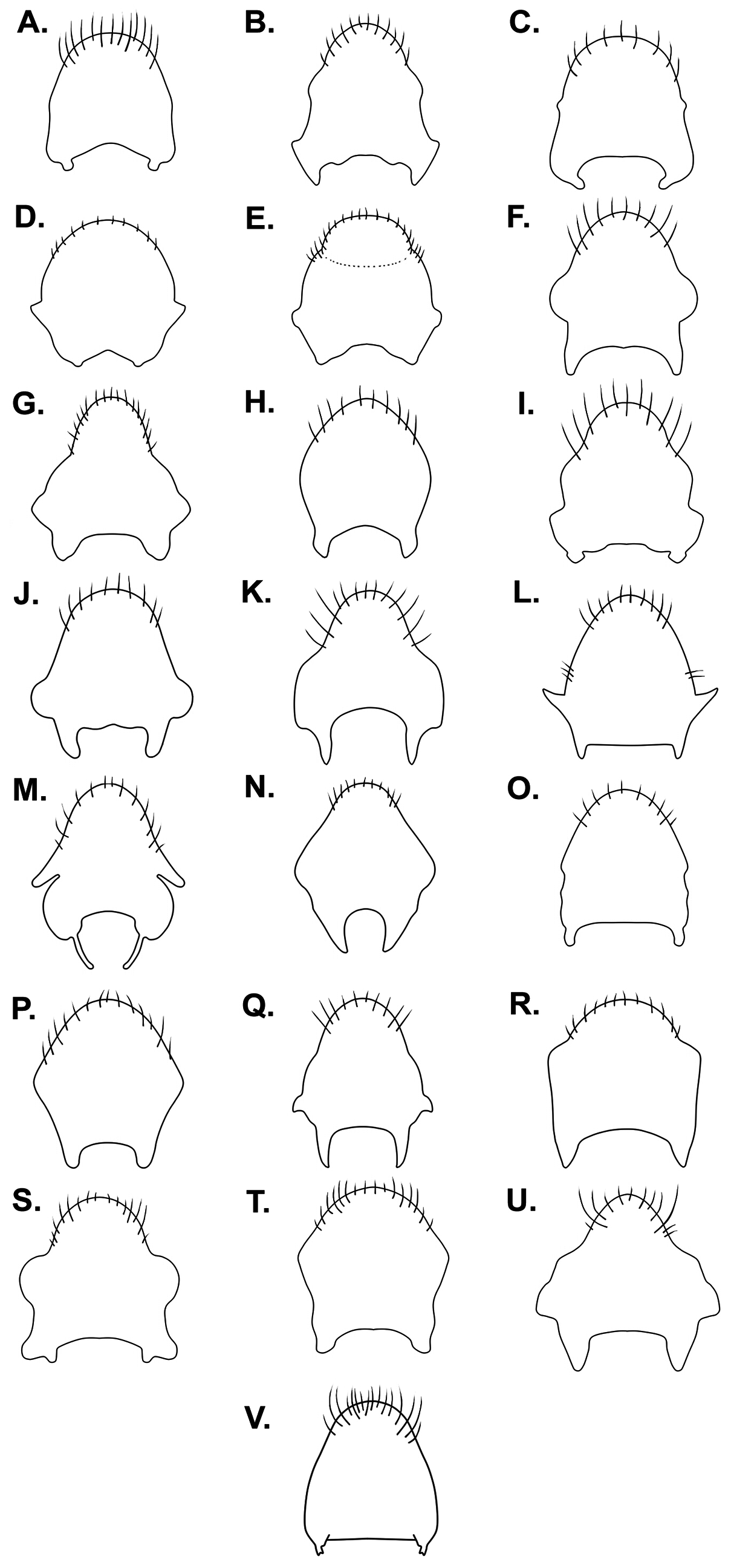
( Figs. 13C View FIGURE 13 , 14C View FIGURE 14 , 15C View FIGURE 15 , 16C View FIGURE 16 , 19Q View FIGURE 19 , 20Q View FIGURE 20 , 23B View FIGURE 23 )
Rhagovelia rosensis Padilla-Gil, 2011: 216 View in CoL .
Rhagovelia espriella Padilla-Gil, 2011: 218 View in CoL (new synonym).
Holotype apterous male. BL 2.63; HL 0.30; HW 0.70; INT 0.21; ANT I 0.70, ANT II 0.35, ANT III 0.45, ANT IV 0.48; EYE 0.29; PL 0.18; PW 0.85; FORELEG: FEM 0.85; TIB 0.90; TAR I 0.04; TAR II 0.02; TAR III 0.22; MIDLEG: FEM 1.30; TIB 0.85; TAR I 0.08; TAR II 0.40; TAR III 0.63; HINDLEG: FEM 1.15; TIB 1.25; TAR I 0.04; TAR II 0.08; TAR III 0.20.
