Setostephanolaimus longiseta, Hao & Hu & Huang, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4999.3.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0A625587-3059-4974-AEEB-93ABAF7D838A |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5119096 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4042879A-E018-FF9D-FF3B-FC01FB54FE47 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Setostephanolaimus longiseta |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Setostephanolaimus longiseta View in CoL sp. nov.
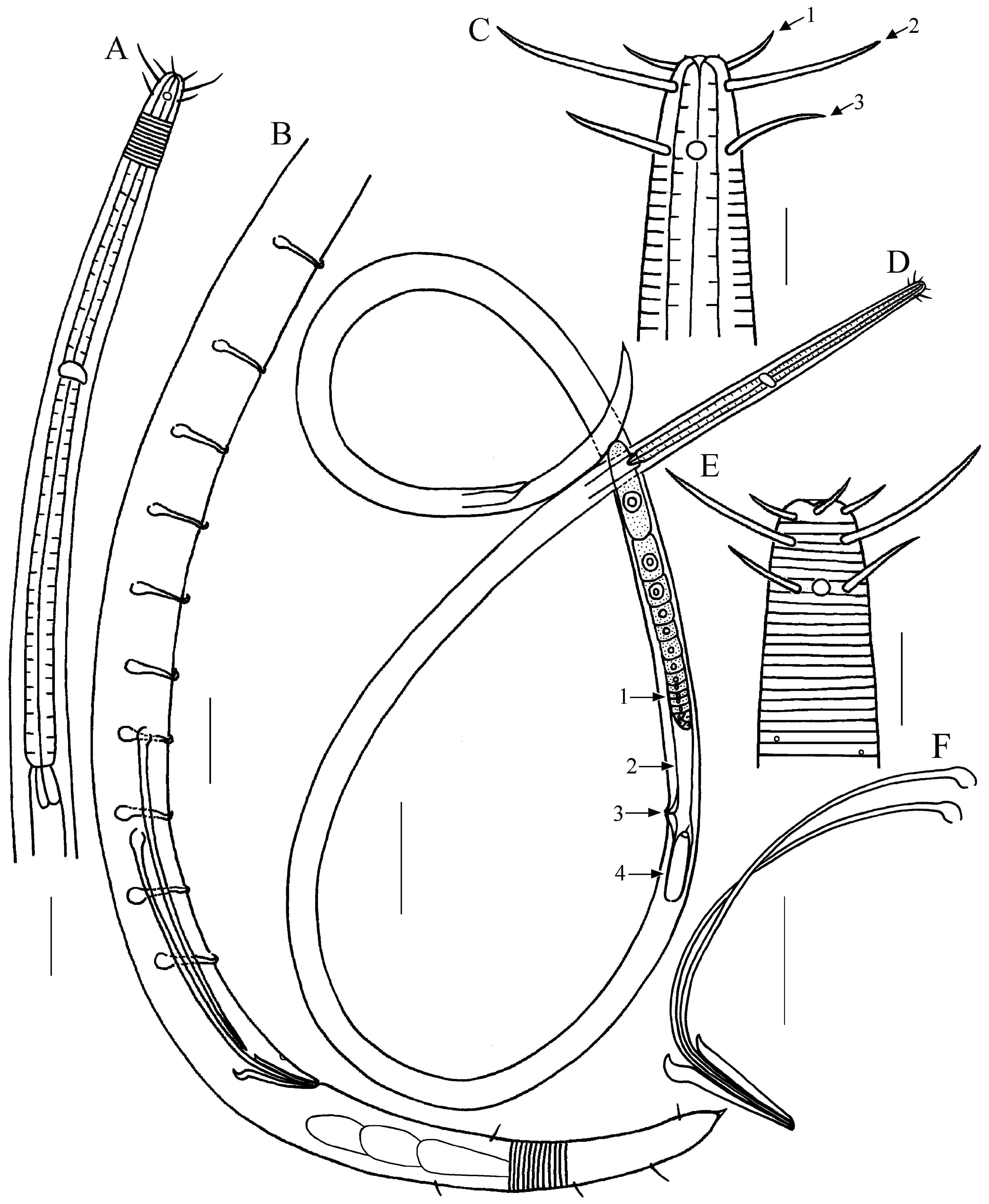
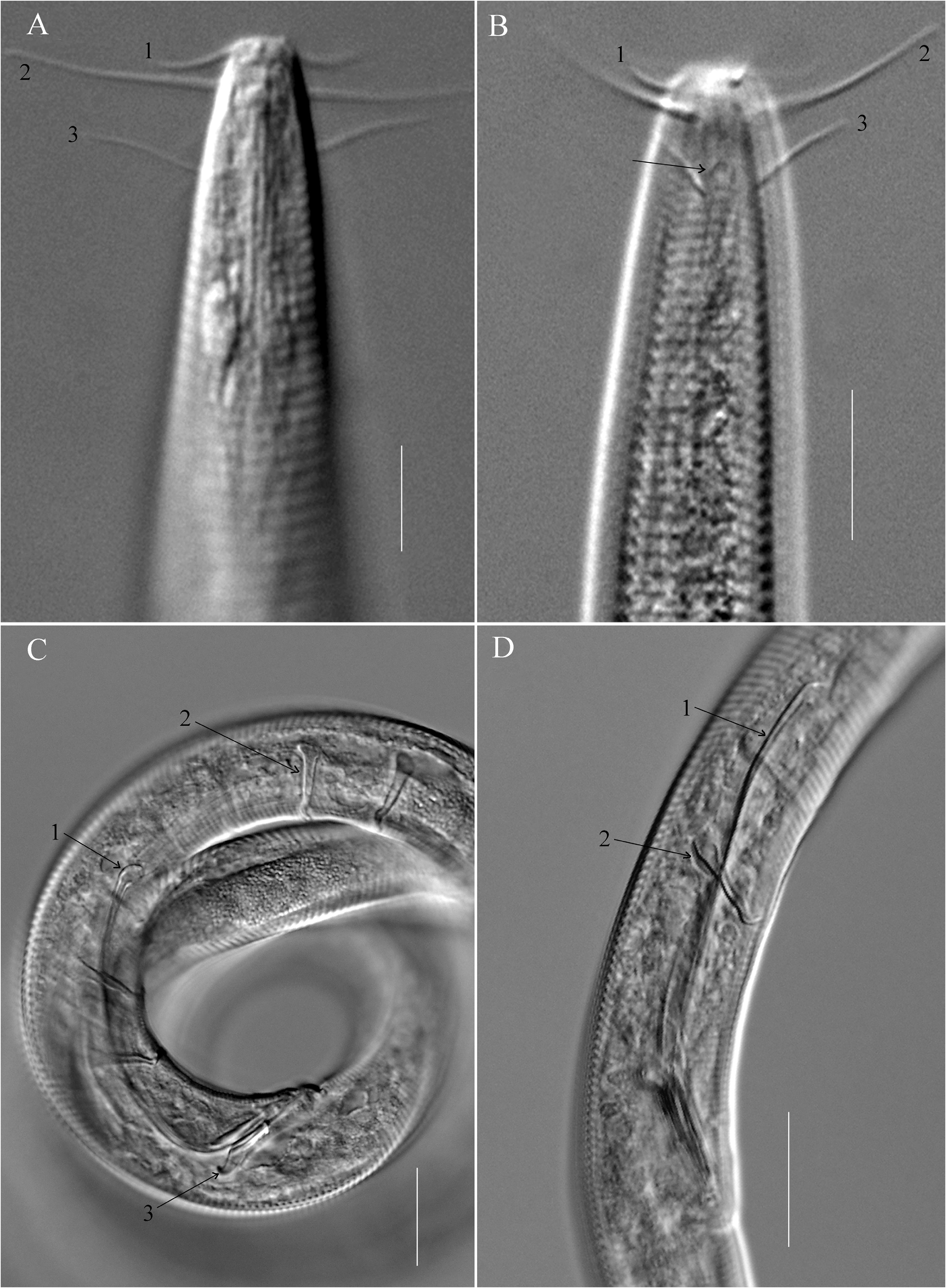
( Figs 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 )
Type material. Two males and two females were acquired. Holotype male was on slide RZWB5-20 - 4 . Paratype male was on slide RZWB98-1 - 9 . Females on slides RZWB71-3 - 5 and RZWB71-1 - 3 , respectively .
Type locality and habitat. Type and all the additional specimens were collected from the fine sand of the surface layer on an intertidal beach along the Rizhao coast of the Yellow Sea, China (35°34′ 21″ N, 119°39′ 29″ E) GoogleMaps .
Etymology. The species name is from Latin adjective longus and seta, referring to the longer cephalic setae compared with the other species in genus Setostephanolaimus .
Measurements. All measurement data are given in Table 1.
Description. Males. Body slender, nearly cylindrical except tapering anteriorly in pharyngeal region and posteriorly in tail region. Cuticle annulated, annulation 4 µm in width, without ornamentation. Small body pores arranged sublaterally along the entire body. Lip area rounded, continuous with the body contour. Inner labial sensilla papilliform. Outer labial sensilla setiform, located on the anterior surface of lips, 7–9 µm long. Cephalic setae long, 20–21 µm in length, situated at 5–6 µm from anterior end. Subcephalic setae 10–13 µm long, located at 11–12 µm from anterior end. Amphideal fovea unispiral, circular in outline, 3–4 µm wide, situated just anterior to subcephalic base. Buccal cavity small, funnel-shaped. Pharynx slender, slightly swollen at base, not forming real terminal bulb. Nerve ring surrounding pharynx at 117 µm from anterior end. Cardia conical, about 12 µm long. Secretory-excretory system not observed. Tail elongated conical, arcuate ventrally, 6.1–6.5 cloacal body diameter long. Caudal seta present, 4–5 in number, arranged in subventral and subdorsal rows. Three caudal glands in tandem. Spinneret large and strongly cuticularized.
Reproductive system monorchic with a single outstretched anterior testis. Spicules elongated, arcuate with cephalated proximal end and long cylindrical shaft. Paired spicules almost equal in length, 96–99 µm long as arc. Gubernaculum tubular with hooked dorsal apophysis. 10–12 tubular precloacal supplements, more or less evenly spaced except for the anteriormost two which are more widely spaced, extending for 222–290 µm from cloaca towards anterior end; posteriormost tubular supplement located 37–50 µm in front of cloaca. Precloacal supplements nearly straight, cephalate proximally and hooked distally.
Females. Similar to males in most morphological characteristics. Reproductive system monodelphic with a single reflexed posterior ovary, located to the left of intestine. Undeveloped anterior ovary looking like a pouch. Uterus a wide tube. Vagina short, with thickened wall, 0.3 times vulval body diameters long. Vulva with slightly raised lips, situated at about middle of the body length.
Differential diagnosis and discussion. Setostephanolaimus longiseta sp. nov. is characterized by long and slender body, long cephalic and subcephalic setae, long spicules (longer than 90 µm), gubernaculum with short dorsal hooked apophysis, presence of 10–12 tubular precloacal supplements in males. It is similar to S. gandavensis ( Jensen, 1976) Tchesunov, 1994 and S. longispiculum ( Vadhyar, 1981) Tchesunov, 1994 in body size and shape, but differs from S. gandavensis in fewer precloacal supplements (11–12 vs 26), longer spicules (97–100 µm vs 53 µm), and monodelphic instead of didelphic reproductive system in females. The present species differs from S. longispiculum in having long subcephalic setae (vs absent), longer spicules (97–100 µm vs 52–85 µm), amphideal aperture unispiral (vs reniform) and gubernaculum with dorsal hooked apophysis (vs without apophysis). Further differences between Setostephanolaimus longiseta sp. nov. and other congeners are specified in the key below.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |