Daptonema papillifera, Sun & Huang & Tang & Zang & Xiao & Tang, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4614.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:2CFBC315-F417-4B3E-B469-6B986344C30E |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/FA2A8793-CA52-F17B-E2CC-8DEEFE228ED5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Daptonema papillifera |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Daptonema papillifera View in CoL sp. nov.
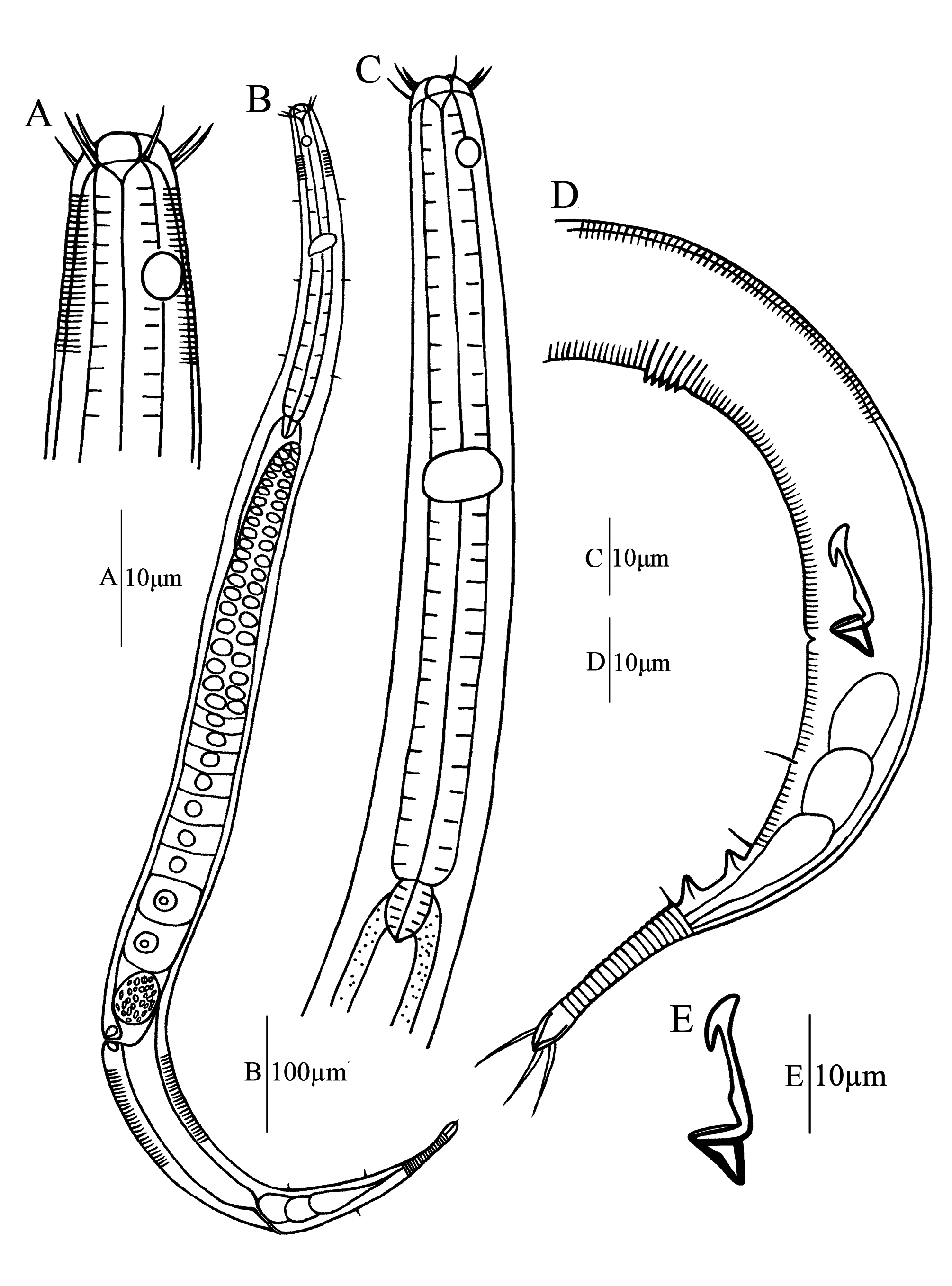
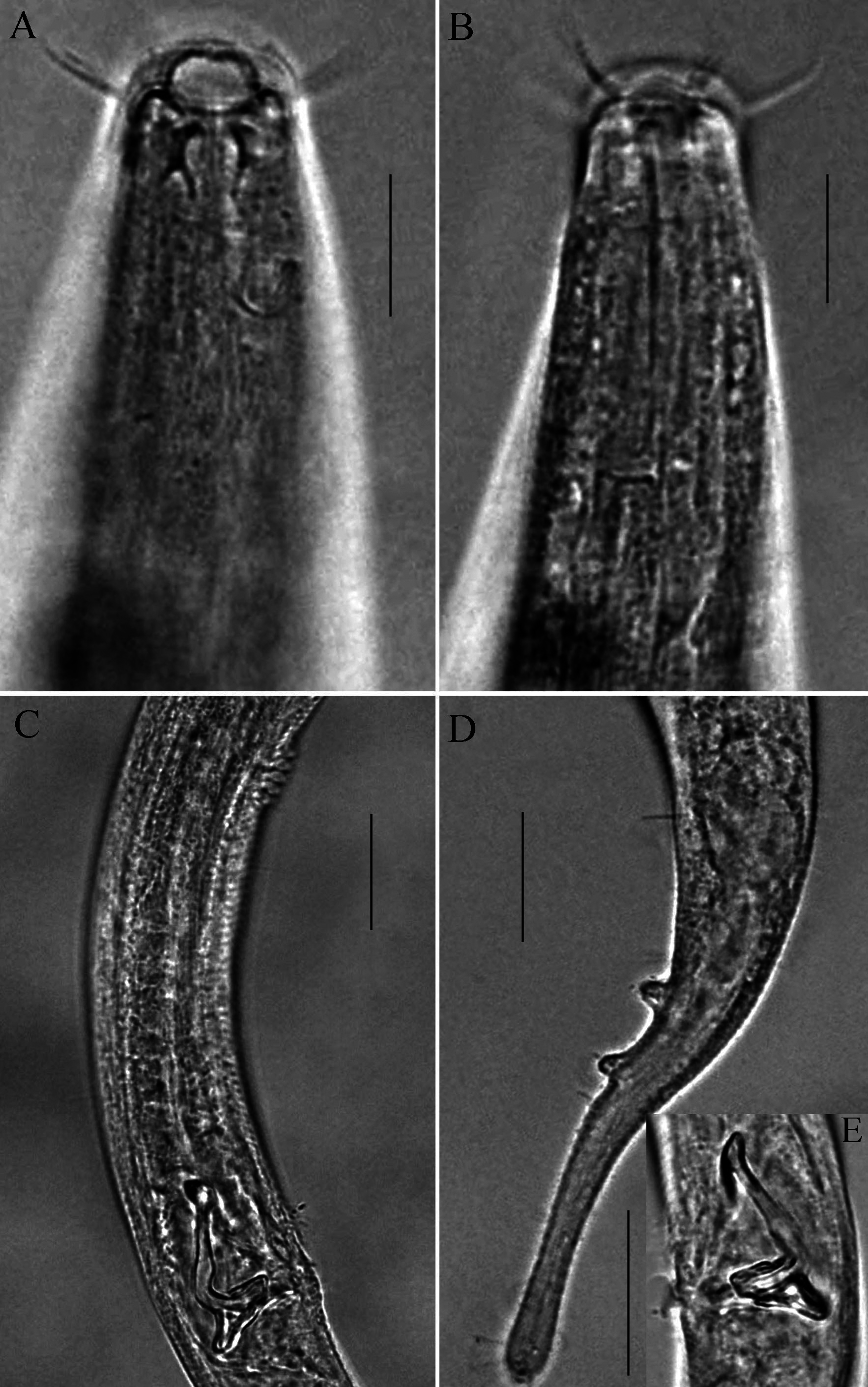
( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 )
Type material. Three males and one female were obtained from the Laizhou Bay. Holotype ♂ 1 on slide WF–40–3. Paratypes ♂ 2, ♂ 3 and ♀ 1 on slides WF–40–4, GL–68–2 and WF–40–3, respectively.
Type locality and habitat. Specimens were collected from the intertidal silt sediment (0–2 cm surface layer) in the Laizhou Bay (37°13′17″N, 119°10′34″E) GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The species name is derived from the Latin papillifera and refers to having two ventral papillae on tail.
Measurements. All measurement data are given in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
Description. Males. Body cylindrical, tapering towards both extremities, 910–950 µm long. Cuticle finely transversely striated. Somatic setae not observed. Head rounded, with six spherical lips. Inner labial sensilla papilliform. Outer labial sensilla setiform. Six outer labial sensilla and four cephalic setae united in one circle. Outer labial setae 9 µm, cephalic setae 6–7 µm. Amphideal fovea circular, 5 µm in diameter, and occupying 30% of corresponding body diameter. Amphideal fovea located at a distance of 15 µm from anterior end. Buccal cavity funnel-shaped and its wall cuticularized, 5–7 µm deep. Tooth absent. Pharynx cylindrical, not broadening at base. Cardia well developed, oval and surrounded by intestinal tissue. Excretory-secretory system not observed. Nerve ring at middle of pharyngeal length. Tail 123–127 µm, i.e. equal to 4.5 cloacal body diameters in length, conicocylindrical with two distinctive ventral papillae at transition region between proximal conical portion and distal cylindrical portion of tail. Row of 3–4 ventral caudal setae, 5 µm long. Three terminal setae, 11 µm long. Three caudal glands present in cloacal region of tail. Spinneret well developed. Reproductive system monorchic. One anterior testis outstretched, on left side of intestine, extending to position of 110 µm below pharyngeal base. Spicules L-shaped, with cephalate proximal end, equal to 1.6–1.7 cloacal body diameters in length. Gubernaculum with triangular blunt dorsal apophysis, 7–8 µm long. Five or six midventral conjoint precloacal cuticularized spines located at a distance of 80–90 µm in front of the cloaca.
Female. Similar to males in most respects but body slightly larger in size and amphideal fovea smaller. Tail conico-cylindrical with two terminal setae, 3 µm long. Short somatic setae (i.e. 5 µm long) scattering at pharyngeal region. Reproductive system monodelphic, one anterior outstretched ovary, extending towards the base of pharynx, situated to left of intestine. Oviduct a wide tube. Spermatheca present. Vagina straight. Vulva located at posterior portion of the body (i.e. at 69% of the body length from the anterior end).
Differential diagnosis and discussion. D. papillifera sp. nov. is characterized by short body, ten anterior setae in a circle, funnel-shaped buccal cavity without tooth, circular amphideal fovea located in the posterior position, Lshaped spicules with cephalated proximal end, precloacal supplement consisting of 5–6 conjoint cuticularized spines, conico-cylindrical tail with two ventral papillae and three terminal setae. From these basic characteristics, the present species should belong to the genus Daptonema . Nevertheless, it is the only one which has 5–6 conjoint precloacal cuticularized spines and two ventral caudal papillae. Using these unique features, the new species can be easily identified from the other species in this genus. In addition, D. papillifera sp. nov. is similar to D. amphorum Leduc, 2015 (900–1200 µm vs. 900–1000 µm) and D. foetidum Gagarin and Thanh, 2010 (900–1200 µm vs. 990–1350 µm) in body size. However, D. papillifera differs from both species in the structure of the spicular apparatus and its gubernaculum with long dorso-caudal apophyses.
D. papillifera sp. nov. resembles D. hirtum ( Gerlach, 1951) , D. phuketense Aryuthaka & Kito, 2018 and D. chonispiculum Aryuthaka & Kito, 2018 in main morphological characteristics, namely in the length of cephalic setae, position of amphideal fovea, structure of spicules and gubernaculum. It differs from D. hirtum in the structure of the spicular apparatus (L-shaped spicules with cephalated proximal end vs. arculate spicules without cephaliate proximal end)), longer spicules (43–44 µm vs. 22–26 µm) and absence of long cervical setae. It differs from D. phuketense in its body length (900–1200 µm vs. 1264–1461 µm), shorter spicules (43–44 µm vs. 52–61 µm), absence of cervical setae, presence of precloacal cuticularized spines and ventral caudal papillae, and shorter tail (123–165 µm vs. 208–233 µm). It differs from D. chonispiculum in having shorter cephalic setae (6–7 µm vs. 15.2–20.4 µm), shorter spicules (43–44 µm vs. 47–53 µm), shorter tail (123–165 µm vs. 182–257 µm) and absence of cervical and somatic setae.
Daptonema is a common and abundant genus. At present, three species were described as new to science from the Chinese territorial waters, namely Daptonema longiapophysis Huang & Zhang, 2010 and D. parabreviseta Huang, Sun & Huang, 2019 were found in the Yellow Sea; D. donghaiensis Wang, An & Huang, 2018 was recorded in the East China Sea.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Daptonema papillifera
| Sun, Yan, Huang, Yong, Tang, Hongshuo, Zang, Yu, Xiao, Hui & Tang, Xuexi 2019 |
D. papillifera
| Sun & Huang & Tang & Zang & Xiao & Tang 2019 |
D. parabreviseta
| Huang, Sun & Huang 2019 |
D. phuketense
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2018 |
D. chonispiculum
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2018 |
D. phuketense
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2018 |
D. chonispiculum
| Aryuthaka & Kito 2018 |
D. donghaiensis
| Wang, An & Huang 2018 |
Daptonema longiapophysis
| Huang & Zhang 2010 |
D. hirtum (
| Gerlach 1951 |
Daptonema
| Cobb 1920 |