Head dorsally black, covered with golden pubescence; longitudinal midline and a pair of oblique indentations at base impressed and shiny. Venter of head black. Buccula brown. Labium black. Eye dark red. Antenniferous tubercle black. Basal 1/4 of antennomere I yellow; apex of I and rest of antenna dark brown. Pronotum dark orange between eyes behind vertex of head, black laterally and posteriorly, covered with golden pubescence. Meso- and metanota black, covered with golden pubescence. Pro-, meso- and metapleura black, covered with greyish and golden pubescence. Pro-, meso- and metasterna black, covered with greyish pubescence. Proacetabulum yellow; mesoacetabulum black with posterior margin yellowish- brown; metacetabulum black, yellow on distal half. Fore and hind coxae and trochanters yellow. Middle coxa and trochanter dark brown. Fore femur with yellow base, then black; middle and hind femora black. Tibiae and tarsi black. Abdominal mediotergites black, covered with brown pubescence; VII with central shiny black spot; tergum VIII shiny black, covered with short golden setae. Abdominal laterotergites black, covered with golden pubescence, lateral margins shiny black. Abdominal sterna black, covered with greyish pubescence, except brown mark medially on segment VII.
Head short, covered with short setae; frons with long setae. Antenna covered with short brown setae, denser on antennomere IV; antennomere I with at least six longer, thicker brown setae; II with one of these setae near apex. Antennomeres I– III cylindrical; IV fusiform; I and IV subequal in width at the middle; II subequal in width to III, slightly thinner than I and IV. Labium short. Ocular setae present. Pronotum short, not covering mesonotum, covered with short golden setae, denser laterally; posterior margin slightly concave. Mesonotum covered with short golden setae, denser on posterior margin; lateral margins slightly depressed, forming a small fovea. Metanotum short; posterior margin straight. Meso- and metasterna with long golden setae. Sides of thorax with long brown setae. Legs covered with short setae, with rows of long, thicker setae on femora and tibiae. Trochanters without spines. Fore tibia slightly curved distally, with weak preapical depression; grasping comb extending slightly beyond apex. Hind femur slightly surpassing apex of abdomen, wider than middle femur, with anterior margin curved, posterior margin sinuous; distal half with row of 9–11 thick spines decreasing in size towards apex. Hind tibia slightly curved; basal third with about 11 short subequal denticles, apical spur straight. Abdominal mediotergites subrectangular; IV– V slightly depressed. Abdominal laterotergites raised, more strongly converging for last three segments, with short golden setae. Abdominal sterna without black denticles, with weak median carina on posterior half of segment VII and anterior portion of VIII, covered with short golden setae. Proctiger with small, subtriangular lateral lobes; apex rounded, densely covered with setae. Paramere short, with long setae at apex; apex rounded.
Paratype apterous female. BL 2.88; HL 0.30; HW 0.80; INT 0.21; ANT I 0.65, ANT II 0.30, ANT III 0.40, ANT IV 0.45; EYE 0.24; PL 0.15; PW 0.85; FORELEG: FEM 0.80; TIB 0.85; TAR I 0.04; TAR II 0.02; TAR III 0.24; MIDLEG: FEM 1.55; TIB 0.95; TAR I 0.10; TAR II 0.60; TAR III 0.65; HINDLEG: FEM 1.10; TIB 1.20; TAR I 0.04; TAR II 0.08; TAR III 0.24.
Similar to apterous male in structure and color. Hind femur slightly thinner and less sinuous than in male, with 6–7 spines distally. Dorsum of abdominal segments VII–VIII with a central shiny black spot each. Abdominal laterotergites vertically elevated. Abdominal sternum VII with shiny black mark medially and brown apex.
