Palaemon antennarius H. Milne Edwards, 1837
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3905.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3DFAB0A2-5CC2-465A-B5D7-858D263532EF |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6121016 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3F6487CC-FFB8-FFE4-14C3-F98797C6ECDC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Palaemon antennarius H. Milne Edwards, 1837 |
| status |
|
Palaemon antennarius H. Milne Edwards, 1837 View in CoL (in H. Milne Edwards, 1834 –1840)
( Figures 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4 View FIGURE 4 , 5 View FIGURE 5 )
Palaemon lacustris View in CoL von Martens, 1857: 183; Plate 10, Figs 1–9 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 .
Pelias migratorius Heller, 1862: 409 ; Plate 2, Fig. 35 (partim).
Anchistia migratoria Heller, 1863: 259 ; Plate 8, Fig. 20 (partim).
Palaemonetes varians View in CoL — Heller, 1869: 157 (partim). Not P. v a r i an s Leach, 1813.
Palaemonetes varians View in CoL var. thermajophilus Garbini, 1879: 187 [nomen nudum].
Palaemonetes varians View in CoL var. termaiophilus Garbini, 1881: 108 [nomen dubium].
Palaemonetes varians View in CoL var. macrogenitor Boas, 1889: 800 ; Figs (partim) 2 (N1–5), 3 (N1–5), 4 (N1–5); Plate 23, Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 , 4 View FIGURE 4 , 6 View FIGURE 6 .
Palaemonetes antennarius View in CoL — Sollaud, 1938: 638; Figs IA, IB.— González-Ortegón & Cuesta, 2006: 99; Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 G, 2C, 3C.—Anastasiadou et al. 2009: Fig 2 View FIGURE 2 .—Tzomos et al. 2010: 38.
Material examined. Lectotype (hereby designated): 1 ♀ (pocl 7.7 mm), MNHN –IU–2013–9296 (= MNHN –Na 1500), Trasimeno Lake, Italy (stn 34). Paralectotypes: 8 ♀♀ (pocl 7.0– 8.1 mm), MNHN –IU–2013–4023 (= MNHN –Na 1500), Trasimeno Lake, Italy (stn 34).
Non– type material. Italy: 9 ♀♀ (2 ovig) (pocl 5.9–8.3 mm), 4 ♂♂ (pocl 4.0– 4.8 mm), Tirso river (mouth), Sardinia (stn 22), 10.4.1984, coll. Mura M.; 7 ♀♀ (1 ovig) (pocl 4.9–8.8 mm), 5 ♂♂ (pocl 4.0–5.0 mm), Frigole, Lecce (stn 23), 1980, coll. Froglia C.; 7 ♀♀ (pocl 4.9–7.0 mm), 3 ♂♂ (pocl 4.9–5.1 mm), Laguna Acquatina, Apulia (stn 24), 1988, coll. Belmonte G.; 1 ♀ (pocl 5.0 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 4.5 mm), Paestum (stn 25), 1990; 4 ♀♀ (pocl 7.8–10.0 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 5.4 mm), Latina (stn 26), 2.2.1991, coll. Ketmaier V.; 2 ♀♀ (pocl 8.0– 9.4 mm), Aniene river, Fiumicino, Roma (stn 27), 12.10.1986, coll. Piersimoni R.; 4 ♀♀ (pocl 6.8–8.4 mm), 10 ♂♂ (pocl 4.9–6.0 mm), Lake of Lesina, Gargano (stn 28), 20.7.1982, coll. Piscitelli C.; 2 ♀♀ (pocl 4.0– 5.1 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 4.5 mm), Portonovo, Ancona (stn 29), 16.10.1973, coll. Froglia C.; 2 ♀♀ (pocl 6.0– 6.8 mm), 2 ♂♂ (pocl 5.0– 5.4 mm), Albinia, Grosseto (stn 30), 10.9.1986, coll. Ugolini A.; 4 ♀♀ (pocl 5.9–7.8 mm), 6 ♂♂ (pocl 4.7–5.8 mm), Tevere river, Paglia (stn 31), 1.9.1975, coll. Froglia C.; 2 ♂♂ (pocl 4.0– 5.1 mm), Chiusi lake - Arezzo (stn 32), 17.9.1986, coll. Ugolini A.; 1 ♀ ovig (pocl 7.3 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 5.2 mm), Ponsacco, Pisa (stn 33), 19.5.1981, coll. Delmastro G.B.; 10 ♀♀ (3 ovig) (pocl 6.8–8.2 mm), 5 ♂♂ (pocl 4.5–6.0 mm), Trasimeno Lake (stn 34), 6.9.1974, coll. Froglia C. & E. Peloni; 4 ♂♂ (pocl 4.6–6.6 mm), Misa river (stn 35), 10.5.1987, coll. Froglia C.; 4 ♀♀ (pocl 5.5–7.0 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 4.0 mm), Serchio river, Tuscany (stn 36), 27.9.1989, coll. Balma G.A.C. & G.B. Delmastro; 5 ♀♀ (3 ovig) (pocl 6.5–9.0 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 5.3 mm), Foglia river, Pesaro (stn 37), 10.7.1989, coll. Artegiani R.; 18 ♀♀ (8 ovig) (pocl 5.7–8.9 mm), 2 ♂♂ (pocl 4.6–5.7 mm), Valli di Comacchio (stn 38), 27.7.1999, coll. Froglia C. & R. Gatelli; 14 ♀♀ (10 ovig) (pocl 6.2–8.0 mm), 14 ♂♂ (pocl 5.5–6.0 mm), Po river (mouth), Goro (stn 39), 7.7.1977, coll. Froglia C. & A. Piersimoni; 4 ♀♀ (2 ovig) (pocl 7.0– 8.7 mm), 2 ♂♂ (pocl 5.3–6.8 mm), Veneto, Venezia (stn 40), 18.5.1982, coll. Barbaro A.; 3 ♀♀ (pocl 6.5–7.2 mm), NHMW 7724, Garda Lake (stn 41); 6 ♀♀ (pocl 5.5–6.0 mm), 3 ♂♂ (pocl 4.8–5.8 mm), NHMW 7732, Monfalcone (stn 42); Croatia: 1 ♂ (pocl 5.0 mm), NHMW 7711, Cepich, Istria (stn 43), coll. Handlirsch A.; 10 ♀♀ (pocl 4.0–6.0 mm), 5 ♂♂ (pocl 4.1–5.5 mm), NHMW 7722, 7723, Bilivir, Pologosa (stn 44), 15.8.1924, coll. Spandl H.; Greece: 3 ♀♀ (2ovig) (pocl 4.5–6.2 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 4.0 mm), ZMAUTH–G2–2266, Corfu Island (stn 45), 4.9.2002, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 3 ♀♀ (pocl 5.2–7.8 mm), 1 ♂ (pocl 5.0 mm), MNHN –IU–2013–4033 (ex MNHN –Na1511), Corfu Island (stn 45); 50 ♀♀ (10 ovig) (pocl 4.5–11.0 mm), 100 ♂♂ (pocl 4.9–8.0 mm), ZMAUTH–G3–28, Sagiada lagoon (stn 46), 29.10.2005, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 50 ♀♀ (pocl 6.5–10.5 mm), 20 ♂♂ (pocl 4.9–8.0 mm), ZMAUTH–G3–29, Lake Pamvotida, (stn 47), 15.11.2003, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 8 ♀♀ (3 ovig) (pocl 5.6–8.6 mm), 5 ♂♂ (pocl 4.8–5.6 mm), ZMAUTH–G2–2267, Acherontas river (stn 48), 2012, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 2 ♂♂ (pocl 5.0– 6.1 mm), ZMAUTH–G2–2268, Arachthos river (stn 49), 2002, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 25 ♀♀ (pocl 5.5–7.6 mm), 10 ♂♂ (pocl 4.5–6.0 mm), ZMAUTH–G2–2269, Louros river (stn 50), 2012, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 12 ♀♀ (pocl 6.5–8.0 mm), 13 ♂♂ (pocl 5.0– 6.6 mm), ZMAUTH–G2–2270, Acheloos river (stn 51), 2002, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.; 4 ♀♀ (pocl 5.5–7.0 mm), 4 ♂♂ (pocl 4.5–6.1 mm), NHMW 7729, Zakynthos Island (stn 52), 1936, coll. Versleuys J. & W. Kuehnelt; 43 ♀♀ (1 ovig) (pocl 5.8–10.0 mm), 43 ♂♂ (pocl 4.0– 7.6 mm), ZMAUTH–G2–2271, Kaiafa Lagoon (stn 53), 24.9.2001, coll. Anastasiadou Ch.
Redescription. Max. pocl: ♂♂ 8 mm, ♀♀ 10.5 mm, ♀♀ ovig 11.0 mm.
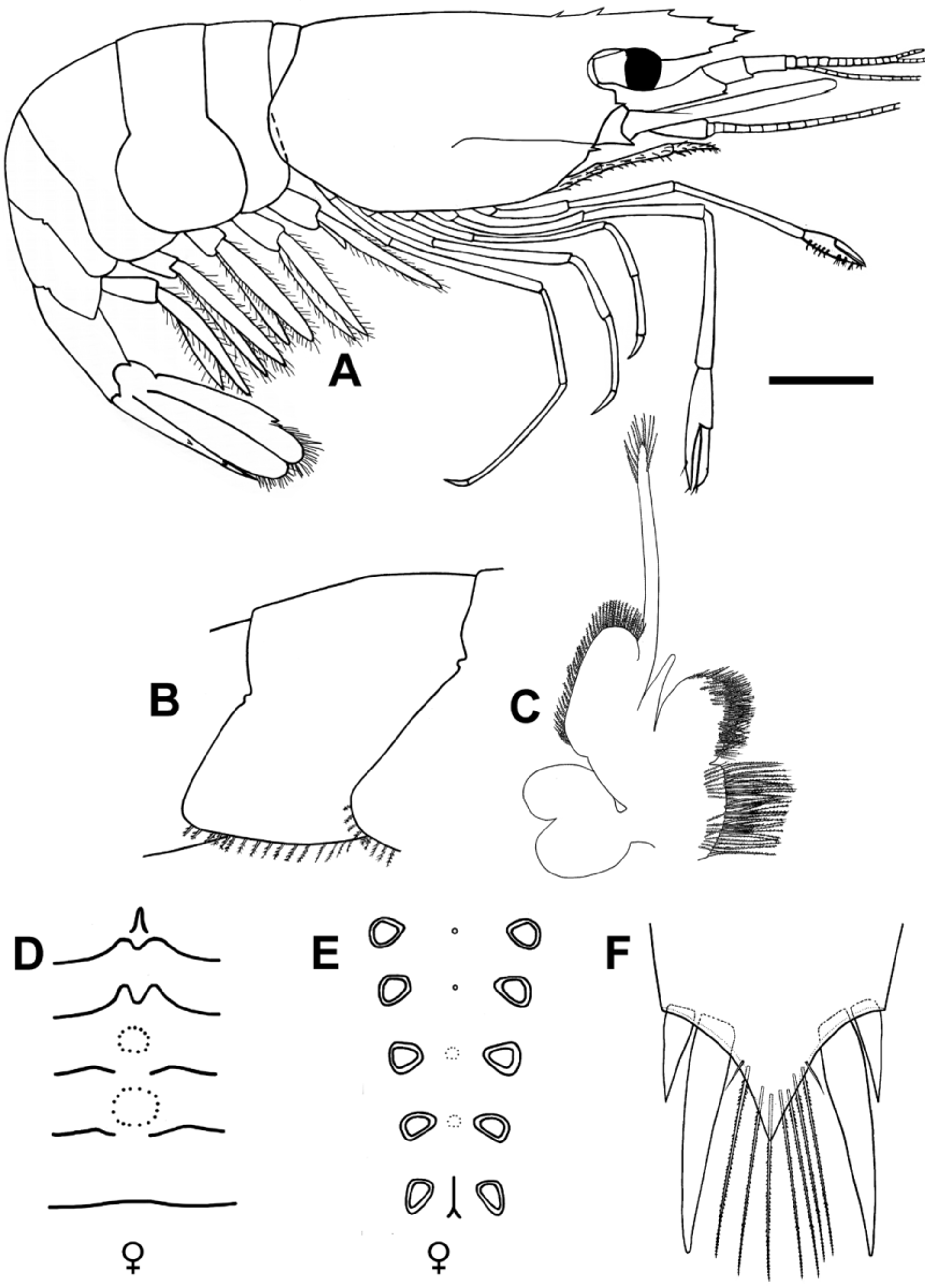
Carapace glabrous. Rostrum ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 A) wide, straight, with posterior ventral curve; approximately 0.8 times pocl, reaching just before the end of scaphocerite; armed with 6–7 dorsal teeth and 2–3 ventral teeth; posterior–most tooth situated behind orbit, second tooth situated above or slightly in front of orbital margin; distal portion with simple (in the 90% of the examined individuals) or bifid (in the 10%) tip; single row of setae dorsally and double row of setae ventrally. Antennal tooth marginal and branchiostegal tooth originating just before anterior margin of carapace. Branchiostegal groove originating dorsal to branchiostegal tooth, trending posteriorly and finishing just in front of half carapace length, slightly lower than at its origin. Suborbital lobe subquadrate to rounded, pterygostomial angle rounded. Béc ocellaire ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 C) globular, with slightly convex anterior margin, slightly hooked median process, pointing upwards approximately 60°, dorsal surface concave. Eye ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 B) well developed, with pigmented cornea; cornea slightly wider but shorter than stalk; ocellus present dorsomesially. Antennular peduncle ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 D) extending to the base of scaphocerite tooth in females and just before the tip of scaphocerite tooth in males; basal segment 2.0 times as long as wide, slightly convex outer margin, stylocerite acute, reaching beyond middle of the segment; antero-lateral tooth slightly exceeding laminar portion, reaching middle of penultimate segment; inner ventro-mesial tooth present; ultimate segment 1.2 times as long as penultimate, their combined length being 0.8 times that of basal segment. Dorsal flagellum of antennula fused for 0.8 times of its length (11–15 segments fused, 4–6 free); more than distal half with 6 aesthetascs on each segment arranged in 2 rows of 3. Scaphocerite ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 G) slender, laminar, 2.5–3.0 times as long as broad; outer margin straight or slightly convex terminating in tooth, falling short of distal margin of lamina; basal segment of antenna with large mesial tooth; antenna articulated to lateral margin of this segment. Flagellum of antenna almost equal to the body length.
Abdominal pleurae, except first, furnished with plumose setae on ventral margin; posterior and ventral margins of the fifth pleuron ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 E) forming an 60° angle and a strongly pointed posterodistal end; sixth segment approximately 1.8 times length of fifth; lateral margin ending in tooth disto-ventrally; median lobe acute, with ventral submedian process.
Thoracic sternal armature sexually dimorphic ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 A). In females, fourth thoracic sternite armed with a sharp, slightly hooked tooth, pointing posteriorly and two submedian lobes on its posterior ridge, fifth sternite unarmed, with more acute submedian lobes on its posterior ridge, sixth to seventh thoracic sternites with low, rounded, median bosses and partial transverse ridges, eighth with low, transverse ridge; in ovigerous females eighth sternite with setose transverse ridge. In males, eighth thoracic sternite with a low transverse ridge, projected anteriorly forming the greek capital letter Lambda (Λ).
Abdominal sternal armature sexually dimorphic ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 B). In females, first to third abdominal sternites with a spicule decreasing in acuteness, fourth with median boss and the fifth with a longitudinal ridge, bifid posteriorly. In males, first to second abdominal sternites bearing acute conical tooth; third to fifth abdominal sternite as in females. Pre-anal carina unarmed in both sexes.
Mandible ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 C) without palp. Incisor process of mandible with 3 teeth on right mandible, the middle of which is the smallest, and 4 teeth on left mandible, the middle 2 being smaller than the outer ones; molar process with 5–6 teeth of varying sizes. Paragnaths covering about half the mandibles; alae formed by broad, transverse slightly bilobed, distal lobes, ventromedial lobes triangular. Corpus short, narrowly separated medially; base with two carinae. Epistome triangular with rounded anterior angle and strong anteromedial carina. Labrum narrow, rectangular. Maxillula ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 D) with lower lacinia near oval, smaller and narrower than upper lacinia; upper lacinia provided with several distal cuspidate and stout setae, bearing 3–4 plumose setae on its upper margin; palp bilobed; upper lobe naked, lower lobe broad with 1 median setiform process. Maxilla ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 E) endopod deeply cleft, ending in a number of plumose setae, 3–4 simple setae proximally on the upper margin of the lower endite; palp well developed, broad and naked, except for a few plumose setae proximally on its outer margin; scaphognathite large, fringed with plumose setae; the lower lobe is broader than the upper. First maxilliped ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 F) endites separated with their inner edges forming an obtuse angle; margins of both endites with dense plumose setae; basal endite bears a row of 13–14 plumose setae before margin; coxal endite without setae before margin; palp slender and slightly twisted with 1–2 distal simple setae; exopod well developed, slender and furnished with plumose setae distally; caridean lobe well developed and broad; epipod large and bilobed. Second maxilliped ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 G) with a broad rectangular ultimate segment; penultimate segment broadly triangular, with convex, semicircular upper margin; exopod well developed; well developed podobranch present. Third maxilliped ( Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 H) pediform; ultimate segment 0.9 times length of penultimate; ischiomerus with strongly curved dorsal margin; exopod equal or slightly longer than ischiomerus; epipodal plate subtriangular; well developed arthrobranch and a second, rudimentary arthrobranch present.
Well developed pleurobranchiae present on all thoracic legs.
First pereiopod ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 A) reaching end of scaphocerite; ischium 1.4 times length of basis; merus 1.9 length of ischium; carpus 1.3 times longer than merus; carpus 2.0 times length of chela, fingers slightly longer than palm, with tufts of setae; carpal-propodal brush well developed. Second pereiopod ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 B) extending beyond scaphocerite by full length of chela; ischium 4.0 times length of basis; merus equal with ischium; carpus elongate, 1.4 length of merus; carpus 1.3 times length of chela, fingers approximately 0.7 length of palm and covered in stout setae.
Ambulatory pereiopods increase in length, pereiopod 3 being the shortest. Third pereiopod ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 C) reaching base of distolateral tooth of scaphocerite; ischium twice length of basis; merus 2.2 times length of ischium; carpus 0.5 length of merus; propodus 1.8 times length of carpus, ventral margin armed with 4–5 pairs of cuspidate setae; dactylus simple, about 0.4 length of propodus. Fourth pereiopod ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 D) reaching beyond end of scaphocerite by half of dactylus; ischium 2.5 times length of basis; merus 2.3 times length of ischium and 2.3 times length of carpus; propodus 2.3 t imes length of carpus and approximately equal to merus, ventral margin provided with 5 pairs of cuspidate setae; propodus 3.3 length of dactylus. Fifth pereiopod ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 E) reaching beyond end of scaphocerite by half of dactylus; ischium 2.0 times length of basis; merus 2.5 times length of ischium and 2.1 times length of carpus; propodus 2.3 times length of carpus and slightly longer than merus, ventral margin armed with 5 pairs of cuspidate setae, grooming brush with 6–7 rows of serrulate setae; propodus 3.3 length of dactylus.
First pleopod sexually dimorphic in proportions, lacking appendix interna in both sexes; in males ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 F) exopod is 1.7 times length of endopod; endopod slightly concave on the mesial portion of the inner margin; both exo- and endopods fringed with plumose setae but mesial portion of the inner margin of endopod devoid of plumose setae, with 8–10 spiniform setae; in females ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 H), exopod is 3.3 times length of endopod; endopod lanceolate. Second to fifth pleopods similar ( Figures 4 View FIGURE 4 I–4K) with the endopod being slightly shorter than the exopod, bearing an appendix interna. Second pleopod of males ( Figure 4 View FIGURE 4 G) with appendix masculina; about 1.5 times length of appendix interna, furnished with 8–14 lateral and 3–4 apical setae.
Telson ( Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 A) subequal in length to sixth pleonite; length:width ratio 3.3:1 proximally narrowing to 7.5:1 distally; dorsal surface with 2 pairs of dorsal spines situated dorsomedially and 2 pairs of simple setae subdistally on median process; proximal pair of spines situated at about 0.6 of telson length, distal pair at about 0.8 length; 0–6 pairs of marginal lanceolate setae present just proximally; posterior margin ( Figure 5 View FIGURE 5 B) prolonged into acute process, with 1 pair of plumose setae and 2 pairs spines; inner pair of spines equal or longer than plumose setae and 3.5–4 times longer than outer pair; median process exceeding outer pair of spines.
Uropods ( Figure 2 View FIGURE 2 F) broadly ovate; endopod overreaching telson by its distal margin; exopod slightly longer than endopod; mobile lateral spine of exopod overreaching fixed tooth by length of tip.
Eggs numerous; 1.1 x 1.5 mm.
Distribution. Sardinia and Italian mainland; Slovenia; Croatia; Montenegro; Albania and Greece (see material examined and Figure 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
Remarks. Palaemon antennarius was first described by H. Milne Edwards in 1837 from "mer Adriatique", but briefly and inadequately. Due to the lack of a comprehensive description and in order to re-evaluate the intrarspecific variability, a redescription of the species was necessary. Thus, efforts to find the species type material were made to the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris ( France) in which H. Milne Edwards was working, leading to a sample with a handwritten label including the following information “Lac de Trasimène / Palaemon antennarius / M. E. / (types)”. In this sample no holotype was designated. Additionally, the locality written on the label was not the same as the type locality given in Milne Edwards’s description.
Heller (1869) in his discussion mentions that he examined "Originalexamplaren" (original samples) of P. antennarius from MNHN and that after communication with Milne Edwards the type locality should be corrected to "Trasimenischen See" (Lake Trasimeno, Italy). Since P. antennarius is a freshwater species and after Heller’s intervention, it is certain that the real type locality of the species is Lake Trasimeno.
Regarding the specimen selected to be the lectotype, this was the best preserved and most anatomically complete among the syntypes.
The species can be distinguished from the other freshwater representatives of the genus in the circum- Mediterranean area, by a set of different characters: the shape of the distal end of fifth pleuron, the form of distal part of telson, the number of marginal lanceolate setae of telson, the arrangement of the first maxilliped endites, the shape of maxillula palp and the length of the third maxilliped exopod in relation to ischiomerus. These are key characters that secure the easy and safe identification of the species.
