Fabifenestella Morozova, 1974
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.4665450 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4664983 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/F157A84D-1A31-FFED-FD36-D4EDF09AFA9B |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Fabifenestella Morozova, 1974 |
| status |
|
Genus Fabifenestella Morozova, 1974 View in CoL
TYPE SPECIES. — Fenestella praevirgosa Shulga-Nesterenko, 1951 . Upper Carboniferous, Russian Platform.
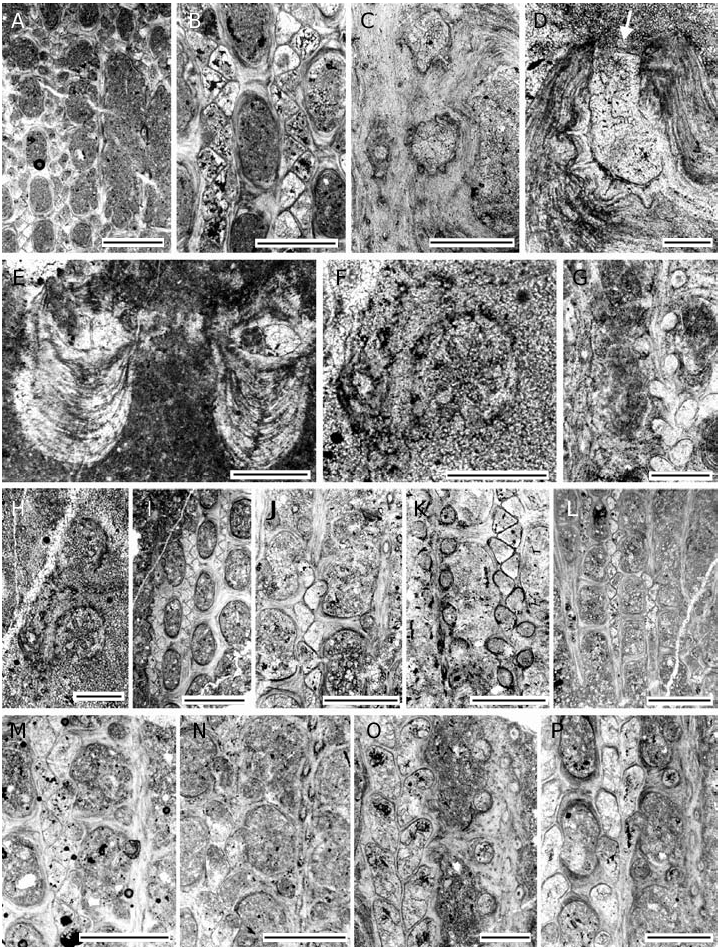
Fabifenestella jabiensis ( Waagen & Pichl, 1885) ( Figs 6O, P View FIG ; 7 View FIG A-C; Table 16)
Fenestella jabiensis Waagen & Pichl, 1885: 778-780 , pl. 87, fig. 4, pl. 88, figs 1, 2. — Sakagami 1970?: 54, 55, pl. 9, figs 4, 5.
Fabifenestella jabiensis – Morozova 2001: 53.
MATERIAL EXAMINED. — 4-4-1, 4-15, 4-16, 4-18, 5-2, 5-8-4, 7-3-1, 7-6, 10-1, 10-2(a), 25-5, 25-8, 25-10, 25-11, 25-12.
OCCURRENCE. — Salt Range: Pakistan, Middle Permian (Guadalupian) ( Waagen & Pichl 1885). Lakaftari: central Iran, Jamal Formation, Middle Permian. Peninsular Thailand, Lower Permian (Artinskian) ( Sakagami 1970).
DESCRIPTION
Micrometric formula: 13-19/7-12//17-21. Reticulated colonies with straight branches, joined by relatively thick dissepiments. Bifurcation common. Autozooecia arranged in 2 alternating rows on branches. Apertures circular, with 8 peristomal nodes, spaced 3-4 per length of a fenestrule. Shape of fenestrules varying from oval to slightly rectangular. Keel low, carrying two alternating rows of small nodes. Some colonies containing larger nodes between smaller ones. Internal granular skeleton thin, continuous with obverse keel, nodes, rods, peristome and across dissepiments. Outer lamellar skeleton moderately thick, containing abundant microacanthostyles 5-15 µm in diameter, with distinct hyaline cores and very thin dark laminated cores. No heterozooecia observed.
INTERIOR DESCRIPTION
Autozooecia rectangular to bean-shaped in the middle tangential section, low and elongated, with well developed vestibule; aperture positioned at distal to distal-abaxial end of chamber. Superior hemisepta long; inferior hemisepta long, low, separating the proximal third of the chamber.
COMPARISON
Fabifenestella jabiensis differs from F. vediensis View in CoL n. comb. in having thicker branches, and larger fenestrules. Sakagami (1970) described a specimen from Artinskian of Peninsular Thailand, which he placed in Fabifenestella jabiensis . However, it has much thicker branches (0.52-0.60 vs. 0.30-0.48 mm in present material), although revealing close morphological similarity to the material described in present paper. Waagen & Pichl (1885) did not give any detailed measurements for F. jabiensis as well as no scale for the plates. Unfortunately, the deposition of the type material for this species is also unknown.
REMARK
Morozova (2001) mentioned two species under different generic names: Minilya jabiensis and Fabifenestella jabiensis . They correspond to the same species, Fabifenestella jabiensis .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Fabifenestella Morozova, 1974
| Ernst, Andrej, Senowbari-Daryan, Baba & Hamedani, Ali 2006 |
Fabifenestella jabiensis
| MOROZOVA I. P. 2001: 53 |
Fenestella jabiensis
| WAAGEN W. & PICHL I. 1885: 780 |