Begonia saxifragoides T.N.Bon & C.W.Lin, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/phytotaxa.600.1.3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8061468 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03D22242-392B-2B26-B598-0E23FB99FA41 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Begonia saxifragoides T.N.Bon & C.W.Lin |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Begonia saxifragoides T.N.Bon & C.W.Lin View in CoL , sp. nov.
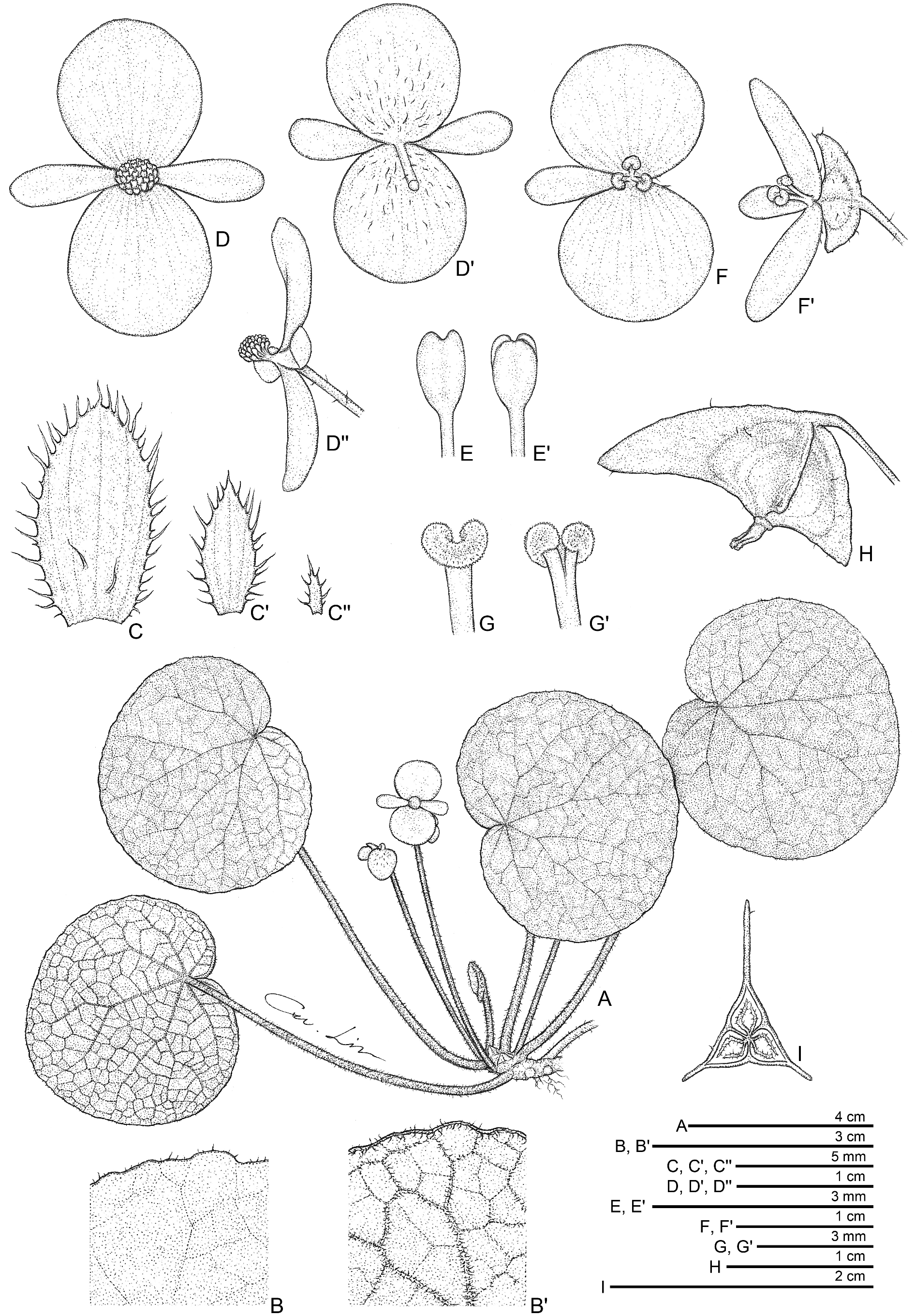
§ Platycentrum ( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 & 3 View FIGURE 3 ).
