Stenophragma borneense, Bechev & Kazandzhieva, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4819.1.12 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0E94B208-8A89-4295-8F50-2CCBB2E7BFF8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4324083 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/6E1BA130-DEE1-48EA-B0A2-5B61543EBBB6 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:6E1BA130-DEE1-48EA-B0A2-5B61543EBBB6 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenophragma borneense |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stenophragma borneense View in CoL sp. n.
( Figs. 1–11 View FIGURES 1–2 View FIGURES 3–6 View FIGURES 7–11 )
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:6E1BA130-DEE1-48EA-B0A2-5B61543EBBB6
Diagnosis. With a yellow-brownish body coloration Stenophragma borneense sp. n. differs from the darker species S. hirtipenne , S. picticorne and S. meridianum in which the body is brown to dark brown, and S. bickeli and S. collessi in which the body is light brown to brown. Body colour in S. paponorum (only females known) is red, reddish-yellow (according to the original description). In the genital structure S. borneense sp. n. resembles S. collessi a little, in having regular rows of short spines, but in S. collessi there are nine rows, while in S. borneense sp. n. there are four rows. Also, spines on gonostyle in S. borneense sp. n. are a greater number and the form of tergite 9 is different. A basic difference from S. paponorum is in the angle in the basal part of the Cu-fork between M 4 and CuA: in S. borneense sp. n. the angle between M 4 and CuA is close to 90 degrees (M 4 is strongly curved basally), in S. paponorum it is close to 45 degrees ( Matile 1991: Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ), also the basal stripe of the wing is incomplete.
