Prodistylomys mongoliensis, Oliver & Carro-Rodríguez & López-Guerrero & Daxner-Höck, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad030 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:995541BE-533A-479B-8ED8-955F5EF30A0E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10496308 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6B7C083C-CA12-893D-FED6-F8CCF581F9F7 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Prodistylomys mongoliensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Prodistylomys mongoliensis sp.nov.
Figs. 6-7 View Figure 6 View Figure 7 , Supporting Information Model S3
Zoobank registration: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:BFCC9D7E-4122-4CF0-8523-9CE6C9CC5891 .
Distylomys / Prodistylomys sp. ( Höck et al. 1999: 118).
Distylomys sp. ( Daxner-Höck and Badamgarav 2007: 16, 18).
Prodistylomys nov. spec. 1 ( Oliver et al. 2017a: 61).
Prodistylomys nov. spec. 1 ( Daxner-Höck et al. 2017: 130, tab. 1, fig. 47k)
Etymology: The species name refers to Mongolia, the country where the new species was found.
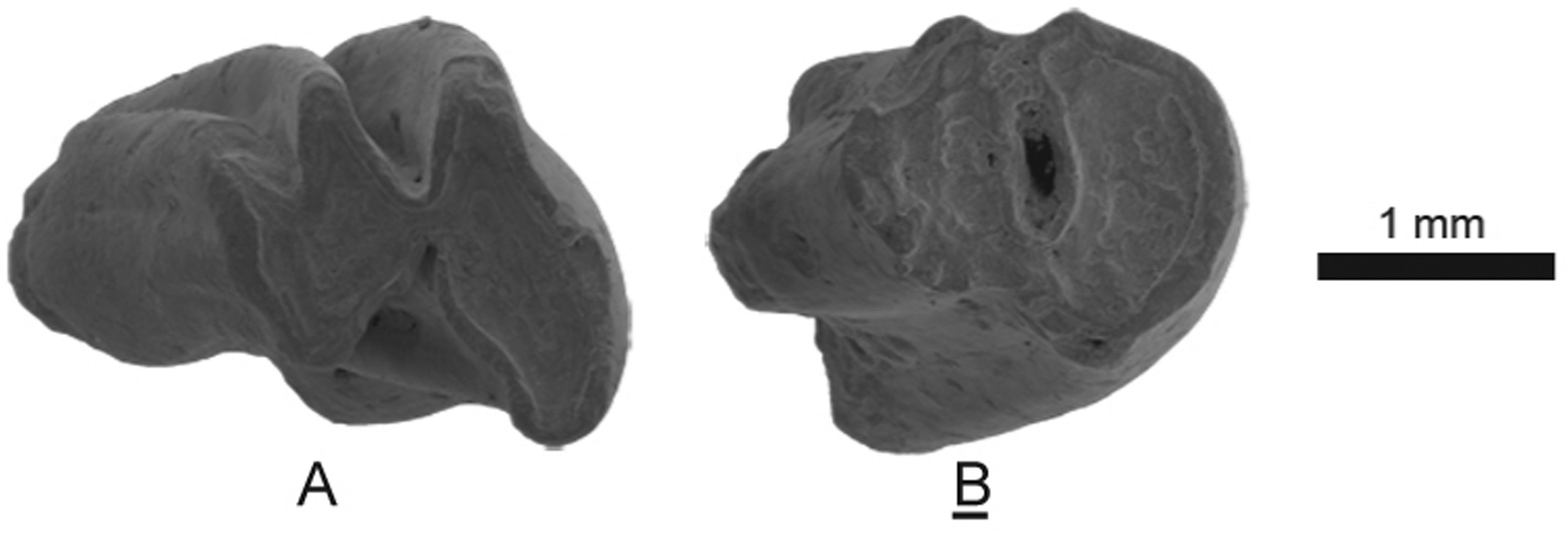
Holotype: NHMW 2012 View Materials /0051/0001, Rightm2 ( Fig.6A View Figure 6 ; ModelS3).
Paratype: HTE-012; NHMW 2012 View Materials /0051/0002-0006 ( Fig. 6B View Figure 6 ) .
Type locality: Hotuliin Teeg (HTE-012).
Diagnosis: Large-sized species of Prodistylomys . Lower m2 with long metaflexid and posterolophid; upper M1 and M2 with metaflexus almost connected to the ectoflexus; M3 with a fossette.
Differential diagnosis: Prodistylomys mongoliensis sp. nov. differs from P. wangae , P. lii , and P. taatsinius by its larger size, m2 with metaflexid, and an M3 with a vertical fossette. Prodistylomys mongoliensis sp. nov. differs from P. xinjiangensis by its larger size and different proportions of the trigonid/talonid ( P. mongoliensis sp. nov. longer and wider trigonid than talonid; the opposite in P. xinjiangensis ).
Prodistylomys mongoliensis sp. nov. differs from P. mengensis by its larger size and upper molars, including M3 with a vertical fossette instead of a dentine isthmus.
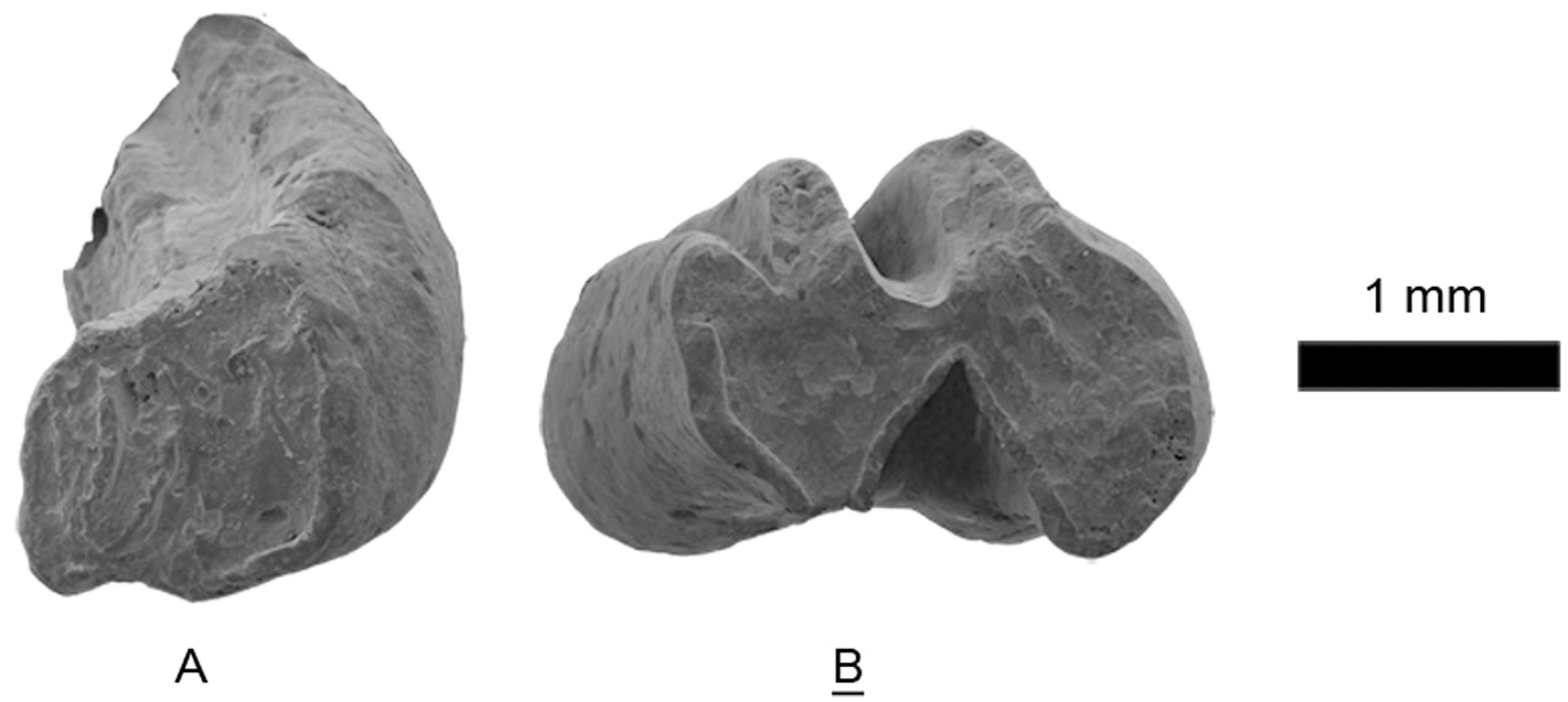
Other fossil layers: HTE-003; NHMW2012/0052/0001-0002 ( Fig. 7 View Figure 7 ).
Measurements: Table 4 View Table 4 .
Stratigraphic range: Early Miocene, Mongolian biozone D.
Geographical range: Valley of Lakes, Mongolia.
Description of the new material flom Hotuliin Teeg (HTE-012)
m1/m2: Bilophodont and hypsodont teeth. The specimens have two roots. The shape of the trigonid is fusiform (2/3) or rhomboidal, with the metaconid and protoconid narrower than the anterolophid (1/3). Both the metaconid and the protoconid are sharp. The trigonid is larger than the talonid in one (1/3) and smaller in two (2/3). The talonid is rhomboidal to subrhomboidal. The entoconid and the hypoconid are sharp. The mesoflexid and the ectoflexid are V-shaped, open, and deep. The metaflexid is deep.
M1/M2: The teeth are hypsodont and rooted with one root. There is cement in the flexus. The trigon is kidney shaped and larger than the talon. The mesoflexus is deep, almost connected reaching the lingual border of the teeth.
M3: The only specimen is broken in the posterior border. It is hypsodont and rooted, with two roots. The flexus is filled with cement. The trigon is kidney shaped, whereas the talon is semicircular. The flexus is closed and forms a fossette.
Remarks: Prodistylomys mongoliensis sp. nov. occurs in two samples of Hotuliin Teeg (HTE-012 and HTE-003) in the region of Taatsin Gol.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Prodistylomys mongoliensis
| Oliver, Adriana, Carro-Rodríguez, Patricia M., López-Guerrero, Paloma & Daxner-Höck, Gudrun 2023 |
Prodistylomys
| Oliver A & Sanisidro O & Pelaez-Campomanes P 2017: 61 |
Prodistylomys
| Daxner-Hock G & Badamgarav D & Barsbold D 2017: 130 |
Distylomys sp.
| Daxner-Hock G & Badamgarav D 2007: 16 |
Distylomys
| Hock V & Daxner-Hock G & Schmid HP 1999: 118 |