Nymphaster arenatus ( Perrier, 1881 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4955.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:E800A72A-C56A-492C-9EE6-FA4F8277DE31 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4701419 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/FF6987EE-FF8E-FFF2-FF54-43F97E7AF8EB |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Nymphaster arenatus ( Perrier, 1881 ) |
| status |
|
Nymphaster arenatus ( Perrier, 1881) View in CoL View at ENA
Figures 19–20 View FIGURE 19 View FIGURE 20
Pentagonaster arenatus Perrier, 1881: 21 View in CoL ; 1884: 236, pl. 7, figs. 3–4.
Nympluister basilicus — Tommasi, 1970: 12, fig. 35.
Nymphaster arenatus View in CoL — Clark & Downey 1992: 254–255, figs. 38d, 41e, f, pl. 61A–C; Entrambasaguas 2003: 95; Entrambasa- guas 2008: 59; Campos et al. 2010b: 149, fig. 5C; Benavides-Serrato et al. 2011: 165; Costa et al. 2015; Soaréz 2016: 78; Sandino et al. 2017: S294; Rubio-Polania et al. 2018: 190; Borrero-Peìrez et al. 2019: 5; Mah 2020b: 230, fig. 13A–E.
Material examined. (4 specs, 45–70 mm R). BRAZIL. Bahia, Canavieiras (15º39’S; 38º32’W)— 1496 m, 26.xii.1887, 4 specs, R GoogleMaps 45–70 mm ( USNM 18524 About USNM ) .
Comparative material. BRAZIL. Rio de Janeiro, Cabo Frio (19°43’S; 38°36’W), 29.vi.1999, 1 spec, R GoogleMaps 52 mm ( EQMN 2325 ) .
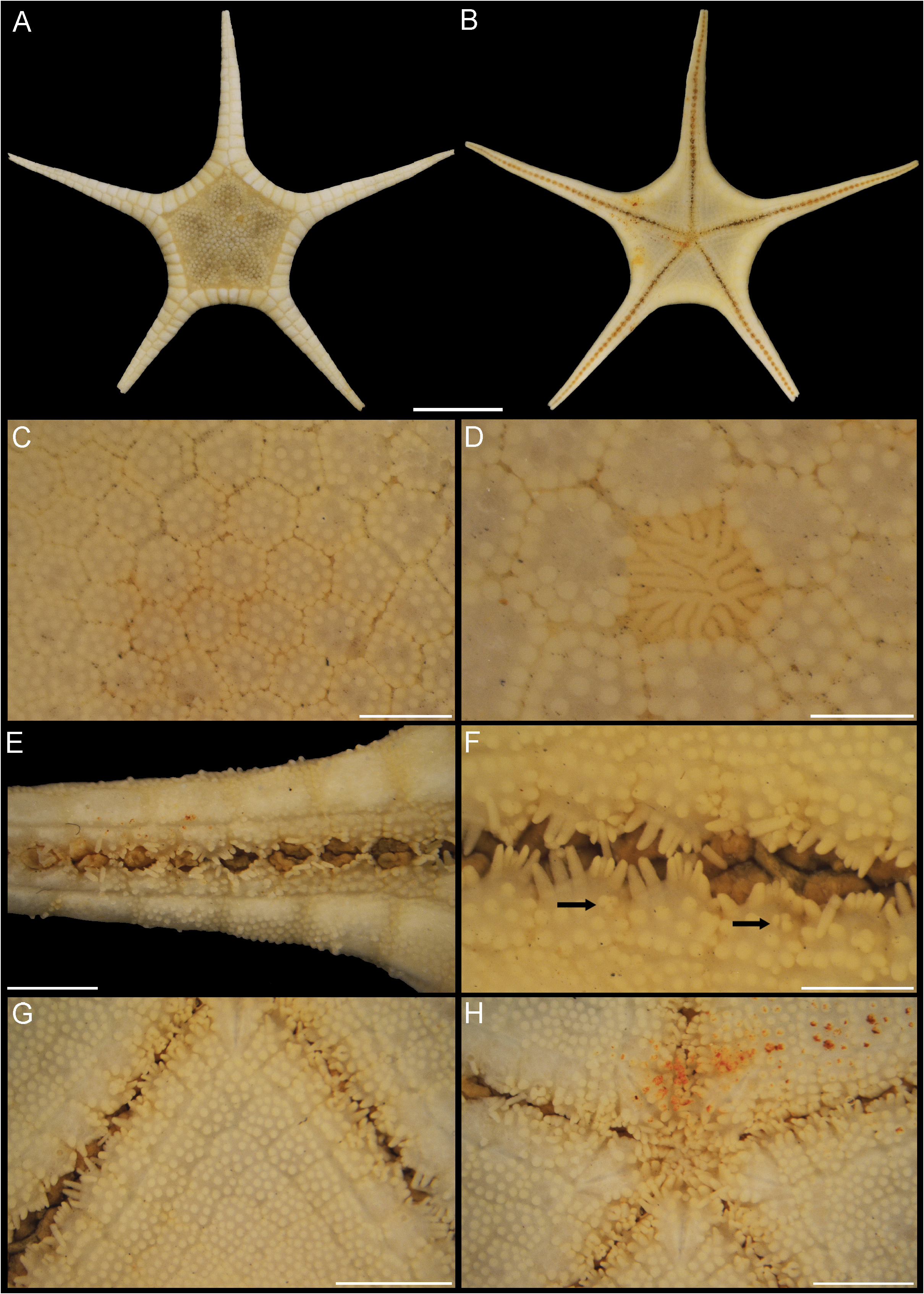
Description (arms broken: R 70 mm, r 21 mm and R 69 mm and r 27 mm). Body stellate, flat, broad disc, long arms ( Fig. 19A–B View FIGURE 19 ); R/r 2.9, 19 SM plates, R/SM# 3.68. Abactinal plates low-tabulate, irregularly round, completely covered by regularly spaced, rounded granules; 4–12 central granules. Some plates with small, excavated sugar-tong pedicellariae ( Fig. 19C View FIGURE 19 ). Papular area includes center of disc; six papular pores surround each plate; single papule in each pore. Madreporite larger than adjacent abactinal plates ( Fig. 19D View FIGURE 19 ). Subcentral anus, surrounded by small, conical spinelets. Superomarginal plates in contact throughout length of arm, covered by large, regularly-spaced, rounded granules. Terminal plates of specimens broken. Inferomarginal plates about twice as wide as long in interradial arc, square-shaped in middle region of arm and about twice as long as wide in distal region of arm. Granulation of inferomarginal plates similar to that of superomarginal plates. Actinal plates rhombic to polygonal, covered by regularly spaced, large, rounded granules slightly larger than those on marginal plates. Some actinal plates with excavate, sugar-tong pedicellariae almost twice as large as abactinal pedicellariae. Adambulacral plates about 1–1.5x as long as wide, half the size of adjacent actinal plates. Furrow margin strongly angular. Apophyses poorly developed from 3 rd –4 th plate, fully developed from eighth plate ( Fig. 19E View FIGURE 19 ). Eight adambulacral spines on proximal plates; number of spines increases with apophysis development, up to 11 spines distally ( Fig. 19F View FIGURE 19 ). Adambulacral spines compressed, moderately long, with rounded tips. 3–4 irregular rows of subambulacral “spines” with 4–5 large, rounded granules slightly taller than actinal granules. Some of first row spines elongated ( Fig. 19F View FIGURE 19 ). Spatulate pedicellariae with 2–4 valves, until 4 th –5 th adambulacral plate. Oral plates long, triangular, with 9–10 spines each, similar to those of adambulacral plates; median spines slightly taller and more compressed than others ( Fig. 19H View FIGURE 19 ).