Type material. Holotype: Male, MALAYSIA: Sarawak, Kubah National Park , 800 m, 1°35’17.9”N 110°11’31.8”E, 21–23.vii.2019, Malaise trap, Leg. Kazandzhieva (in DBPC–University of Plovdiv, Bulgaria) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: 21 males, same locality and date. (in DBPC–University of Plovdiv, Bulgaria) GoogleMaps .
Type locality: Kubah National Park , Sarawak , Borneo island , Malaysia .
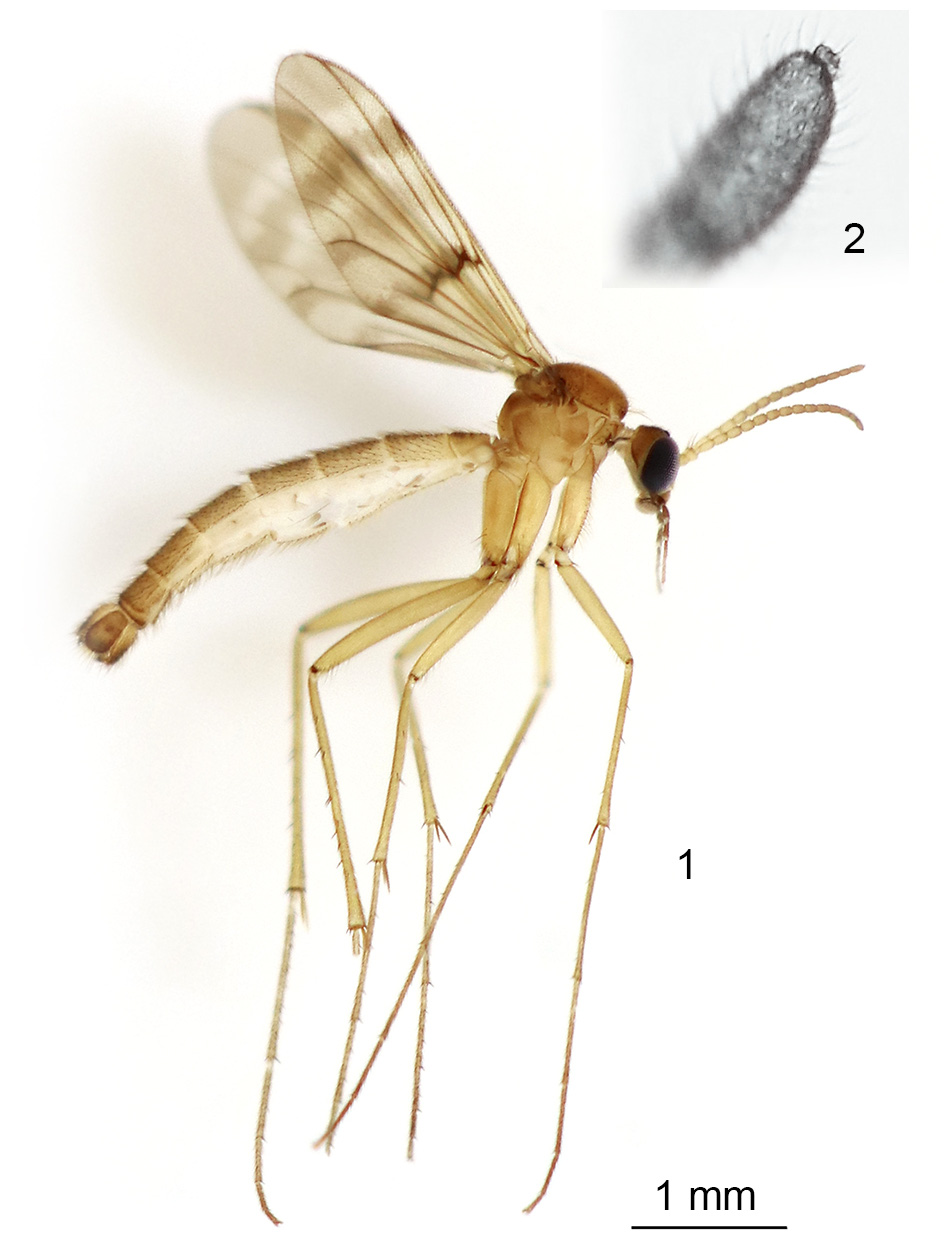
Description. Male ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–2 ). Head. Face, frons and vertex yellowish, brownish around medial margin of ocelli. Ocelli two, separated from eye margin by less than their own diameter. Scape, pedicel, and 1–4 flagellomeres yellowish, and flagellomeres 5–14 light brownish. Length ratio first to second flagellomere 1:0.8. Apex of fourteenth flagellomere with “sensory papilla” ( Fig. 2 View FIGURES 1–2 ). Clypeus, mouthparts, and palpomeres light brownish. Palpomeres length ratio 3:4:4:11.
Thorax. Scutum yellow-brownish, with pale brownish lateral areas and very pale indistinct brownish longitudinal bands. Scutellum, pleura and mediotergite yellowish, with very pale brownish marks. Scutellum with small setae on periphery and in indistinct longitudinal rows. Pronotum setose. Anepisternum and katepisternum bare. Anepimeron with a few setulae in upper posterior part. Laterotergite with setae in posterior half. Scutellum with long and shorter setae. Halter yellow.
Legs. Coxae yellowish, hind with dark posterior surface. Femora, tibiae and tarsi yellowish. First tarsomere of fore legs 1.5 the length of second one. Trichiation dark. Tibiae and tarsi with erect dark short bristles. Tibial spurs 1-2-2, about twice the length of tibial width at apex.
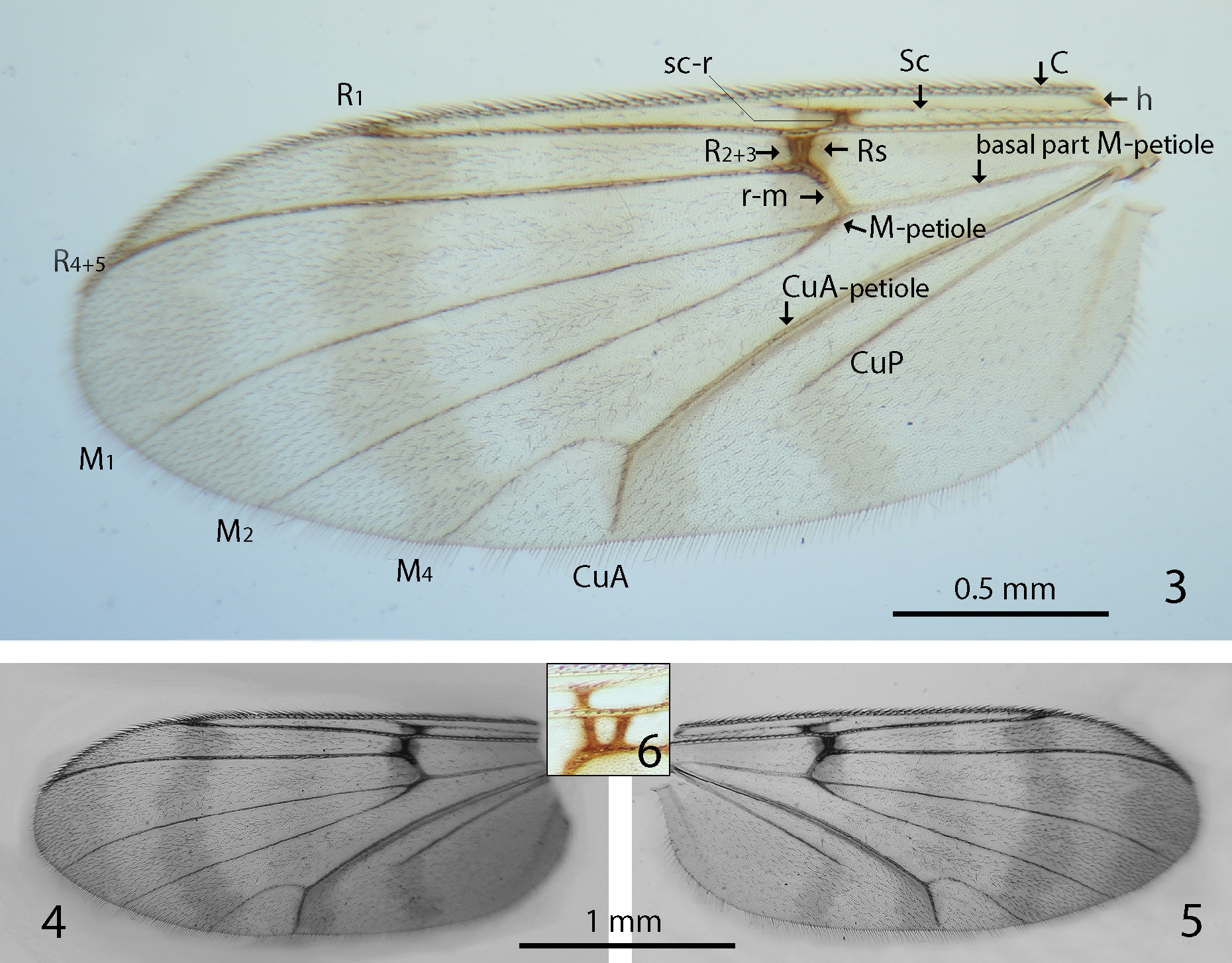
Wings ( Figs 3–6 View FIGURES 3–6 ). Length 2.7 mm (n=5). Wing with four transverse light brown stripes (including apical). Membrane hyaline, covered with microtrichia and macrotrichia, the last more sparsely on basal half and more densely on apical half. C ending before wing apex, extending for just a short distance beyond R 5, h at the base of wing, slender. Sc complete, reaching C just beyond the base of Rs. Sc-r before basal part of Rs. Rs transverse, about half of length of r-m. R 4+5 slightly curved in apical part. R 2+3 present or absent, including on the left and right wings of the same specimen. R-cell (between Rs and R 2+3), if present, is triangular, trapeziform or almost squared. M-petiole (M 1+2) very short, CuA-petiole very long. M 4 short, strongly curved basally, the angle between M 4 and CuA is close to 90 degrees. CuA short, almost straight. CuP comparatively long, ending freely. C with two rows of setae. Sc, R, R 1, R 4+5, proximal half of r-m, distal part of CuA-petiole, M 1, M 2, M 4, CuA, and CuP with setae on both surfaces. Basal part of M-petiole (M 1+2 or tb according to other authors) with few setae. Sc-r, Rs, R 4+5, distal half of r-m, proximal part of CuA-petiole and proximal part of CuP without setae.
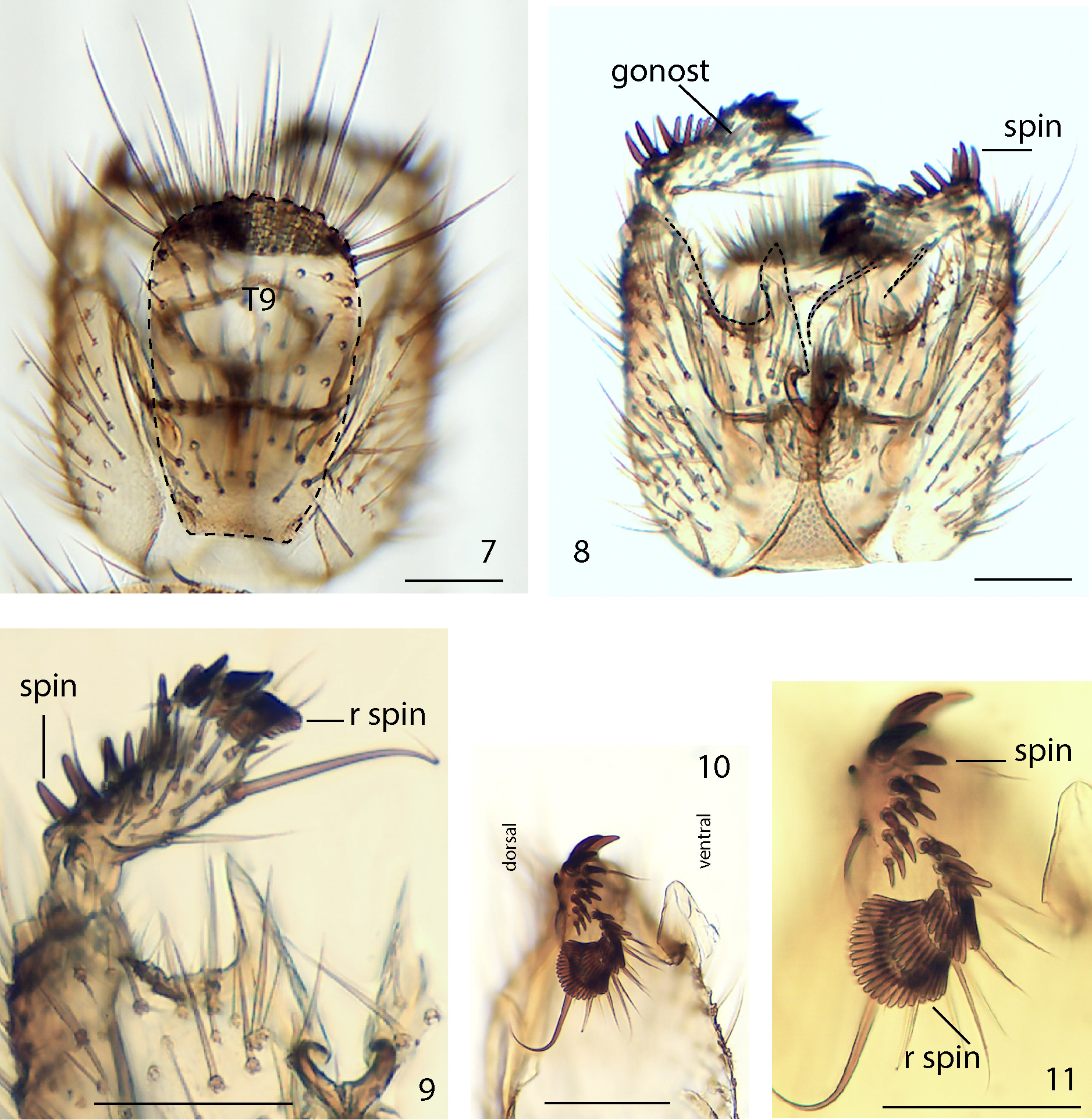
Abdomen yellowish, tergites 6‒8 slightly darkened near posterior margin. Terminalia yellowish basally and brownish distally, setose. Gonostyle in ventral view with one long and one very long setae directed medially, numerous spines directed externally and four regular rows of short spines in distal part ( Figs 9–11 View FIGURES 7–11 ). Tergite 9 ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7–11 ) elongate, oval, apex wider than base, setose. Apical setae very long, apical part in inner surface with great number of setae.
Female. Unknown.
Etymology. Named after the type locality in Borneo.
