Momordica rostrata, ZIMM.
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5252/adansonia2022v44a10 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6390568 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03E087F9-FF83-FF8A-FCB5-FBA8FA0820A3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Momordica rostrata |
| status |
|
MOMORDICA ROSTRATA ZIMM. View in CoL
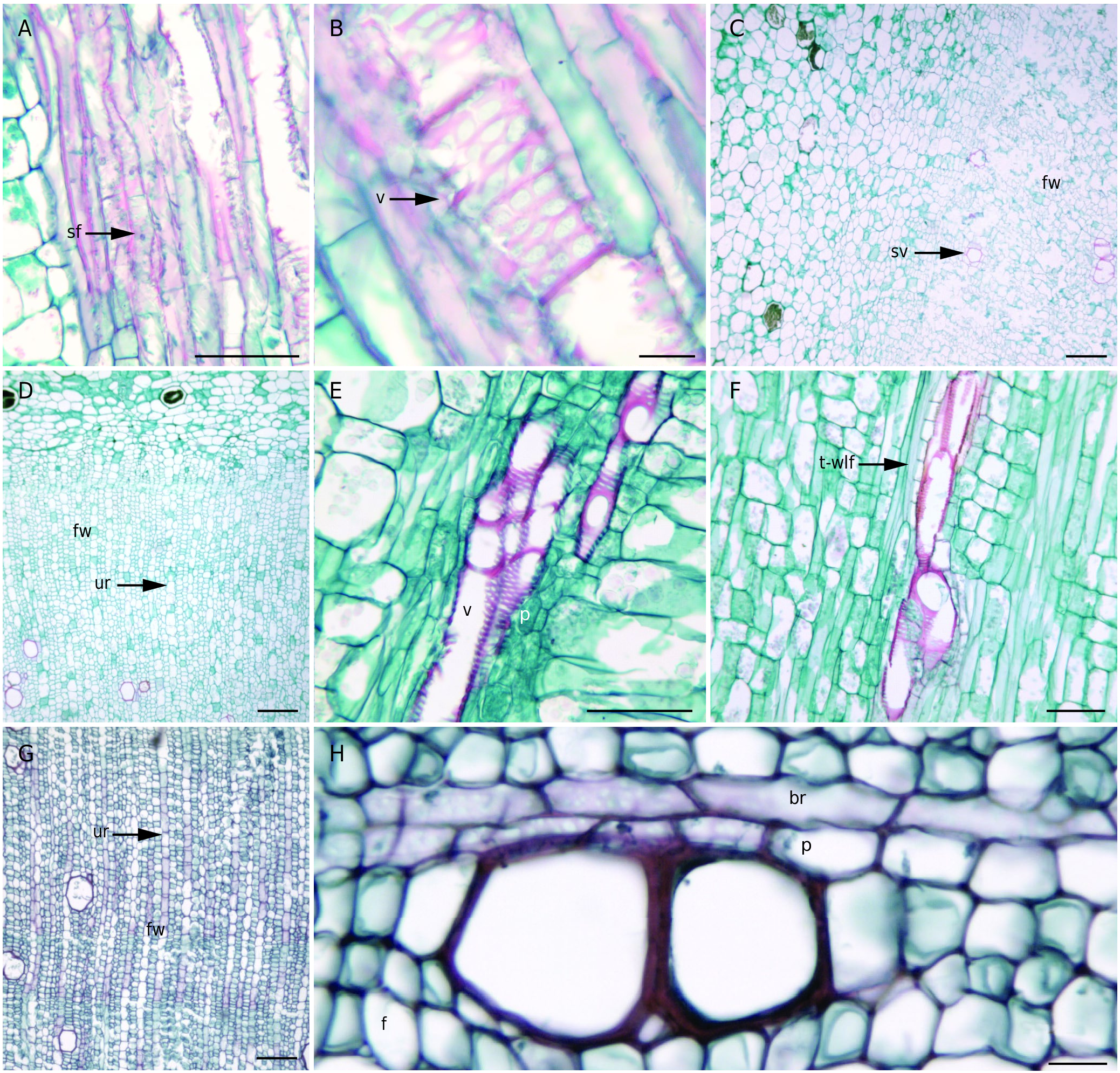
Stem ( Fig. 1G View FIG ) and caudex ( Fig. 1H, I View FIG ) have similar anatomical features. Cortex cells have abundant chloroplasts, and the inner part has a ring of parenchyma cells that are lignified. Wood is parenchymatous, it has large amount of latex and is formed by successive vascular cambium ( Fig. 1H, I View FIG ). The axial matrix has scanty axial parenchyma, libriform, septate fibers ( Fig. 2A View FIG ), and solitary vessels with circular bordered pits ( Fig. 2B View FIG ). Rays are multiseriate and ray cells have undergone proliferation, making them to be confused with the conjunctive tissue. Bands of conjunctive tissue and ray parenchyma have formed a matrix of ground parenchyma. Secondary phloem has some functional cells, and few phloem cells are collapsed.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |