Fimoscolex bartzi, Bartz, Marie Luise Carolina, James, Samuel Wooster, Pasini, Amarildo & Brown, George Gardner, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.282225 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:632E318C-BAFD-423A-A546-A8E4B4F463B2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6177009 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03EB87EE-FFF5-FFAA-3EBD-4377DF714354 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Fimoscolex bartzi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Fimoscolex bartzi n. sp. Bartz & James
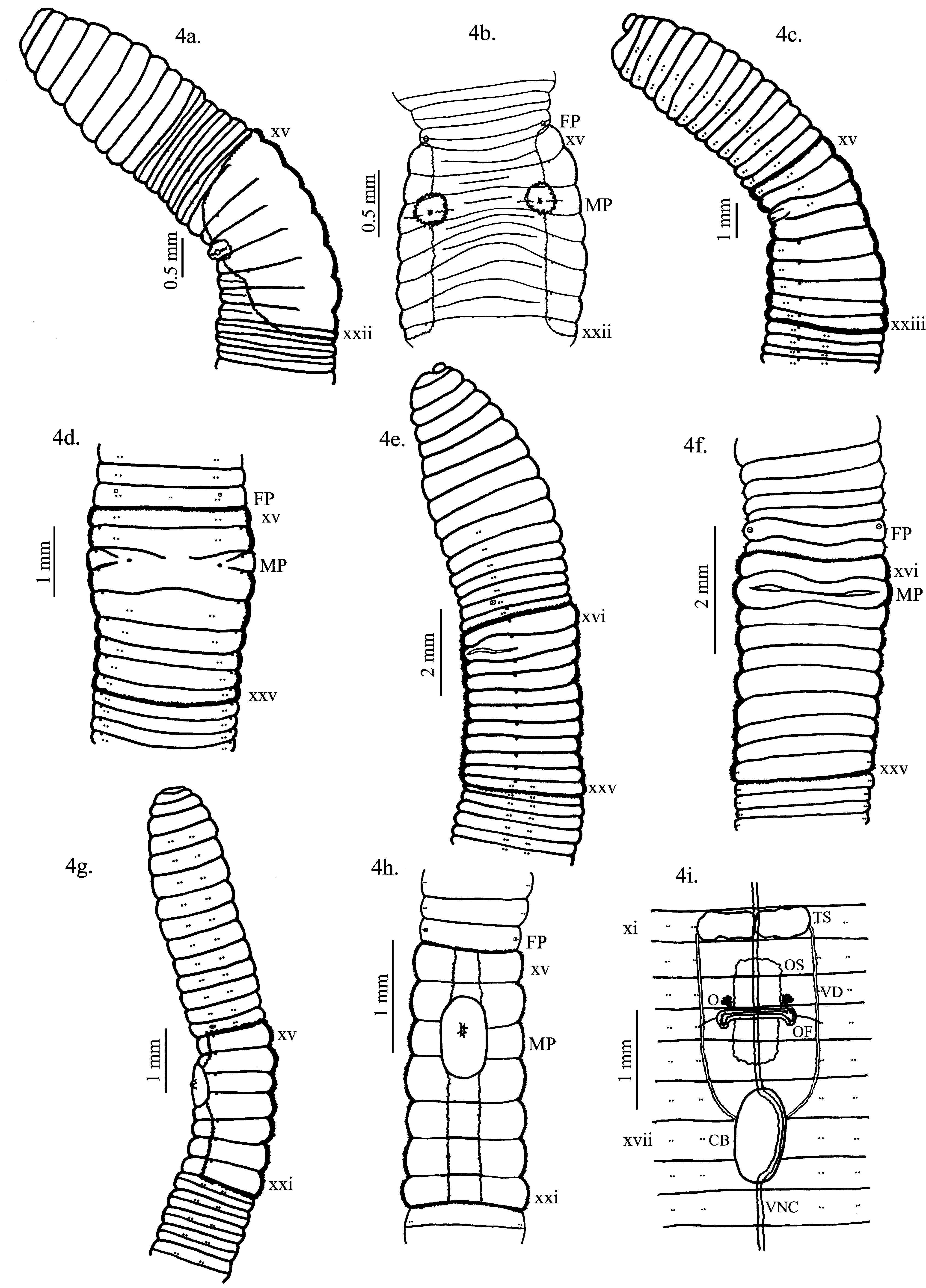
( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 g,h,i, Table 1)
Holotype. COFM BRPR 0129 one adult, pasture converted into annual crop (wheat), São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil: 23º24.872’S, 51º18.847’W, 666 masl, 30 September 2009, M.L.C. Bartz and A.Pasini colls.
Paratype. COFM BRPR 0132 one adult, soybean field under 35 years no-till, Rhenânia Farm, Rolândia, Paraná, Brazil; 23° 23.075’S, 51° 21.477’W, 675 masl, 19 June 2008, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.
Other material. COFM BRPR 0324 four adults, pasture converted into annual crop (wheat), São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil: 23º24.872’S, 51º18.847’W, 666 masl, 30 September 2009, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls. COFM BRPR 0130 one adult and two juveniles, pasture, São José Farm, Londrina, Paraná, Brazil: 23º24.872’S, 51º18.847’W, 666 masl, 30 September 2008, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.; COFM BRPRP 0131 one adult, black oats field under 35 years no-till, Rhenânia Farm, Rolândia, Paraná, Brazil; 23° 23.075’ S, 51° 21.477’W, 675 masl, 19 March 2008, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.; COFM BRPR 0325 one adult, soybean field under 35 years no-till, Rhenânia Farm, Rolândia, Paraná, Brazil; 23° 23.075’S, 51° 21.477’W, 675 masl, 19 June 2008, M.L.C. Bartz and A. Pasini colls.
Etymology. The species is named in honor of the farmer Herbert Arnold Bartz, considered the pioneer of the no-till system in Latin America and manager of the Rhenânia Farm from 1965 to 2007.
Description. Dimensions: Holotype 39 mm by 1.7 mm at x, 1.5 mm at clitellum, 1.6 mm at xl, 119 segments; paratype 37 mm by 1.2 mm at x, 1.0 mm at clitellum, 1.1 mm at xl, 166 segments. Body cylindrical. Setae ab and cd commence on iv, setae very tiny and hardly visible. Setae closely paired throughout; genital setae absent; setal formula AA:AB:BC:CD:DD = 20:1:4:1:30 at x and 28:1:6:1:32 at xxx. Prostomium prolobous. Unpigmented. Ovipores on very small papillae in a, in xiv; single male pore on xvii as an oval conical protuberance occupying 2/ 3xvi–1/3xviii. Clitellum saddle, xv–xxi ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 g). Segments after clitellum with post-setal second or third annulations. Nephropores just above b.
Septa 6/7 and 10/11 thin muscular, 7/8–9/10 equally thick muscular, 11/12 membranous, around heart and testes sacs, septa 12/13/14 united by circumesophageal membrane isolating villous interior from other septal contents of xiii, which are medial to membrane. Alimentary canal with large cylindrical gizzard in vi, esophagus with wide angle lamellae chevron pattern vii–ix, esophagus valvular in xiv, intestinal origin xv; typhlosole origin xvi, end xci, cxxi, simple lamella in open folds xvi–xxiv, thicker lamella xv–xxvii, after xxviii gradually becoming simple and straight. Calciferous glands paired in xii, composite-tubular type, bean shaped, sessile on dorsal esophageal wall; blood vessels to gland include large branch of dorsal vessel to approximate center of each gland, two coalescing vessels from ventral gland margin to extra-esophageal vessel. Gland opening to esophagus near dorsum. Holonephric, vesiculate; ducts to body wall near level of b.
Vascular system with ventral trunk, single dorsal trunk, lateral vessels in vii–ix, latero-esophageal hearts in x–xi. Extra-esophageal vessel visible near pharyngeal glands, passes along ventral-lateral face of gizzard and esophagus, ending in calciferous glands; supraesophageal vessel in x–xi.
Ovaries in xiii; modified funnels, C shaped in xiv and a flat sac in 1/ 3 xii – 2/3 xv, under ventral nerve cord ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 i); spermathecae absent. Male sexual system metandric, testes and funnels in sac with enclosed hearts; seminal vesicles start on the back side of the testes sacs in xi, penetrate septa and range posteriorly along intestine to xiv–xv as simple elongate sacs with parallel blood vessels on median side of longitudinal axis of vesicle; vasa deferentia long, looped from xi, on body wall in line of ab to the ventro-lateral face of the large single oval copulatory bulb (intersegmental line xvi/xvii); bulb extends over 2/3 xvi–1/3 xviii but occupies septally-defined space of xvii. Copulatory bulb with thin muscular outer layer, dense, delicate glandular inner surface with small lumen leading to male pore at approximate center of bulb connection to body wall; lumen undulating in three dimensions; no transverse muscle bands crossing over bulb; bulb attached by muscles to body wall.
Remarks. Fimoscolex bartzi is part of the genus Fimoscolex defined by Michaelsen (1900) as glossoscolecid worms having a single male pore and a single copulatory bulb. There are 7 species presently known in this group ( James & Brown, 2010). Fimoscolex bartzi is most similar to Fimoscolex angai minor Zicsi & Csuzdi, 1987 , with the differences between F. bartzi and F. angai minor as follows, the characteristics of the latter in parentheses: length 35–57 mm (77 mm), number of segments 119–188 (189–201), setae beginning between ii and iv (setae beginning in segment iv), setal ratios 28:1:6:1:32 (ab=cd, aa = 3bc), testes in sac in xi extending to 13 (ventral single testes sac, cone form), ovaries associated to flat sac (ovaries normal), last heart pair enclosed (free).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.