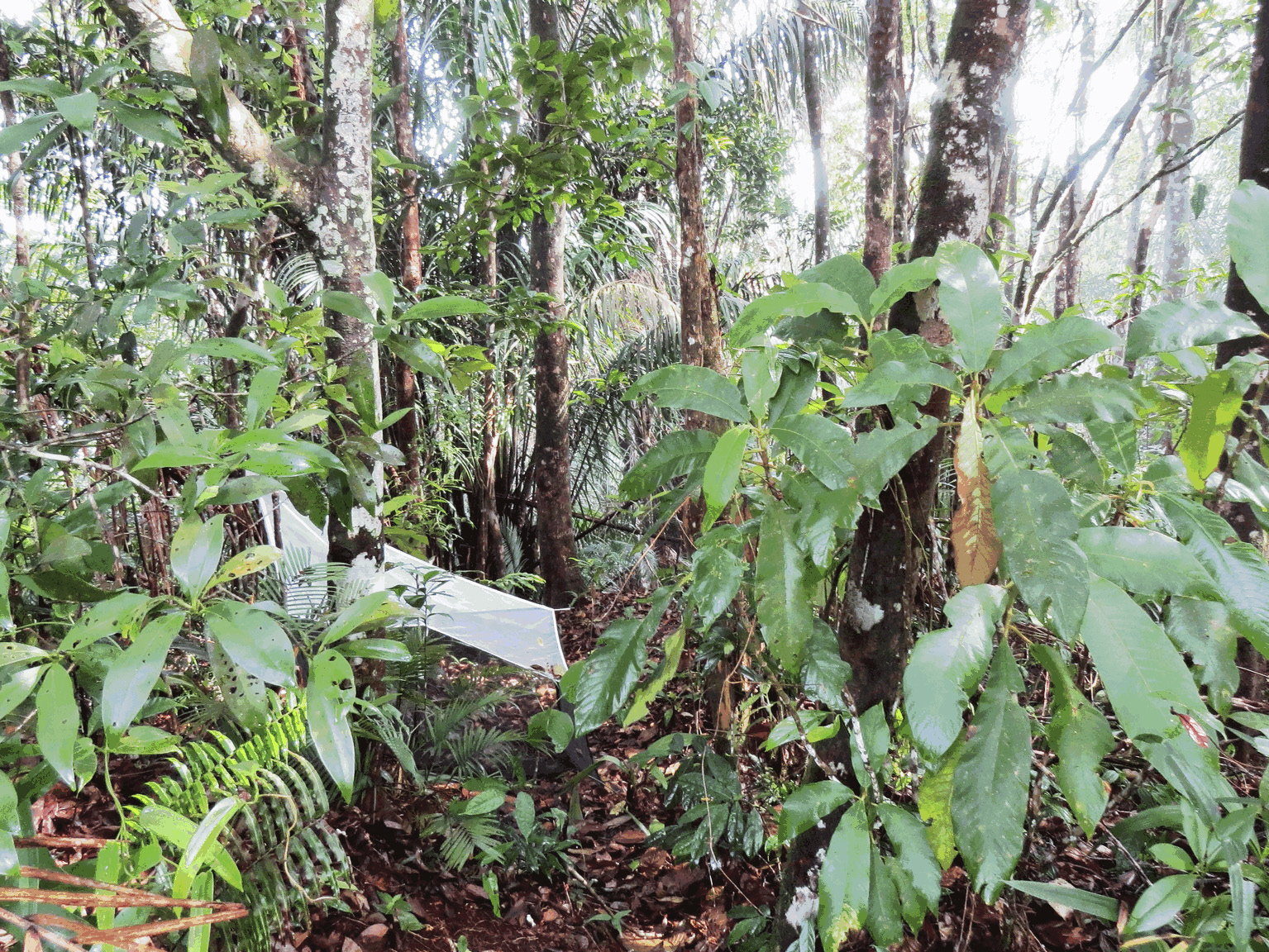
Habitat. The studied material has been collected by a single Malaise trap in mixed dipterocarp forest with presence of trees of Moraceae and Arecaceae , and with a variety of fern species (Polypodiopsida) ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ).
Note. An interesting matter is that, the specimens captured in the Malaise trap are only males.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Sciophilinae |
|
Genus |