Zoosphaerium bambusoides Wesener & Bespalova, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5733/afin.051.0102 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FFFB20B0-9B5E-4A78-88EC-3EDD7EB197BA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7911554 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/FA7D68F1-37F7-418A-B62C-92A342BA0F48 |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:FA7D68F1-37F7-418A-B62C-92A342BA0F48 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Zoosphaerium bambusoides Wesener & Bespalova |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Zoosphaerium bambusoides Wesener & Bespalova View in CoL , sp. n.
Figs 6–8 View Fig View Fig View Fig , 17B View Fig
Etymology: The name refers to the bamboo-like colour of the species.
Differential diagnosis:The posterior telopods ( Figs 7A–C View Fig ) clearly mark Z. bambusoides as a member of the Z. coquerelianum species-group. The body size, colour, and shape of the posterior telopods closely resemble those of Z. smaragdinum Wesener, 2009 . Z. bambusoides differs from the latter in the presence of up to 10 spines on the walking legs ( Fig. 6C View Fig ), a tarsal spine on leg 3, 27–29 and sensory cones on the antenna ( Fig. 8B View Fig ), the absence of sclerotised teeth on antennomere 4 ( Fig. 8A View Fig ), longer marginal bristles on the endotergum ( Fig. 17B View Fig ), and the absence of a membranous lobe on the posterior telopods ( Fig. 7C View Fig ).
Description:
Male.
Body length: Holotype: length 22.7 mm, width of thoracic shield 12.4 mm, height of thoracic shield 6.5 mm.
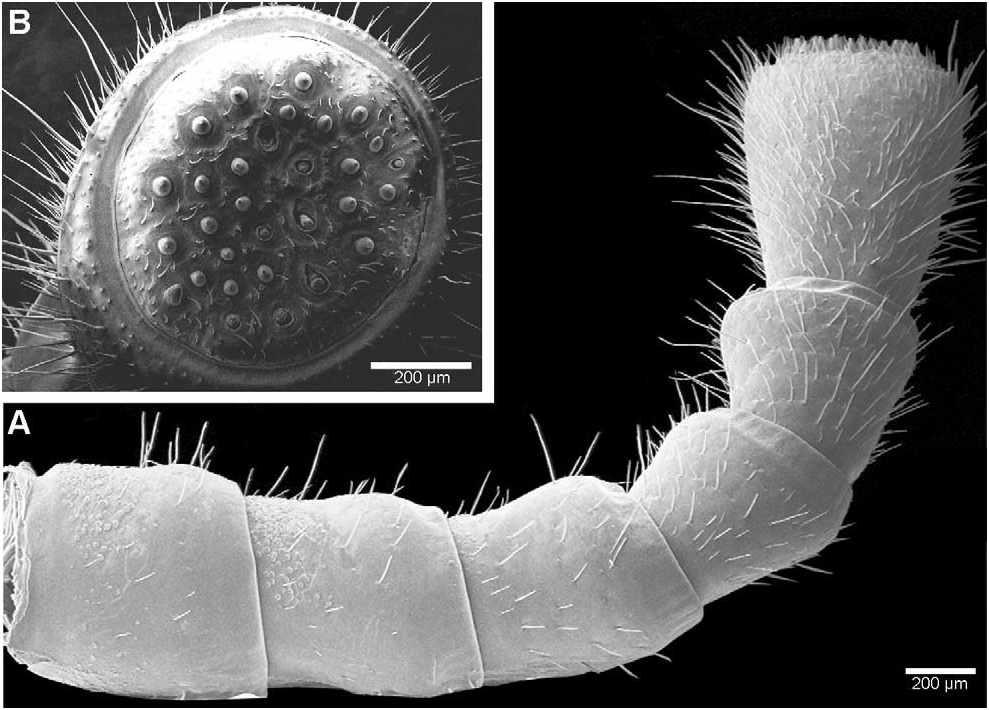
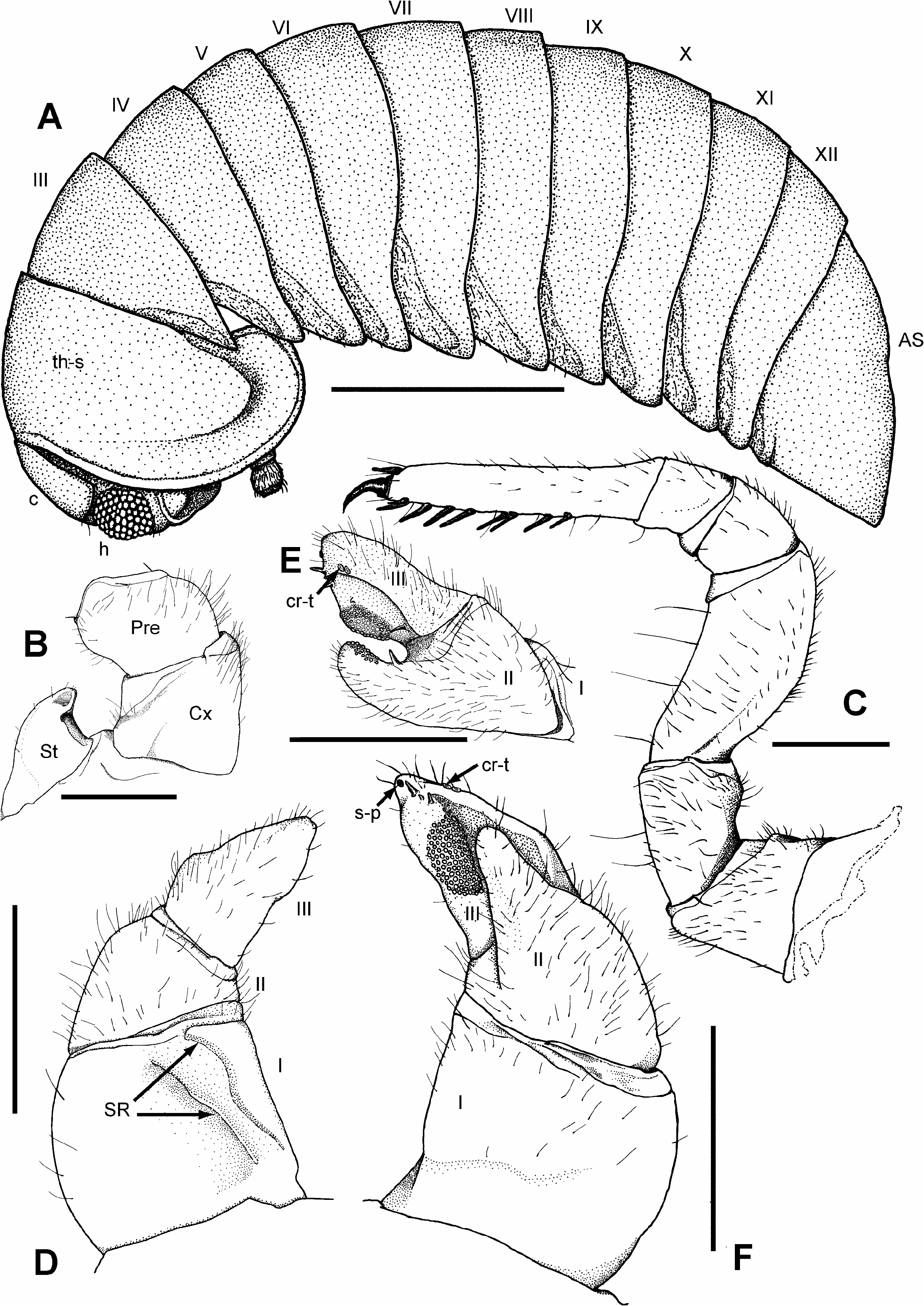
Habitus: Small, glabrous pill-millipede ( Fig. 6A View Fig ).
Colouration: Some discolouration may have occurred because of preservation in alcohol. When observed in alcohol, tergites reminiscent of bamboo leaves. Tergites vibrant dark green with thin sand-coloured strip at posterior margin. Dorsal side of anal shield same colour as tergites, while ventral side of anal shield, as well as ventral side of thoracic shield under light has a bright teal tint. Legs close to colour of tergite, though with tealtinted tarsi. Head and collum also close to colour of tergite, though with a more yellow tint, and brown area around the mandibles. Antennae olive-green.
Head: Eyes with ca 92 ocelli. Antennae long and thin, with cylindrical joints ( Fig. 8A View Fig ). First antennomere with groove but without sensilla basiconica. Sclerotised teeth at base of antennomere 1–3. Length of antennomeres: 1>2=3>4>5<6. Apical disc bearing 27– 29 sensory cones ( Fig. 8B View Fig ). Mouthparts not dissected. Collum glabrous, with 1–3 setae at corners on either side of head.
Thoracic shield: Surface like tergites.
Tergites: Surface glabrous, shiny, covered with minute depressions like orange peel (50×). Tips of paratergites project posteriorly, forming sharp points ( Fig. 6A View Fig ).
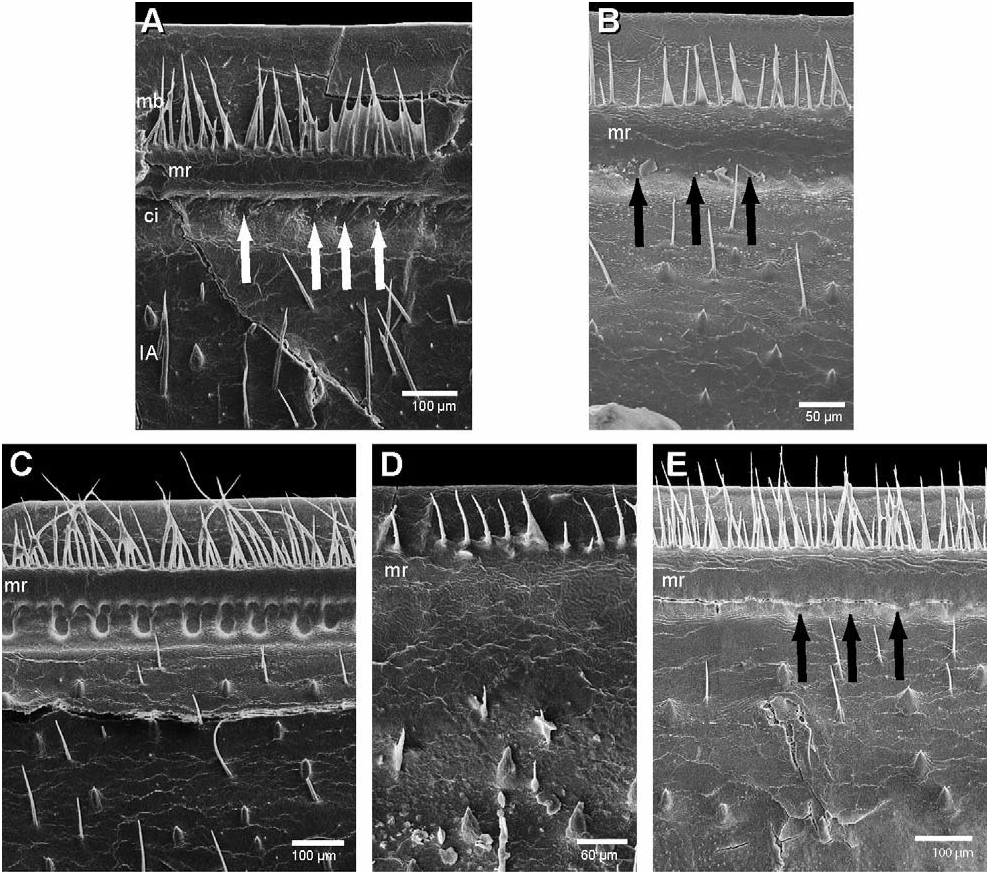
Endotergum: Single row of marginal bristles reaching 2/3 of distance to edge of margin. Single row of elliptical cuticular impressions. Internal section with short spines and very few isolated long bristles ( Fig. 17B View Fig ).
Anal shield: Fairly well-rounded with a very slight indication of a bell shape because of a small bulge toward dorsal side ( Fig. 6A View Fig ). Surface like tergites. Underside carrying two brown locking carinae, anterior one very short, about 1/6 the length of posterior one. Carinae separated by a space about as long as 2× the anterior carina. Posterior carina slightly curved towards margin of anal shield.
Legs: Tarsi 1 with 5, 2 with 6, 3 with ca 7, and 4–21 with 8–10 ventral spines. First two leg pairs with an apical spine. Tarsi of legs 4–21 with an apical spine. In leg 10 femur 1.89×, tarsi 5.4× longer than wide ( Fig. 6C View Fig ).
Stigmatic plates: First plate with triangular lobe. Lobe short and stout, with a thin, pinched, triangular area at apex projecting towards coxa ( Fig. 6B View Fig ).
Female. Unknown.
Male sexual characters: Gonopore covered with a single undivided, elliptical sclerotised plate. Small apical portion of plate membranous. Covers 1/2 height and 2/3 width of coxa. Anal shield with slight bell shape, glabrous.
Anterior telopods ( Figs 6D–F View Fig ): Harp with 2 strongly pronounced stridulation ribs – one long and well pronounced rib lying mesally to a less pronounced and shorter one. Top rib steep and step-like. Process of second podomere slightly hooking towards third podomere; apical portion facing third podomere covered with sclerotised spots. Below spots at base of projection lies a sclerotised spine. Third podomere basally also includes sclerotised spine. Large lobe covered by a mound of sclerotised spots located on mesal half of process. Deep concavity located on lateral half. Vertical row of three spines lying at apex following a brown sclerotised spot. Two sclerotised, crenulated teeth sitting on apicolateral margin of concavity. Small fifth sclerotised spine lying close to lateral margin of mound of sclerotised spots. Anterior telopods curve gently towards each other, creating a circular laurel wreath shape more than a horseshoe shape.
Posterior telopods ( Figs 7A–C View Fig ): Movable finger moderately thick (2.46× longer than wide), weakly hooking towards fixed finger. In total, there are 10 sclerotised spines located mesally on movable finger; 5 in a clump on a raised mound located in middle of process (4 arranged in a square, with a tiny fifth spine located basally), 2 apically, and 3 laterally of medial area in a triangular formation. On apical posterior margin are 14 sclerotised, crenulated teeth. Fixed finger slightly shorter than movable finger, curving towards latter. Sclerotised spine located basally. Tip of fixed finger flat, inner part containing a slightly squared off depression. Area above depression covered by a few sclerotised spots. Some sparse hair located on movable finger on upper half of posterior side, and on lateral margin of anterior side. Second podomere covered by numerous hairs on anterior and posterior sides. First podomere with some hairs on upper portion of posterior side as well as mesal portion of anterior side. Inner lobes quite thin and flat, curving steeply inwards to create deep bowl shape. Tips of inner horns curving slightly inward.
Holotype: ơ ( BLF 13126 -B ( CASENT 9032797 )). MADAGASCAR: Toamasina Prov.: Reserve Betampona, Camp Rendrirendry 34.1 km, 332° Toamasina, 390 m, rainforest, 17°55'26"S: 49°11'59"E, B.L. Fisher et al., general collecting in camp, 28.xi.2005. GoogleMaps
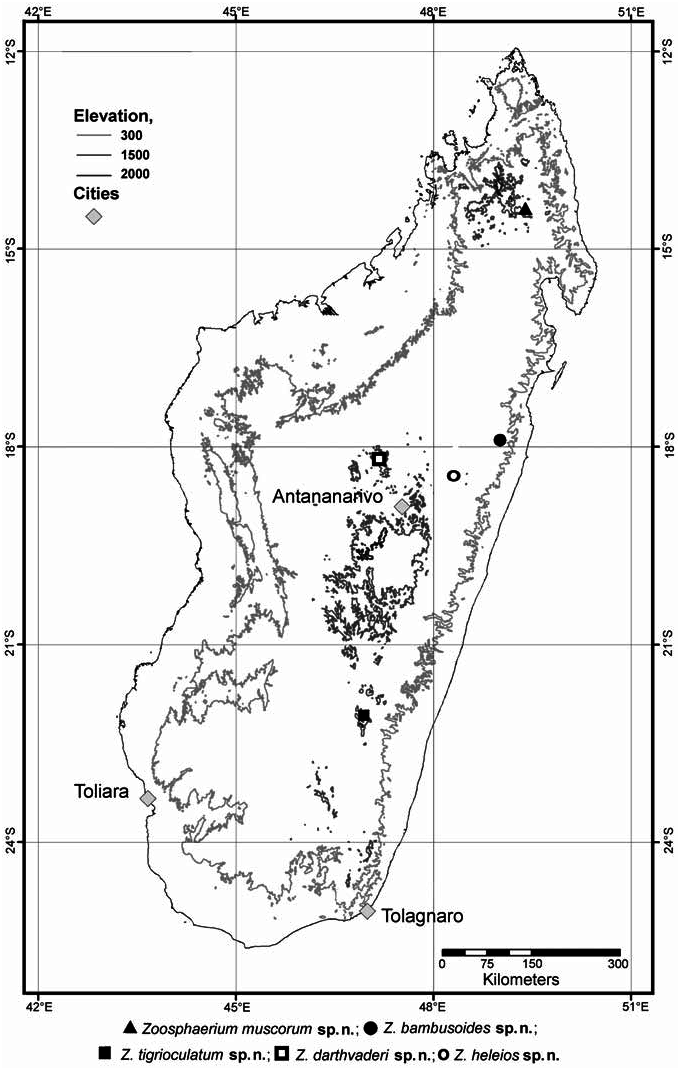
Distribution & Ecology: Z. bambusoides is currently only known from the lowland rainforest of Betampona ( Fig. 2 View Fig ). The lowland rainforests of Madagascar are impacted severely by human development ( Moat & Smith 2007).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.