Thrichomys fosteri, Thomas, 1903
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6623649 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6620169 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03C5A071-FFE3-FFD7-FFC4-5FA559B3F21E |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Thrichomys fosteri |
| status |
|
Foster’s Punare
Thrichomys fosteri View in CoL
French: Punaré de Foster / German: Foster-Punaré / Spanish: Punaré de Foster
Taxonomy. Thrichomys fosteri Thomas, 1903 View in CoL ,
“Sapucay,” Paraguari, Paraguay .
Thrichomys foster : was considered a subspecies of T. apereoides (sensu lato) by S. Anderson in 1997. It was included as a junior synonym of T. pachyurus by L. M. Pessoa and colleagues in 2015, butits karyotype differs from that species (2n = 34, FN = 64 vs. 2n = 30, FN = 56) and its position as a molecular clade basal to one collectively joining 7T. apereoides , T. laurentius , and T. pachyurus . Monotypic.
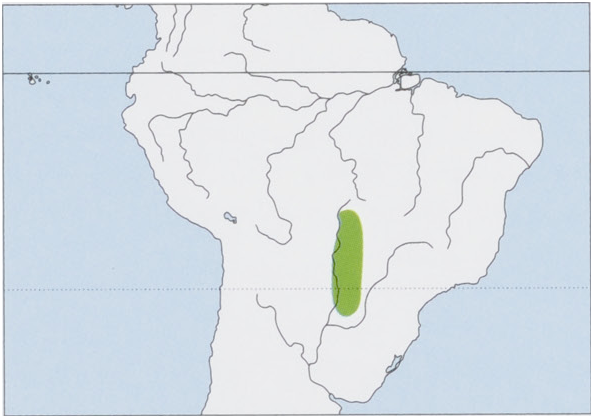
Distribution. SC Brazil (Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sulstates) and Paraguay. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 119-225 mm, tail 111-200 mm; weight 350 g. Dorsum of Foster’s Punare is generally ash-gray, with ventral hairs completely white or light gray at bases; dorsal tail hairs are blackish brown, sharply contrasting color of middorsum; and underside oftail is whitish gray. Its shares distinct cranial characteristics with the Jacobina Punare (7. inermis ) and the Pantanal Punare (71. pachyurus ), including wide incisive foramina with slight lateral constriction at premaxillomaxillary suture and broadened, rectangular hamular processes of pterygoid bones. Foster's Punare (7. foster) and the Pantanal Punare have broad, robust skulls, large and inflated auditory bullae, wide jugal dorso-ventrally, paroccipital processes that are not appressed to each bulla, and wide plates (c.2 mm) between oval and masticatory foramina; this combination of characteristics separate both species from the Jacobina Punare.
Habitat. Southern Cerrado ecoregion at elevations of 90-370 m. Foster’s Punare is considered a rocky outcrop specialist within dry forest communities.
Food and Feeding. There is no information available for this species.
Breeding. There is no information available for this species.
Activity patterns. There is no information available for this species.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. There is no information available for this species.
Status and Conservation. Not assessed on The IUCN Red Lust.
Bibliography. Anderson (1997), Bonvicino et al. (2008), Fredericksen et al. (2003), Moojen (1952b), Nascimento et al. (2013), Pessoa, Tavares, Neves & da Silva (2015), Thomas (1903a).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Hystricomorpha |
|
InfraOrder |
Hystricognathi |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Thrichomys fosteri
| Don E. Wilson, Thomas E. Lacher, Jr & Russell A. Mittermeier 2016 |
Thrichomys fosteri
| Thomas 1903 |