Laviactis lucida
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3826.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FD0A7BBD-0C72-457A-815D-A573C0AF1523 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6140451 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/855187F4-8258-D775-FF48-9E94E158F82E |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Laviactis lucida |
| status |
|
Laviactis lucida View in CoL (Duchassaing de Fombressin & Michelotti, 1860) comb. nov.
( Figs. 20–21 View FIGURE 20 View FIGURE 21 , Table 7)
Capnea lucida Duchassaing de Fombressin & Michelotti, 1860 Heteractis lucida: Duchassaing de Fombressin & Michelotti 1864 Heteractis Lucida View in CoL [sic]: Duchassaing de Fombressin 1870 Ragactis lucida: Andres 1883 ( 1884)
Aiptasia lucida: Duerden 1897 View in CoL
Bartholomea pseudoheteractis Watzl, 1922 View in CoL
Bartholomea lucida: Carlgren 1949 View in CoL
Material examined. (See Appendix 1).
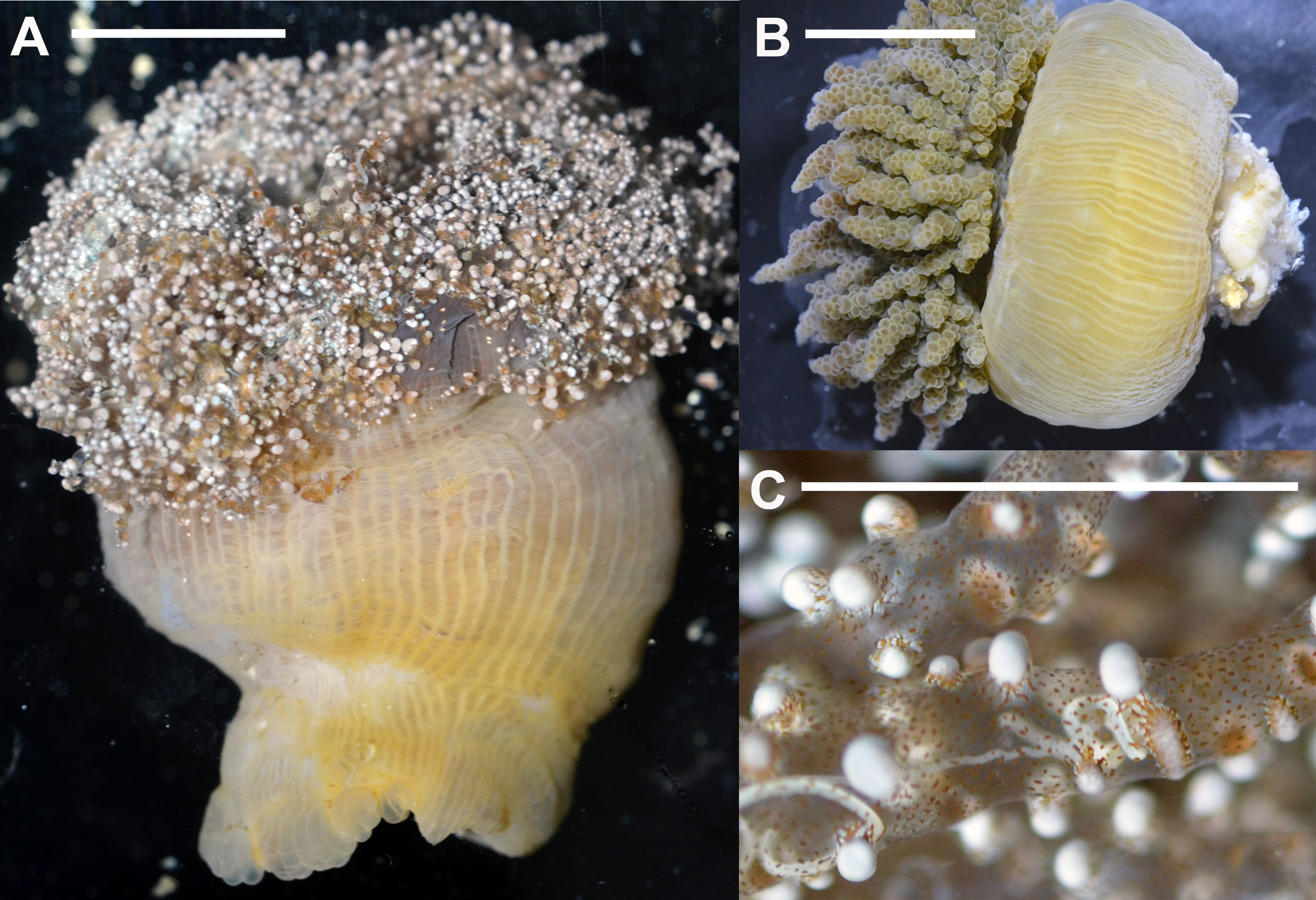
Description. External anatomy ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 ): Pedal disc to 50 mm diameter in preserved specimens, wider than column in living specimens. Column elongate, divisible in scapus and capitulum, to 50 mm height and to 30 mm diameter in preserved specimens (to 120 mm height and 50 mm diameter in living specimens). Cinclides in midcolumn, very numerous, in up to five rows, corresponding with endocoels of first two cycles of mesenteries ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 B). Rounded, relatively large oral stoma. Mesenterial insertions visible ( Figs. 20 View FIGURE 20 A, B). Oral disc to 30 mm diameter in preserved specimens. Tentacles to 192, tapering toward tips, all of same length, 10–30 mm in preserved specimens (50–70 mm length in living specimens). Tentacles not fully retractile, with hollow vesicles containing batteries of microbasic p -amastigophores and basitrichs ( Figs. 20 View FIGURE 20 A, C).
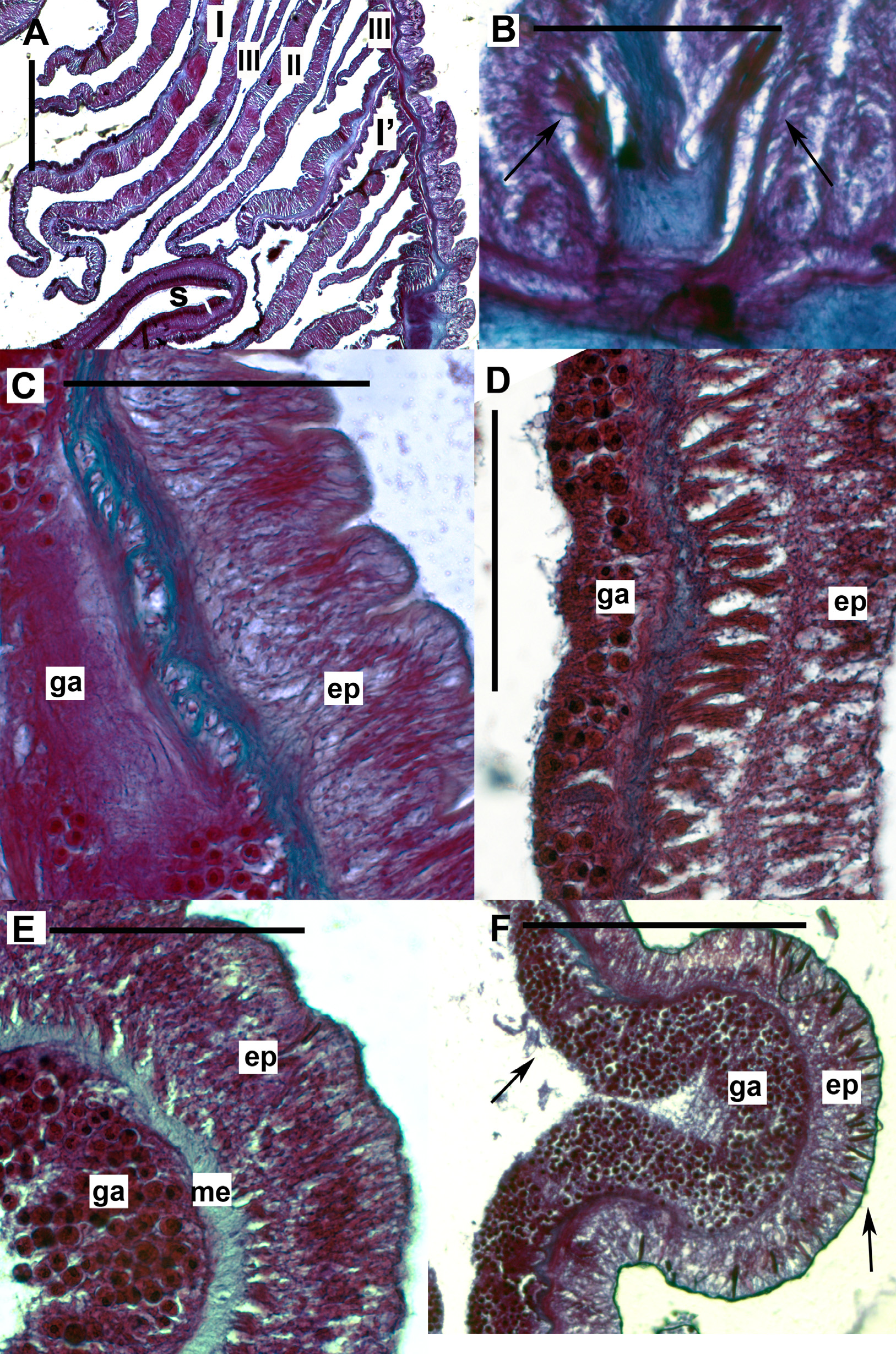
Internal anatomy and microanatomy ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 ): Marginal sphincter muscle mesogleal, diffuse, weak, alveolar ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 C). More mesenteries distally than proximally. Mesenteries hexamerously arranged in five cycles. All cycles fertile, including directives. Two pairs of directives each associated with a deep siphonoglyph ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 A). Retractor muscles diffuse, long, occupying entire mesentery ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 A). Parietobasilar muscles well differentiated with strong processes. Longitudinal muscles of tentacles ectodermal ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 E). Strong longitudinal ectodermal muscles in distal end of column ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 D). Basilar muscles well differentiated, distinct, strong, with fibers on long mesogleal pennon ( Fig. 21 View FIGURE 21 B). Acontia very numerous, long.
Color ( Fig. 20 View FIGURE 20 ): Living specimens with yellowish-translucent column proximally, darker distally; tentacles translucent with brown small spots and distinct white vesicles ( Figs. 20 View FIGURE 20 A, C). Preserved specimens with yellowish column proximally and slightly darker distal column and tentacles; vesicles visible in preserved specimens.
Cnidom: Spirocysts, basitrichs, microbasic b -mastigophores and p -amastigophores ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 ). See Table 7 for size and distribution.
Geographic and bathymetric distribution. From Bahamas to Barbados, along the entire Caribbean Sea ( González-Muñoz et al. 2012). This is a shallow water species found between 1– 15 m.
Taxonomic remarks. Laviactis lucida comb. nov. has a complicated taxonomic history (reviewed in González-Muñoz et al. 2012). We agree with González-Muñoz et al. (2012) that, based on morphology, L. lucida comb. nov. clearly belongs within Aiptasiidae . Available information on the other species of the genus, L. hyalina comb. nov., is too scarce to determine the identity of the species ( Le Sueur 1817; Milne Edwards 1857) and type material is not available; thus, the status of L. hyalina comb. nov. and its relationship with L. lucida comb. nov. remains unclear.
As previously suggested (e.g. Dunn 1981; González-Muñoz et al. 2012), our results show that Laviactis lucida comb. nov. and Bartholomea annulata differ primarily in the morphological structure of the tentacles. We consider the different morphology of the tentacles sufficient to maintain the genera as separate until the status of the additional species within both genera is studied further.
TABLE 7. Size ranges of the cnidae of Laviactis lucida comb. nov. x, mean; SD, standard deviation; S, ratio of number of specimens in which each cnida was found to number of specimens media examined; N, Total number of capsules measured; F, frequency; +++, very common; ++, common; +, rather common; Abbreviations: M, Microbasic.
Categories Range of length and width x ± SD S N F
of capsules (µm)
PEDAL DISC
M p -amastigophores (20.4–34.7) x (3.5–6.3) 23.8±3.2 x 4.9±0.7 2/2 38 +++
Basitrichs (11.9–27.7) x (1.9–5.7) 16.6±1.1 x 5.7±1.1 2/2 32 +++
COLUMN
M p -amastigophores (13.1–22.3) x (3.2–5.6) 17.1±2.7 x 4.2±0.5 2/2 35 +++
Basitrichs (11.1–17.1) x (1.4–2.9) 13.6±1.8 x 2.3±0.4 2/2 34 +++
M b -mastigophores (16.6–24.8) x (3.2–5.1) 21.9±1.8 x 4.1±0.5 2/2 34 +++
TENTACLES
M p -amastigophores (36.1–54.7) x (18.1–25.2) 41.8±3.8 x 6.5±0.9 2/2 30 +++
Basitrichs (18.1–25.2) x (1.5–3.1) 21.2±2.3 x 2.5±0.5 2/2 28 ++
Spirocysts (15.1–30.3) x (2.3–6.7) 22.4±4.4 x 3.9±0.9 2/2 37 +++
ACTINOPHARYNX
M p -amastigophores (34.1–40.1) x (4.7–5.8) 37.4±1.8 x 5.1±0.4 2/2 41 +++
Basitrichs (18.2–26.5) x (2.2–3.5) 22.3±2.4 x 2.9±0.4 2/2 38 ++
FILAMENTS
M p -amastigophores 1 (12.2–14.2) x (2.3–3.1) 13.2±0.6 x 2.8±0.2 2/2 31 +++
M p -amastigophores 2 (38.6–44.5) x (5.3–7.2) 40.7±1.8 x 6.2±0.7 2/2 30 +++
Basitrichs (11.6–12.9) x (1.9–3.6) 12.2±0.4 x 2.4±0.6 2/2 27 +
ACONTIA
M p -amastigophores 1 (15.6–16.5) x (3.2–3.3) 67.1±2.8 x 9.5±0.5 2/2 33 ++
M p -amastigophores 2 (61.8–71.1) x (8.4–10.3) 16.1±0.6 x 3.3±0.1 2/2 32 +++
Basitrichs (22.7–35.1) x (1.5–3.2) 30.6±2.4 x 2.3±0.4 2/2 35 +++
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Laviactis lucida
| Grajales, Alejandro & Rodríguez, Estefanía 2014 |
Bartholomea lucida:
| Carlgren 1949 |
Bartholomea pseudoheteractis
| Watzl 1922 |
Aiptasia lucida:
| Duerden 1897 |
Ragactis lucida:
| Andres 1883 |