P. antennarius can be easily discriminated from P. mesopotamicus , P. migratorius and P. minos sp. nov. by the pointed distal end of fifth pleuron vs. rounded in P. mesopotamicus , P. migratorius and P. m i n os sp. nov. ( Figures 2 View FIGURE 2 E vs. 6B, 9B) and vs. subquadrate in shape in P. turcorum and P. zariquieyi ( Figures 10A View FIGURE 10. A in present study; 6b in Holthuis, 1961).
Regarding the form of the distal part of telson, P. antennarius has 2 plumose setae failing to overpass the inner spines. This character allows for easy separation of the species from P. migratorius , P. mesopotamicus , P. zariquieyi and P. mesogenitor that have 4–7, 10–12, 4–6 and 2–6 setae respectively ( Figures 5 View FIGURE 5 B vs. 6F, 10D, 10E in present study; 13 in Azzouna, 1994). On the other hand, P. minos sp. nov. and P. varians have 2 plumose setae always overpassing the inner spines ( Figures 9 View FIGURE 9 C, 10C in present study; 5B in De Grave, 1999) and the same occurs when P. mesogenitor has only 2 setae. Thus, the length of the plumose setae can be assistantly used to distinguish P. antennarius from P. m i no s sp. nov., P. v ar i a ns and P. mesogenitor . In case of P. antennarius only minor variation exists in the number and length of the plumose setae which is accompanied by asymmetrical development of the telson’s apex and probably is consistent with regeneration after partial damage. Nevertheless, the stability of this character permits its reliable use to discriminate at least some species of the genus ( De Grave, 1999).
P. antennarius also differs from P. colossus sp. nov. and P. varians by the presence of 0–6 pairs of lanceolate setae on the ventral margins of telson (vs. 40–50 pairs in P. colossus sp. nov. and about 80–100 pairs forming a narrow naked zone before the proximal pair of dorsal spines in P. varians ; Figures 5 View FIGURE 5 A vs. 8C, 8D).
Regarding first maxilliped endites, in P. antennarius , the two endites are arranged in such a way that the endites form an obtuse angle mesially, while in P. migratorius , P, mesopotamicus , P. mesogenitor , P. turcorum , P. varians and P. zariquieyi the endites are arranged almost in a straight line forming just a notch between them ( Figures 3 View FIGURE 3 F vs. 6C, 10F in present study; 6 in Azzouna, 1994; 7a in Holthuis, 1961).
Based on the shape of maxillula palp and the presence of 1 setiform process on it, P. antennarius can be distinguished from, P. varians and P mesogenitor (vs. 3–4 in P. v a r i a ns and P. mesogenitor ; Figures 3 View FIGURE 3 D vs. 10B in present study; 5 in Azzouna, 1994).
In addition, P. antennarius differs from P. mesopotamicus and P. mesogenitor , also, by the length of the third maxilliped exopod in relation to ischiomerus. In P. antennarius the exopod is equal or longer than isciomerus but in P. mesopotamicus and P. mesogenitor is always shorter ( Figures 3 View FIGURE 3 H vs. 10G in present study; 7 in Azzouna, 1994). Finally, in P. antennarius the outer edge of scaphocerite is straight or slightly convex but in P. mesopotamicus is always concave ( Figures 2 View FIGURE 2 G vs. 10H).
In light of the current study, P. antennarius did not show important interpopulational variability. However, Greek populations are characterized by a shallowly bilobed maxillula palp, which in the Italian populations is more deeply bilobed. In addition, in north Italy, large specimens often bear 2 rather 1 setiform processes on maxillula palp.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Palaemon antennarius H. Milne Edwards, 1837
| Tzomos, Theodoros & Koukouras, Athanasios 2015 |
Palaemonetes varians
| Boas 1889: 800 |
Palaemonetes varians
| Garbini 1881: 108 |
Palaemonetes varians
| Garbini 1879: 187 |
Palaemonetes varians
| Heller 1869: 157 |
Anchistia migratoria
| Heller 1863: 259 |
Pelias migratorius
| Heller 1862: 409 |
Palaemon lacustris
| Martens 1857: 183 |