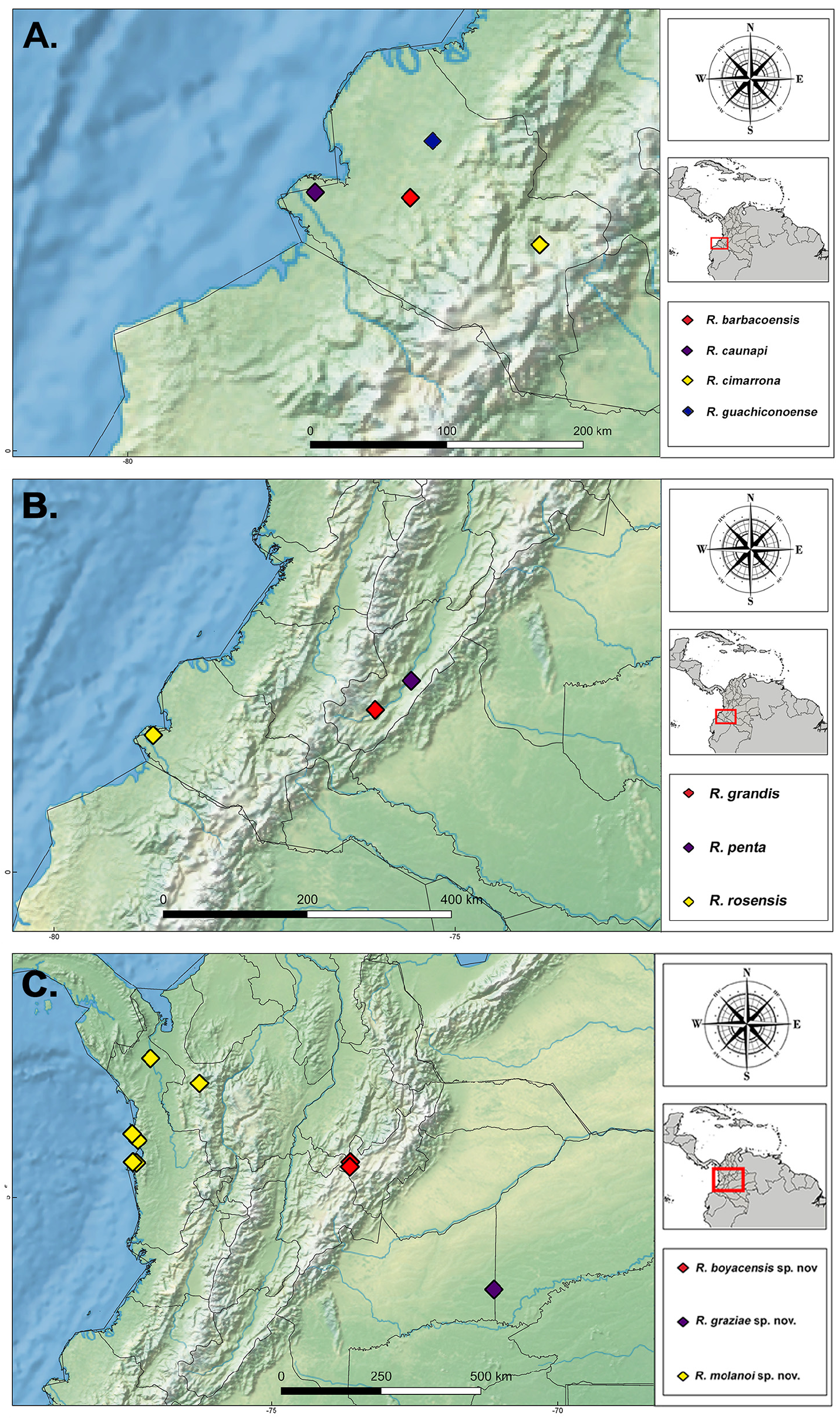
Distribution. Colombia: Nariño (Padilla-Gil 2011, Padilla-Gil 2017), Tolima ( Parra-Trujillo et al. 2014) ( Fig. 23B View FIGURE 23 ).
Comments. Rhagovelia rosensis and R. espriella run to couplet 9 in the key provided by Padilla-Gil (2011). According to this author, they would be separated by the mesonotum “depressed slightly in the centre” in R. rosensis , opposed to “depressed on distal half” in R. espriella , in addition to different shapes of male proctiger and paramere. Examination of the types of both species proved that the parameres are not different between them; neither are the mesonotum and other characteristics such as body and leg measurements, and spination of the hind femur. The drawings provided with the original descriptions are not accurate and, although it seems that the female abdominal laterotergites are reflexed over the mediotergites in R. espriella (Padilla-Gil 2011: Fig. 32 [mistakenly labeled as R. pacifica ]), they are in fact vertical ( Fig. 15C View FIGURE 15 ). Additionally, the type localities of both species are only about 20 km apart from each other. Considering these facts, we propose synonymizing R. rosensis and R. espriella .
Type material examined. Holotype ♂ apterous of R. rosensis ( ICN 054097 View Materials ): ‘ Colombia \ Nariño \ municipio de Tumaco \ vereda Santa Rosa \ Río Mejicano \ 06.II.2009 \ Col: D. N. Padilla’ . Paratype ♀ apterous of R. rosensis ( ICN 054098 View Materials ): same data as holotype . Holotype ♂ apterous of R. espriella (ICN) : ‘ Colombia \ Nariño \ Tumaco \ La Espriella \ km 43 vía Tumaco \ 2009-IV-07 \ Col: N. Nicola’ . Paratypes of R. espriella , 2 ♂ apterous, 2 ♀ apterous ( ICN): same data as holotype .
| PL |
Západoceské muzeum v Plzni |
| PW |
Paleontological Collections |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
| ICN |
Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, Museo de Historia Natural |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Rhagovelia rosensis Padilla-Gil, 2011
| Galindo-Malagón, Ximena Alejandra, Morales, Irina & Moreira, Felipe Ferraz Figueiredo 2021 |
Rhagovelia rosensis
| Padilla-Gil 2011: 216 |
Rhagovelia espriella
| Padilla-Gil 2011: 218 |