Ontogenetic variation (arms broken: R 45 and 55 mm, r 15 mm). Average R/r 3.3. Differ from largest specimen by having 4–8 central granules on abactinal plates ( Fig. 20C View FIGURE 20 ); six adambulacral spines in the proximal region; 2–3 irregular rows of subambulacral “spines”, with 2–5 granules ( Fig. 20F View FIGURE 20 ); pedicellariae until the tenth adambulacral plate ( Fig. 20F View FIGURE 20 ); eight oral spines ( Fig. 20H View FIGURE 20 ).
Coloration. The abactinal surface is orange and the actinal surface is cream-colored ( Halpern 1970b).
Distribution. Gulf of Mexico, Mexico, Nicaragua, Colombia (Soaréz 2016; Sandino et al. 2017; Rubio-Polania et al. 2018; Borrero-Peìrez et al. 2019; Mah 2020b). BRAZIL: Bahia, Rio de Janeiro ( Ventura et al. 2007; Campos et al. 2010b; Costa et al. 2015). Depth. 100–3000 m ( Clark & Downey 1992; NMNH 1592525; FSBC I 74877).
Biological notes. Nymphaster arenatus lives on soft, unconsolidated sediment and is classified as scavenger and predator ( Costa et al. 2015; Wagstaff et al. 2014; Mah 2020b). It feeds on fouling organisms, debris, epifauna and decomposing organisms ( Ventura et al. 2007). Campos et al. (2010b) filmed a specimen with an inflated disc in the Campus Basin, between 700–1000 m of depth. A species of polychaete has been found within thestar’s interradius, possibly in a commensal interaction in which the polychaete consumes leftovers from food caught by the sea star ( Mah 2020b).
Lectotype. MCZ 437 About MCZ (designated by Halpern [1970b]).
Type locality. Off Barbados ( Halpern 1970b).
Remarks. All specimens examined here have broken arm-tips such that the number of superomarginal plates could not be counted. Some of the ontogenetic variation observed here were also noted by Halpern (1970b). The variation in number of proximal adambulacral spines, however, is not consistent across studies. The specimens R 45–55 mm described here and the specimen from Rio de Janeiro (R 52 mm) have six spines, the specimen described by Clark & Downey (1992) (R 61 mm) has about seven spines; the specimens R 69–70 mm described here have 7–8 spines, and the specimen described by Halpern (1970b) (R 96 mm) has 6–7 spines. The variation in the number of irregular rows of subambulacral “spines” seems to be more consistent. The specimens R 45–55 mm have 2–3 rows, the specimen R 61 mm has 1–4 rows, and the specimens R 69–96 mm have 3–4 rows. The same applies for the number of oral spines as follows: the specimens R 45–55 mm have 6–8 spines, the specimen R 61 mm has 8–12 spines, the specimens R 69–70 have 9–10 spines and the specimen 96 mm has 10–11 spines. Fisher (1913) used this character to separate species of Nymphaster from the Philippines and most likely overestimated the number of species recorded: a total of nine.
Genus Plinthaster Verrill, 1899
Type species. Plinthaster dentatus ( Perrier, 1884) View in CoL (type by subsequent designation by Fisher, 1910).
Remarks. Plinthaster has four valid species: P. ceramoidea ( Fisher, 1906) (Pacific Ocean), P. dentatus ( Perrier, 1884) (Amphiatlantic, and Pacific Ocean), P. lenaigae Mah, 2018 and P. untiedtae Mah, 2018 (Indian Ocean). Only P. dentatus is recorded in Brazil.
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Nymphaster arenatus ( Perrier, 1881 )
| Cunha, Rosana, Martins, Luciana, Menegola, Carla & Souto, Camilla 2021 |
Pentagonaster arenatus
| Perrier, E. 1884: 236 |
| Perrier, E. 1881: 21 |