Lepidocyrtinus betamponensis, Cipola & Morais & Bellini, 2020
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4898.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3F66CE1D-1036-4226-BC28-029F9961E069 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4421086 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7B6687A7-FFB2-FFDB-FF12-D710FCAFF8CD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lepidocyrtinus betamponensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Lepidocyrtinus betamponensis View in CoL sp. nov. Cipola & Bellini
Figs 55 View FIGURE 55 , 72–76 View FIGURE 72 View FIGURE 73 View FIGURE 74 View FIGURE 75 View FIGURE 76 , Tables 1 View TABLE 1 and 5 View TABLE 5
Type Material. Holotype female on slide (54128/ CAS): Madagascar, Toamasina, Réserve Nationale Intégrale Betampona, 17°54’58”S, 049°12’07”E ( Fig. 55 View FIGURE 55 ), Rainforest , 550 m, 24.iv-04.v.2008, Malaise trap, BL Fisher coll. 67 paratypes: 1 male and 5 females on slides and 30 specimens in alcohol (54128/ CAS); 1 male and 2 females on slides and 15 specimens in alcohol (54128/ CAS donated to INPA-CLL 000032 ), same data as holotype; 13 specimens in alcohol (54120, 54153-54, 56/ CAS), same data as holotype, except 3-10.viii.2008, 31.viii-07.ix.2008, 28.ix-05- x.2008, 21-28.xii.2008. GoogleMaps
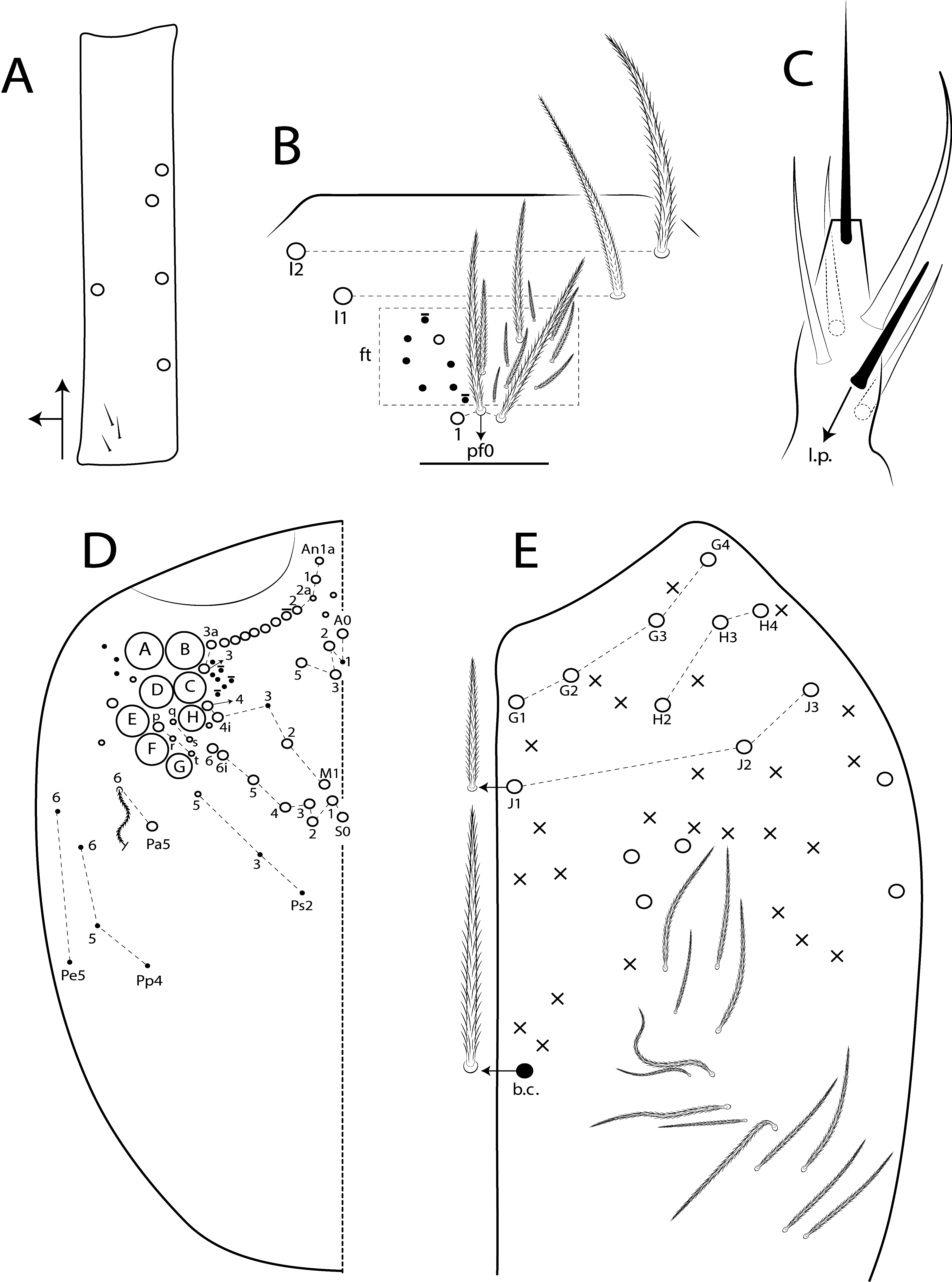
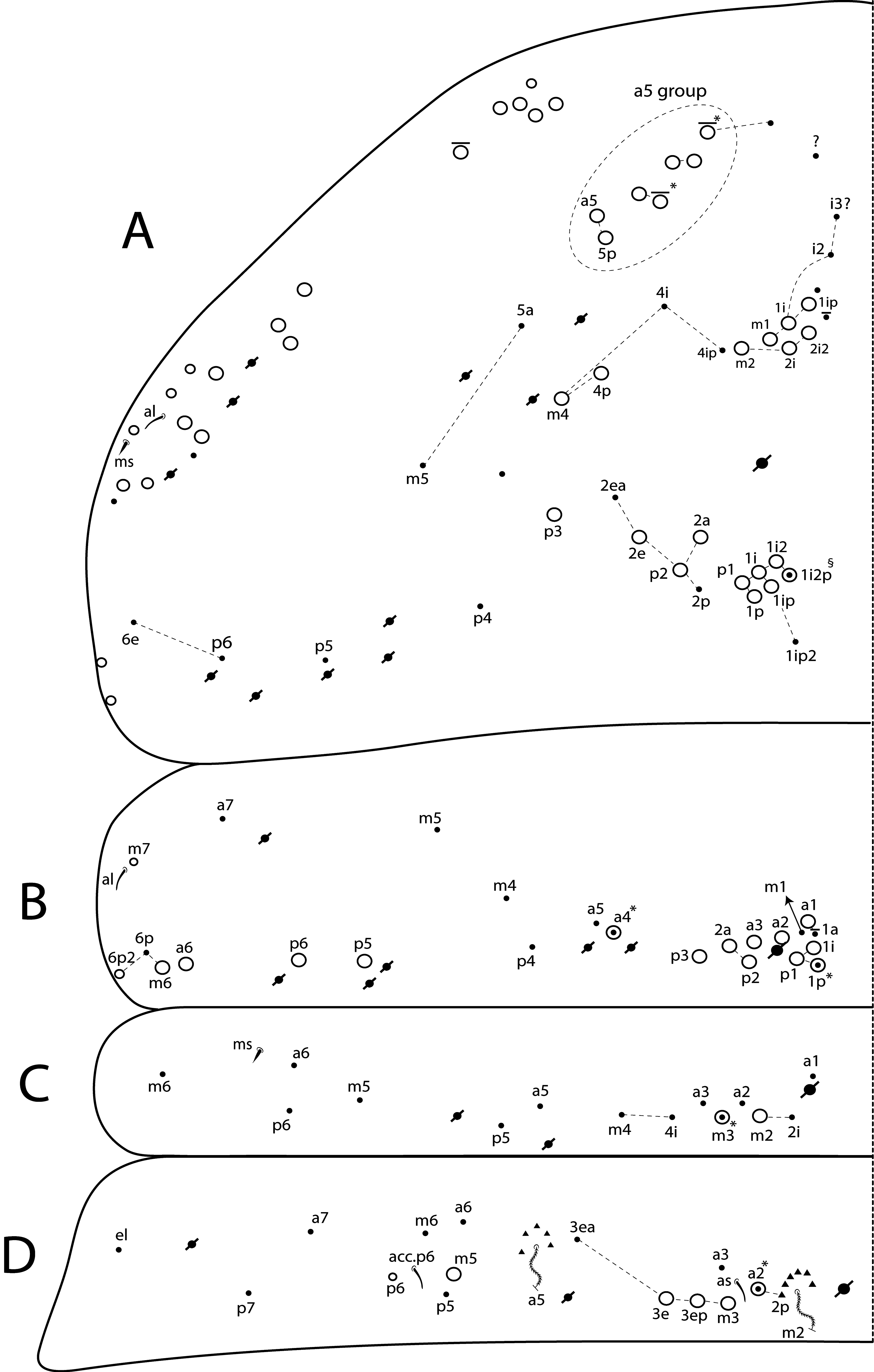
Diagnosis. Body with dark pigments on Ant II–IV and Th II laterally ( Fig. 72 View FIGURE 72 ); head mac A0, A2–3, A5, M1–2, S0–3 and S5–6 present; prelabral chaetae smooth; labial papilla E with l.p. conical and not reaching the base of a.a.; basolateral and basomedian labial fields with chaetae R (smaller than the others) and L1–2 ciliated, e smooth ( Figs 73 View FIGURE 73 B–E); Th II projected anteriorly and with 5–7 anterior, 8 median (m1ip, m4–4p present, m4i mac absent) and 9–10 posterior mac (p2ep absent, p3 as mac); Th III–Abd II with 8–10, 1–2, 3–4 central mac respectively; Abd IV with 12 central mac and 12–15 lateral mac ( Figs 74 View FIGURE 74 , 75B View FIGURE 75 ); unguis a.t. absent; unguiculus pe lamella smooth and with a small proximal tooth; collophore anteriorly with 9 spine-like chaetae and 5–6 ciliated chaetae apically acuminate, posteriorly with 8 spines, smooth chaeta present ( Fig. 76E View FIGURE 76 ); manubrium ventrally with 0/4 subapical chaetae; manubrial plate with 2 blunt mac abruptly acuminate at the apex; dens with 5–9 blunt mac apically bullet-like abruptly acuminate at the apex ( Figs 76 View FIGURE 76 F–G).
Description. Total length (head + trunk) of specimens 3.03–3.70 (n=4), holotype 3.70 mm. Specimens pale white with dark blue pigment on Ant I–IV (darker on distal Ant II, proximal and distal Ant III and IV), lateral Th II–III, femur I–II with one distal band and III with proximal and distal bands, and tibiotarsus almost completely (except distally); eyepatches black ( Fig. 72 View FIGURE 72 ). Scales present on Ant I to proximal one quarter of Ant IV, dorsal and ventral head, dorsal thorax and abdomen, legs (except empodia), anterior collophore, ventral and dorsal manubrium and dens ventrally.
Head. Antennae subequal or smaller than trunk length ( Fig. 72 View FIGURE 72 ); ratio antennae: trunk = 1: 1.10–1.21 (n=3), holotype 1: 1.21; antennal segments ratio as I: II: III: IV = 1: 1.28–1.48: 1.41–1.48: 2.83–3.00, holotype 1: 1.40: 1.48: 2.85. Ant IV annulated on distal three fourths, with apical bulb apically bilobed. Ant III not annulated, apical organ with 2 short rods, 3 spiny guard sens and s-blunt sens of different sizes. Ant I dorsally with 4–5 median mac and 3 smooth mic at the base, without spines. Eyes A and B larger, G and H smaller, others subequal, and with 5–6 ‘IO’ chaetae; head dorsal macrochaetotaxy with 10–13 An, 4 A, 3 M and 7 S mac ( Fig. 73D View FIGURE 73 ). Clypeal formula with 4 (l1–2), 7 (ft), 5 (pf0–2) ciliated chaetae, l1–2 larger than the others, l1 apically acuminate, 1 ft smaller, others subequal ( Fig. 73A View FIGURE 73 ). Prelabral chaetae smooth but sometimes with a small median filament, outer chaetae rarely with two median filaments ( Fig. 73B View FIGURE 73 ). Labral p0 chaeta sometimes with median filament or rarely bifurcated, p1 larger than the others. Labral papillae with two inner rounded projections, outer papillae absent. Maxillary palp with smooth t.a. and b.c. weakly ciliated, thicker and 1.29 longer than the a.a. Labial papilla E with l.p. conical and not reaching the base of a.a. ( Fig. 73C View FIGURE 73 ). Basolateral and basomedian labial fields with chaetae M1–2, R (smaller than the others), L1–2 ciliated, e smooth ( Fig. 73E View FIGURE 73 ). Ventral head with about 16 ciliated chaetae, postlabial formula with 4 (G1–4), 3 (H2–4), 4 (J1–4) chaetae, and 3 larger chaetae, 2 b.c. surrounding the cephalic groove ( Fig. 73E View FIGURE 73 ).
Thorax chaetotaxy ( Fig. 74 View FIGURE 74 A–B). Th II projected anteriorly, a, m and p series with 5–7, 8 and 9–10 mac, respectively, and about 11 secundary psp. Th III a, m and p series with 4–5, 1 and 7–8 mac, respectively, and about 6 secundary psp. Ratio Th II: III = 2.25–1.92: 1 (n=4), holotype 2.13: 1.
Abdomen chaetotaxy ( Figs 74 View FIGURE 74 C–D, 75A–C). Abd I a, m and p series with 0, 1–2 and 0 mac, respectively, and at least 2 secundary psp. Abd II a, m and p series with 0–1, 4 and 0 mac, respectively, and at least 2 secundary psp. Abd III a, m and p series with 0, 3 and 1 mac, respectively, and about 8 secundary psp. Abd IV with 12 central mac on A–T series and 12–15 lateral mac on E– Fe series; about 9 secundary psp, at least 8 posterior sens (ps type I, others type II) and 6 posterior mes. Abd V a, m and p series with 1, 4 and 6 mac, respectively. Ratio Abd III: IV = 1: 4.51–5.44 (n= 4), holotype 1: 4.53.
Legs. Subcoxa I with 6 chaetae on a row, 2 anterior chaetae and 2 psp; subcoxa II with an anterior row of 12 chaetae, posterior row of 7 chaetae and 6 psp; subcoxa III with one row of 12 chaetae and 2 posterior psp ( Figs 76 View FIGURE 76 A–C). Trochanteral organ with about 78 spine-like chaetae ( Fig. 76D View FIGURE 76 ). Tibiotarsus III sometimes subdivided on distal two thirds, outer side with 4 proximal large chaetae apically acuminate, inner side with 7 mac weakly ciliated. Unguis with 3 inner teeth, b.t. subequal to m.t. in length, a.t. absent. Unguiculus with all lamellae smooth and acuminate, except pe with a small proximal tooth (as in Fig. 51E View FIGURE 51 ); ratio unguis: unguiculus = 1: 0.63. Tibiotarsal smooth chaeta 1.18 larger than unguiculus and tenent hair 0.72 smaller than unguis outer edge.
Collophore. Anterior side with 18–20 chaetae, 9 proximal spine-like chaetae, 1 thin and 1–2 normal ciliated chaetae, 5–6 ciliated chaetae apically acuminate and 2 mac distally; posterior side with 18–19 chaetae (2 unpaired), 8 spines, 9–10 thin ciliated chaetae widely distributed and 1 smooth chaeta distally; lateral flap with about 67 chaetae, 10 smooth and 57 ciliated ( Fig. 76E View FIGURE 76 ).
Furcula. Manubrium ventral formula with 0, 0, 0, 0/4 (subapical), 12–16 (apical) ciliated chaetae plus approximately 24 elongated apical scales per side ( Fig. 76F View FIGURE 76 ); manubrial plate with 2 blunt mac ciliated abruptly acuminate at the apex, 12 ciliated chaetae of different sizes and 3 psp. Dens dorsally with one proximal row of 5–9 blunt mac weakly ciliated, 3 proximal apically bullet-like and up to 6 abruptly acuminate at the apex, holotype with 7+7 ( Fig. 76G View FIGURE 76 ).
Etymology. Refers to its type locality: Betampona Reserve, Madagascar.
Remarks. Lepidocyrtinus betamponensis sp. nov. resembles others species from Madagascar ( Table 5 View TABLE 5 ). See the comparison among them in the remarks of L. iegoi sp. nov.
| CAS |
California Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |