Trigonidium rubrumoculus He & Ma, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5124.5.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:44583ED8-7474-4821-8989-DEE025AA4067 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6416917 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03A5DD62-FFD6-8E0D-FF2D-FE62FC30F96B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Trigonidium rubrumoculus He & Ma |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Trigonidium rubrumoculus He & Ma View in CoL , sp. nov.
Chinese name: Ḕ瞳ṅDz
Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4A–C View FIGURE 4
Holotype. China: Male, Yunnan, Baoshan, Taibaoshan Forest Park , 8.VIII.2021, 99.12°E, 25.12°N, on leaf of low plants at night, Zhixin He, Ning Wang & Wei Yuan coll. GoogleMaps Paratypes. 1 male & 2 females, same collection site as the holotype ( SNNU).
Description. Male ( Figs. 2A View FIGURE 2 , 3A, C, E View FIGURE 3 ). Body size small for the genus. Head small, slightly wider than pronotum. Antennal scape as wide as rostrum. Eyes very large, laterally protruding, and slightly elongated in dorsal view. Cheek swelled. Clypeus slightly convex, anterior and posterior margin almost straight. Labrum relatively narrower than clypeus. Maxillary palpi somewhat extended, the third joint longer than the end one, and the end joint apically broad. Labial palpi relatively short, the end joint longer than the proximal two combined. Pronotum almost oblong and laterally hirsute. Tegmen extending to abdominal apex. Dorsal field bears five elevated longitudinal veins and false veins. Transverse veins between longitudinal veins inconspicuous. Hindwings absent. Tympanum absent. Hind legs long and hind tibiae armed with three pairs of dorsal spurs.
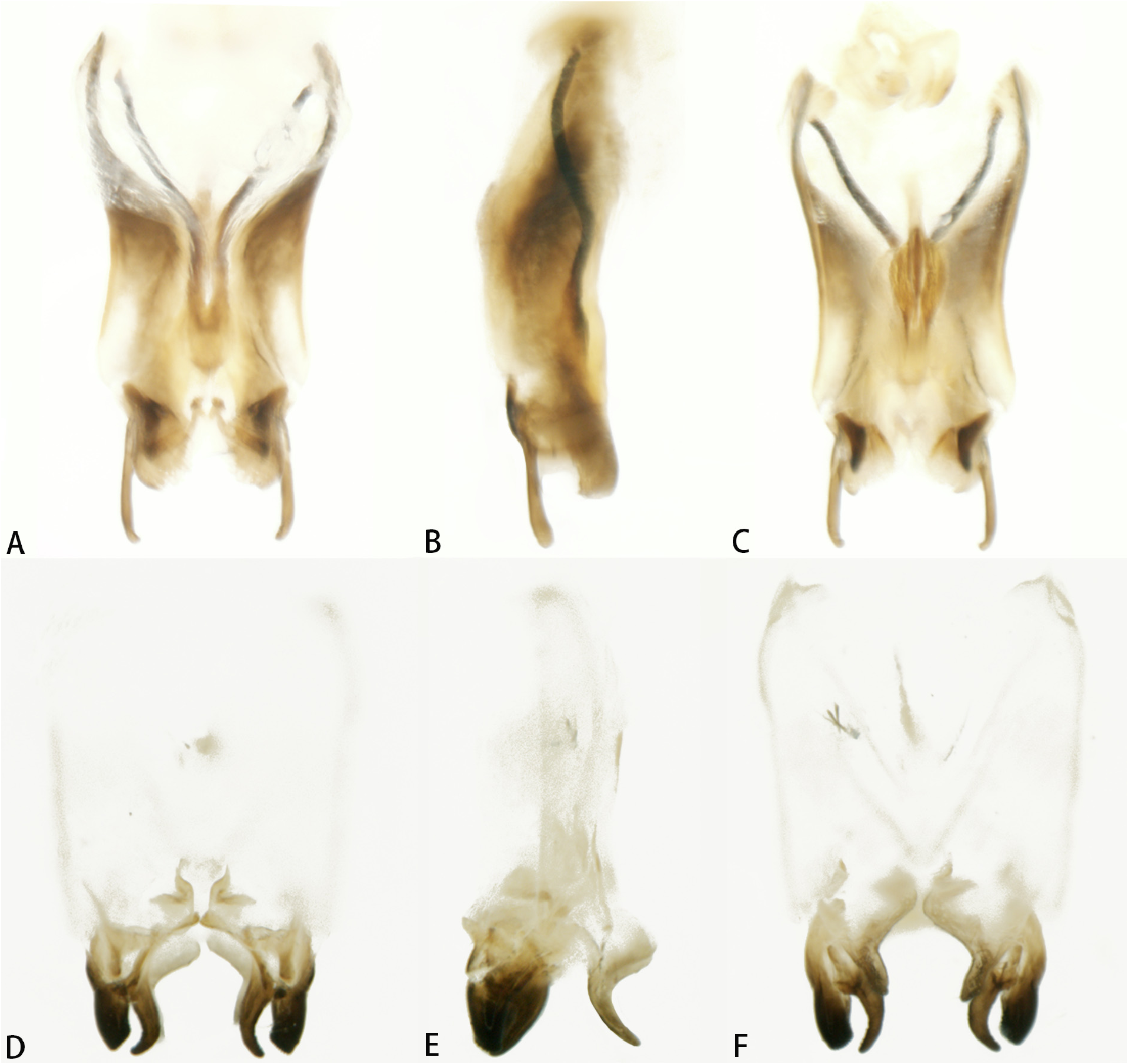
Genitalia ( Fig. 4A–C View FIGURE 4 ). In dorsal view, epiphallus broad and apical margin of the epiphallic lateral lobe round. Ectoparamere bifurcated: the upper branch long, thin, apically blunt and slightly bent inwards; the lower branch conspicuously short and boomerang-like.
Female ( Figs. 2B View FIGURE 2 , 3B, D, F View FIGURE 3 ). Body size slightly larger than male. Ovipositor blade-shaped.
Coloration. Body blackish-brown. Eyes reddish. Tibiae, tarsus, tegmen, and cercus light yellowish. Except two dark brown proximal segments, antenna light yellowish.
Measurements. Male (n=2). BL 4.36±0.23, PL 0.87±0.08, TL 2.91±0.10, HFL 3.42±0.21; Female (n=2). BL 5.04±0.37, PL 1.02±0.13, TL 3.07±0.36, HFL 3.86±0.33, OL 1.72±0.41.
Etymology. The name refers to the red eye of this species.
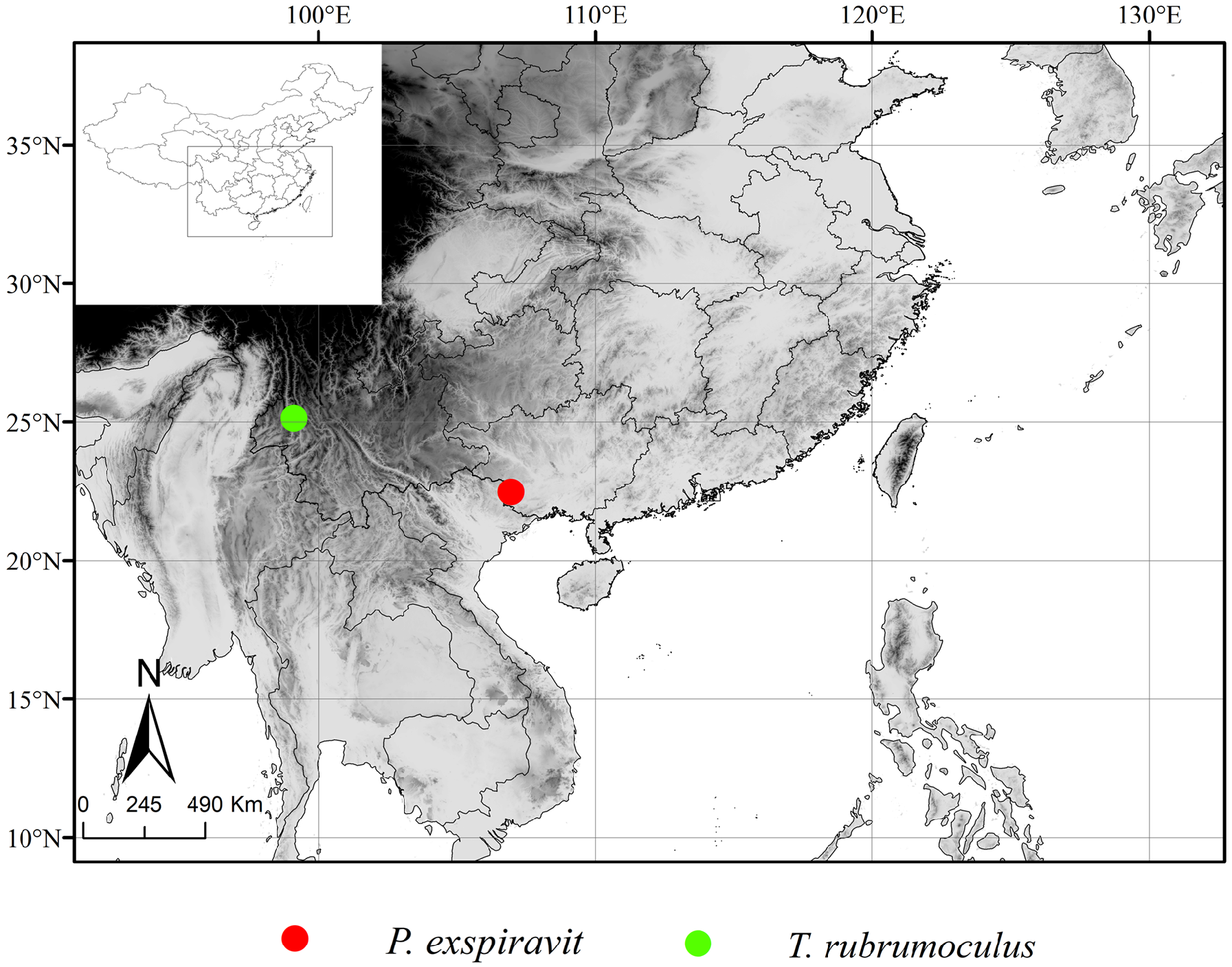
Distribution ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). China (Yunnan).
Remark. The new species is similar to Trigonidium solis Tan et al., 2019 in shape of ectoparamere (upper branch of ectoparamere is long and thin), but differs in its distinct coloration: blackish-brown body with yellowish tibiae and reddish eyes (body of T. solis is yellowish). It differs from other members with similar coloration of the genus (e.g., T. cicindeloides , Trigonidium erythrocephamlum (Walker, 1869) and Trigonidium japonicum Ichikawa, 2001 ) in bifurcated ectoparamere (inner edge of upper branch smooth and apically obtuse, and lower branch short and shaped as a boomerang). It differs Trigonidium rubellongigrum Gorochov, 1987 (female type) in color of eyes (red vs. black), pronotum (black vs. yellow), and femur (black vs. yellow).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Trigonidiinae |
|
Genus |