Type: — VIETNAM. Son La Province: Muong La District, Ngoc Chien Commune , 1,900 m elevation, 18 September 2022, Trinh Ngoc Bon, Thi Thanh Ha Do, Thi Hanh Le, Minh Duc Lo, Heidi Zimmer, Lo Van Chieu, Sung A Giang & Sung A Chu SCU2022-03 About SCU (Holotype VAFS) .
Monoecious rhizomatous herb. Rhizome stout, greyish-red to reddish-brown, 10−15 cm or longer, 8−12 mm thick, internodes congested, densely pilose or villous. Stipules persistent, reddish-brown, triangular, ca. 5 × 6 mm, herbaceous, strongly keeled, midrib scattered with hirsute, margin entire, apex aristate, arista 2.5–5 mm long. Leaves alternate, petiole terete, greyish-red to pale brownish-red, 9−13 cm long, 3.5−4.5 mm diameter, densely rosy pink to white pilose or villous, turning pale brown with age; leaf blade asymmetric, oblique, orbicular to reniform, 6.5−8.3 × 6.7–9 cm, broadside 3.6–5.4 cm wide, basal lobes cordate, 1.5–2.2 cm long, apex rounded, margin denticulate to crenulate, recurved and undulated, with a line of magenta to white pilose or puberulous hairs; leaf thinly coriaceous, succulent, adaxially glabrous or subglabrous, greyish-green to olive green, venation blackish-green and slightly impressed; abaxially pale reddish-green to magenta; venation basally ca. eight palmate, primary veins branching dichotomously or nearly so, tertiary veins reticulate; all veins densely pink to magenta pilose or puberulous on abaxial surface. Inflorescences axillary, bisexual, cymose arising directly from the rhizome, ca. two orders of branching; peduncle pink to red, 5.5−7 cm long, pinkish-white pilose or villous. Bracts caducous, yellowish-green to pinkish-green, at basal node of inflorescence ovate, ca. 6.5 × 3 mm, abaxially sparsely pilose or glabrous, margin fimbriate; bracts on upper nodes similar but gradually smaller. Staminate flower: pedicel pinkish-yellow to pale pinkish-green, 8−10 mm long, sparsely pilose, tepals 4, pinkish-white to pink, outer two suborbicular to widely obovate, 8.5−13 × 10−15 mm, abaxially pilose or villous, margin entire, apex rounded, inner two narrowly obovate to oblong, 8−10 × 4−5 mm, glabrous, apex obtuse or rounded; androecium zygomorphic, 3.5−5 mm across; stamens yellow, 40−45; filaments ca. 1.3 mm long, fused at base; anthers oblong to obovate, ca. 1 mm long, 2-locular, apex retuse. Pistillate flower: pedicel pinkish-white to pale pinkish-green, 6−8 mm long, very sparsely pilose or glandular hairs, tepals 3, whitish-pink; outer two suborbicular to very widely obovate, 8.5−9 × 10−12 mm, abaxially pilose or puberulous, margin entire, apex rounded, inner one oblanceolate to narrowly elliptic, ca. 7.5 × 3 mm, apex obtuse; ovary widely trigonous-globose, 2.5–4 mm long, 3–4.5 mm thick (wings excluded), rosy pink to pale pinkish-yellow, sparsely pilose or glandular hairs; 3-winged, wings unequal, pinkish-white to yellowish-pink, sparsely pilose or glandular hairs, margin entire; wings triangular to falcate, 3.5–4.5 mm long, lateral wings narrower, 1.5–2 mm wide, abaxial wing 3–4 mm wide; ovary 3- locular, placentae bilamellate; styles 3, C-shaped, shortly fused at base, golden yellow, ca. 3.5 mm long, stigma slightly spirally twisted. Capsule body trigonous-globose, 6–7 mm long, 8–9.5 mm thick (wings excluded), yellowish-red to reddish-green when fresh; wings unequal, ca. 10 mm long, lateral wings triangular, 3–4 mm wide, abaxial wing triangular to falcate, 8–9 mm wide, truncate distally, rounded proximally.
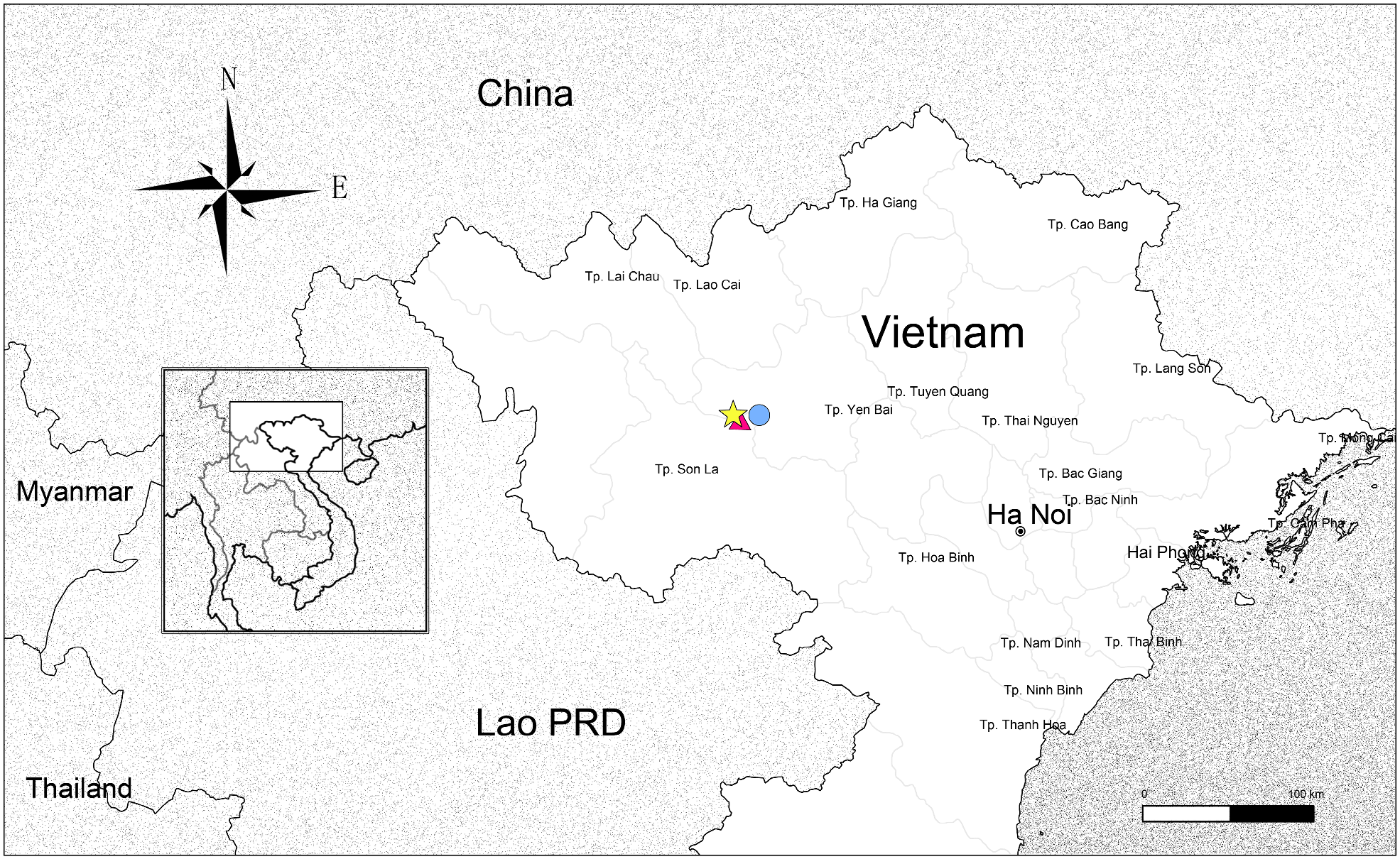
Distribution and ecology: —Endemic to Ngoc Chien Commune, Muong La District, Son La Province: northern Vietnam ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). Grows on mossy cliff faces or steep slopes in semi-shaded and consistently humid areas in montane cloud forest at 1,200 –1,900 m elevation. Begonia saxifragoides is only known from a secondary evergreen forest. The following plants are recorded as associations, co-occurring with the new species: Selaginella tamariscina (Selaginellaceae) , Angiopteris yunnanensis (Marattiaceae) , Cyathea yunnanensis (Cyatheaceae) , Dicranopteris linearis (Gleicheniaceae) , Pteris semipinnata and other Pteris sp. (Pteridaceae) , Tectaria sp. (Tectariaceae) , Lindera rufa , Litsea cubeba (Lauraceae) , Alpinia calcarata (Zingiberaceae) , Cyrtococcum patens (Poaceae) , Altingia yunnanensis (Altingiaceae) , Elatostema balansae (Urticaceae) , Betula alnoides (Betulaceae) , Choerospondias axillaris (Anacardiaceae) , Tetradium glabrifolium (Rutaceae) , Schima wallichii (Theaceae) , Alniphyllum eberhardtii (Styracaceae) , Saurauia tristyla (Actinidiaceae) , Lasianthus sp. , Lerchea micrantha , Ophiorrhiza baviensis (Rubiaceae) and Staurogyne sp. (Acanthaceae) .
Etymology: —The specific epithet derives from the genus name of Saxifraga stolonifera , and the Latin suffix -oides, referring to the orbicular leaves with crenulate margin.
Conservation:— Begonia saxifragoides is considered Vulnerable (VUD2) according to IUCN criteria (2022), because of its isolated occurrence. The species has a small population size estimated at less than 2,500 mature individuals, which matches criterion EN C1, however there are no observed or projected declines. In eight survey routes conducted in 2022, we encountered two populations. Population 1 (elevation 1,200 m) consists of 18 individuals scattered across an area of 1000 square meters along the survey route. Population 2 (elevation 1,900 m) consists of six individuals scattered in an area of 500 square meters along the investigation line.
Ngoc Chien Commune is renowned for its abundant tourism resources, and the type locality is not under the jurisdiction of a protected forest. This implies that the habitat of this species may be vulnerable to damage from unforeseen events.
Notes: — Begonia saxifragoides shares characteristics with B. minhaniae , such as rhizomatous habit, hairy petioles, 4-tepaled staminate flowers and 3-tepaled pistillate flowers and 3-locular ovary. However, the distinctive characteristics of B. saxifragoides (compared to B. minhaniae ) are its orbicular to reniform (vs. widely ovate) leaves, apex rounded (vs. acute to acuminate), petiole densely rosy pink to white pilose or villous (vs. yellowish-brown tomentose), stamens 40–45 (vs. ca. 15), ovary trigonous-globose (vs. ovary trigonous-ellipsoid) and wings sparsely pilose or glandular hairs (vs. glabrous or sparsely tomentose).
Among Vietnamese Begonia species of sect. Platycentrum , B. saxifragoides is also similar to B. sinovietnamica C.Y. Wu (1997: 50) , but this species has widely ovate lamina that is hirsute on the upper surface (vs. orbicular to reniform and glabrous in B. saxifragoides ), anther apex truncate to rounded (vs. retuse in B. saxifragoides ) and pistillate flowers having five tepals (vs. three tepals in B. saxifragoides ).
Based on several morphological characters, such as orbicular lamina with a hairy petiole and the number of tepals in both staminate and pistillate flowers, the new species bears a superficial resemblance to B. crystallina Y.M.Shui & W.H.Chen (2005: 360) . However, it is morphologically distinct from B. crystallina on account in the following diagnostic characters: leaves upper surface glabrous or subglabrous (vs. setulose), 3-locular (vs. 1-locular) ovary with triangular to falcate (vs. lunate) wings.
A comparison of the salient characters of the four species is presented in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
| A |
Harvard University - Arnold Arboretum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |