Zaglyptogastra piyachudasringi Chansri, Quicke & Butcher, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5188.2.8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7102086 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2270879E-FFC1-FFB8-0DF5-ABC862CEAEC5 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Zaglyptogastra piyachudasringi Chansri, Quicke & Butcher |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Zaglyptogastra piyachudasringi Chansri, Quicke & Butcher , sp. nov.
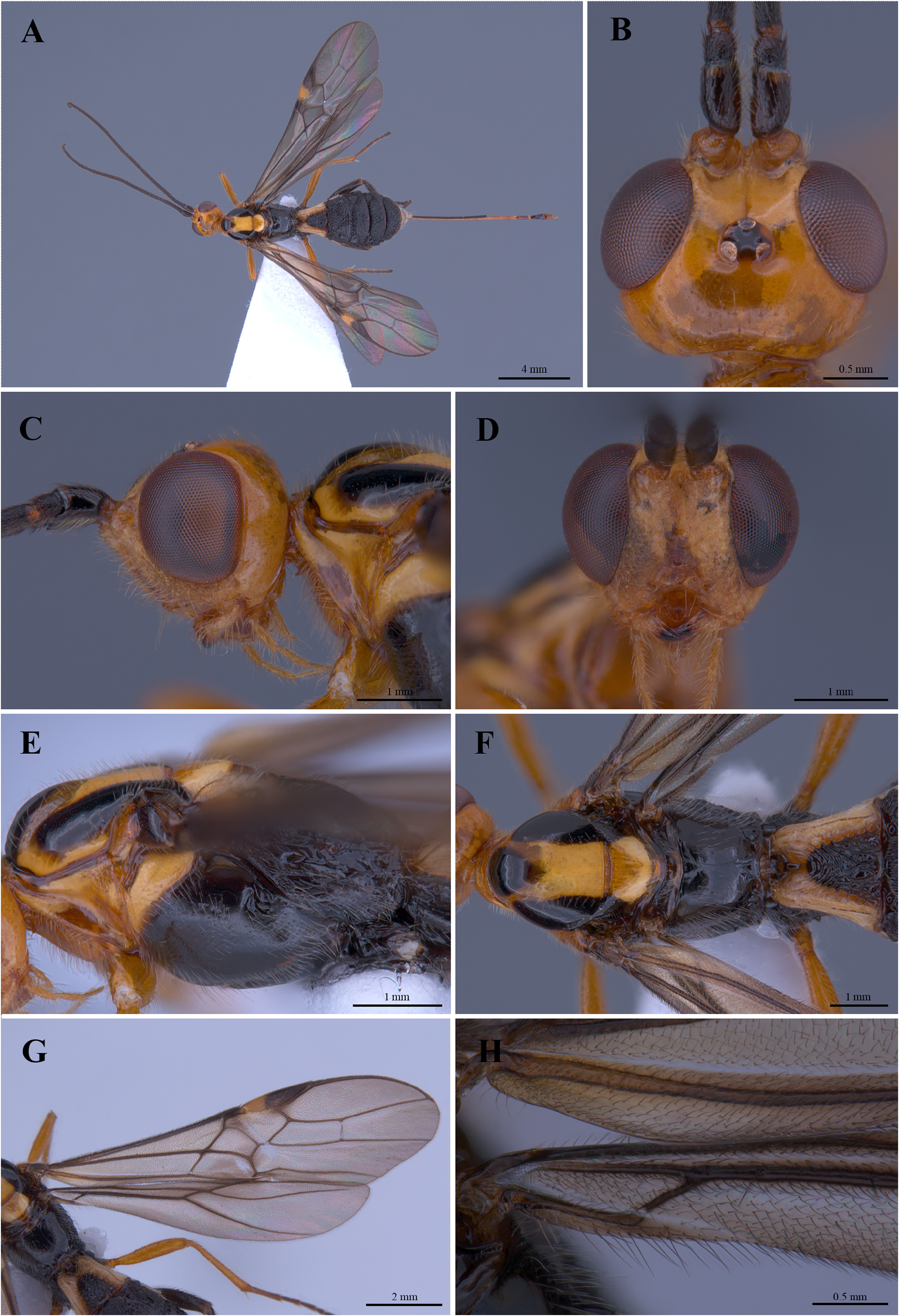
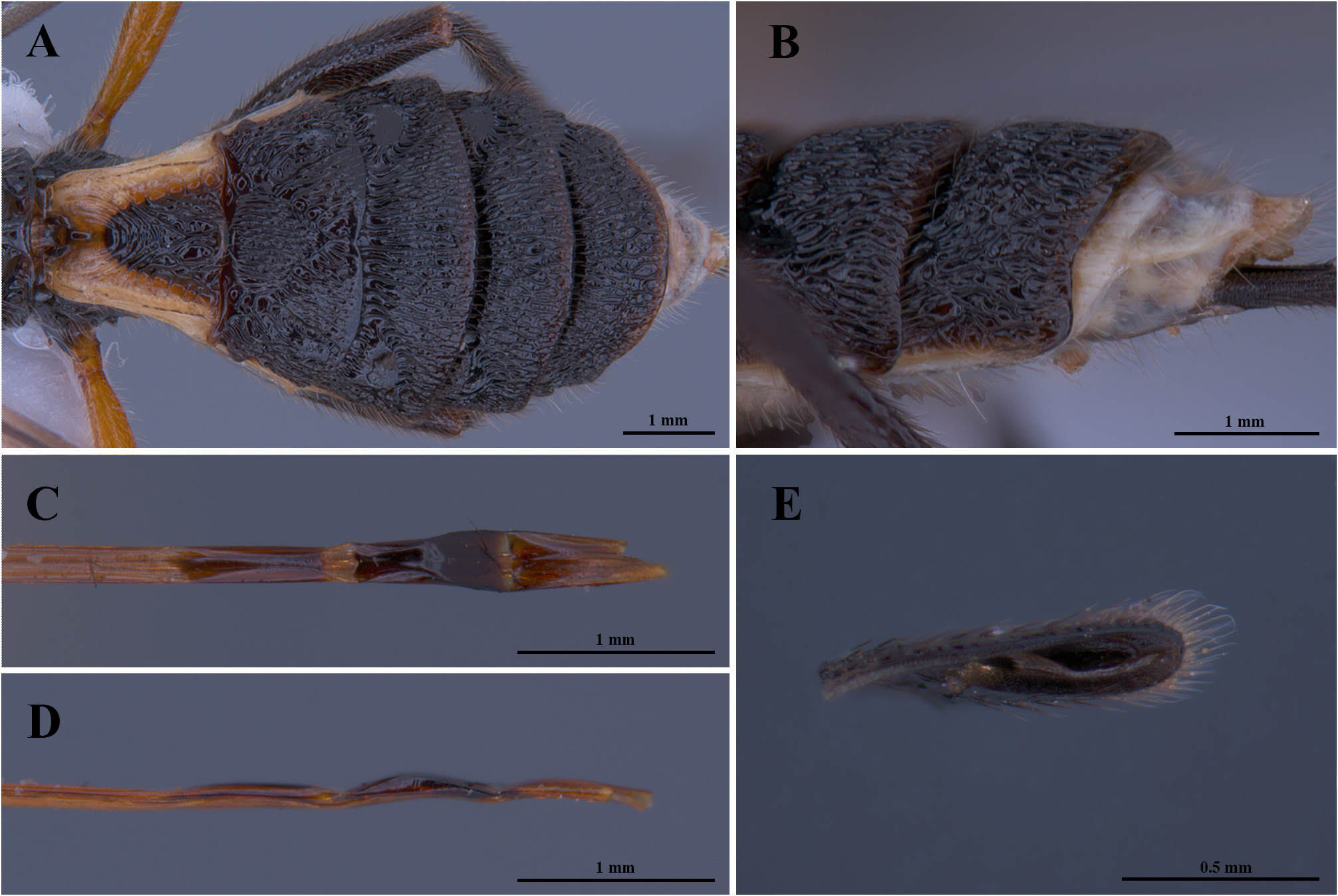
( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 , 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Material examined. HOLOTYPE female THAILAND, Nakhon Ratchasima, Wang Nam Khiao district, Udom Sap subdistrict, Sakaerat Environmental Research Station , dry evergreen forest, 14°49.672՛N, 101°91.615՛E, 496m, 12.ix.2021, Malaise trap, col. K. Chansri ( CUMZ).
Description. Holotype female. Length of body 12.0 mm, fore wing 10.0 mm, and antenna 9.5 mm, ovipositor part exserted beyond apex of metasoma 8.0 mm ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ).
Head. Antenna with 50 flagellomeres, terminal flagellomere acuminate, median flagellomeres 1.7 × longer than width and first flagellomere 2.0 × longer than width. Malar space short, height of eye 4.0 × vertical distance separating lower margin of eye from mandible. Face superimposes with densely deep setiferous puncture and sparsely long setose, intertentorial distance: tentorio ocular distance = 1.45: 1.0 Height of eye: width of face: width of head = 1.4: 1.0: 2.3. Length of face almost equal width of face ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ). Horizontal length of eye 1.8 × horizontal length of head behind eye ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ). Post-ocellar length: transverse diameter of posterior ocellus: shortest distance between posterior ocellus and eye = 1.0: 1.2: 2.0. Frons depressed behind antennal socket with narrow midlongitudinal groove. Top of head smooth with sparsely setose ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ).
......continued on the next page
Mesosoma. Length of metasoma 1.8 × longer than high ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ). Mesoscutum smooth, sparsely setose and flat posteriorly, notauli absent. Scutellum with anterior pit. Mesopleuron smooth, sub-protruded to antero-dorsally lobe. metapleuron sparsely striate setose. Propodeum smooth, sparsely setose laterally, with weak mid-longitudinal ridge anteriorly ( Fig. 1F View FIGURE 1 ).
Wings. Fore wing: pterostigma 3.83 × longer than wide; length of veins SR1: 3-SR: r = 5.5: 3.0: 1.0; vein 1-SR+M strongly curved with approximately 0.67 × 1-M; veins 2-SR: 3-SR: r-m = 1.5: 2.3: 1.0; vein cu-a antefurcal and strongly inclivous with 1-M ( Fig. 1G View FIGURE 1 ). Hind wing: apex of hind wing vein C+SC+R with two thickened setae (basal harmules); veins M+CU:1-M = 1.0: 2.7; base of hind wing evenly setose ( Fig. 1H View FIGURE 1 ).
Legs. Length of fore femur: tibia: tarsus = 1.0: 1.2: 1.7. Length of hind femur: tibia: tarsus = 1.0: 1.5: 1.67. Hind basitarsus 7.33 × longer than deep.
Metasoma. First metasomal tergite approximately 1.2 × longer than wide, anteriorly with dorsal carina forming a continuous curve, with several other fine curved carinae parallel to it; lateral areas wide, raised median area rugose. 2 nd –5 th metasomal tergites largely sculptured, scabrous, rugose or striate. Second metasomal tergite 2.0 × longer than wide, coarsely rugosely sculptured, with large shield-shaped midbasal area with fine rugulose sculpture ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Second suture deep, weakly bisinuous, strongly crenulate. Third metasomal tergite approximately 3.0 × wider than medially long with large, smooth anterolateral triangular areas. Third and fourth metasomal tergites without mid-longitudinal groove, fifth metasomal tergite with transverse crenulate subposterior groove, posterior laterally margin of fifth metasomal tergite weakly concave laterally, with corner smoothly rounded ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). Ovipositor 0.73 × of fore wing length; apex compressed and formed into three arch-liked sections (tip broken and retained) ( Figs 2C, D, E View FIGURE 2 ). Ovipositor sheath with long and dense setosity.
Coloration. Antenna, apex of mandibles, and stemmaticum, black. Head brownish yellow. Mesosoma largely black, except propleuron, pronotum, anterodorsal part of mesopleuron, notauli, medioposterior part of mesoscutum and scutellum, brownish yellow. Fore legs (except apex of tarsus); middle legs (except coxae and apex of tarsus) brownish. Apical segments of fore and middle legs, hind legs, black. Fore wing veins dark brown (except vein C+SC+R, black); pterostigma black except 0.3 basally yellow. Hind wing veins dark brown. Metasomal tergites black except anterior and lateral parts of first tergite ivory. Metasomal sternites, ivory, with a pair of black stripes on 2 nd –5 th segments. Ovipositor sheath and setae, black.
Distribution. Sakaerat Environmental Research Station, Nakhon Ratchasima province, Thailand.
Host. Unknown.
Etymology. Named after Piya Chudasring, late friend of the second author.
Diagnosis. The new species can be distinguished from all other Asian species by three character states: (i) strongly reclivous antefurcal fore wing vein cu-a; (ii) small body size (fore wing length 1.0 cm); (iii) apex of ovipositor dorsoventrally depressed and formed into three arch-liked sections ( Table 1 View TABLE 1 ).
| CUMZ |
Cameroon University, Museum of Zoology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |