Pelomedusa gehafie ( Rüppell, 1835 )
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3795.5.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9394634C-9836-4973-868B-BDEE414E4EA8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5082955 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CB02879F-F93C-FFCC-FF74-F97FFF3DFAEA |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Pelomedusa gehafie ( Rüppell, 1835 ) |
| status |
|
Pelomedusa gehafie ( Rüppell, 1835)
1835 Pentonyx gehafie Rüppell —Type locality: eastern slope of coastal mountains, Eritrea; lectotype ( Mertens 1937): Senckenberg-Museum, Frankfurt am Main, SMF 7947 ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 top in Fritz et al. 2014)
1910 Pelomedusa galeata var. disjuncta Vaillant & Grandidier —Restricted type locality (by lectotype designation, Fritz et al. 2014): eastern slope of coastal mountains, Eritrea; lectotype ( Fritz et al. 2014): Muséum National d’Histoire naturelle, Paris, MNHN 7870 About MNHN
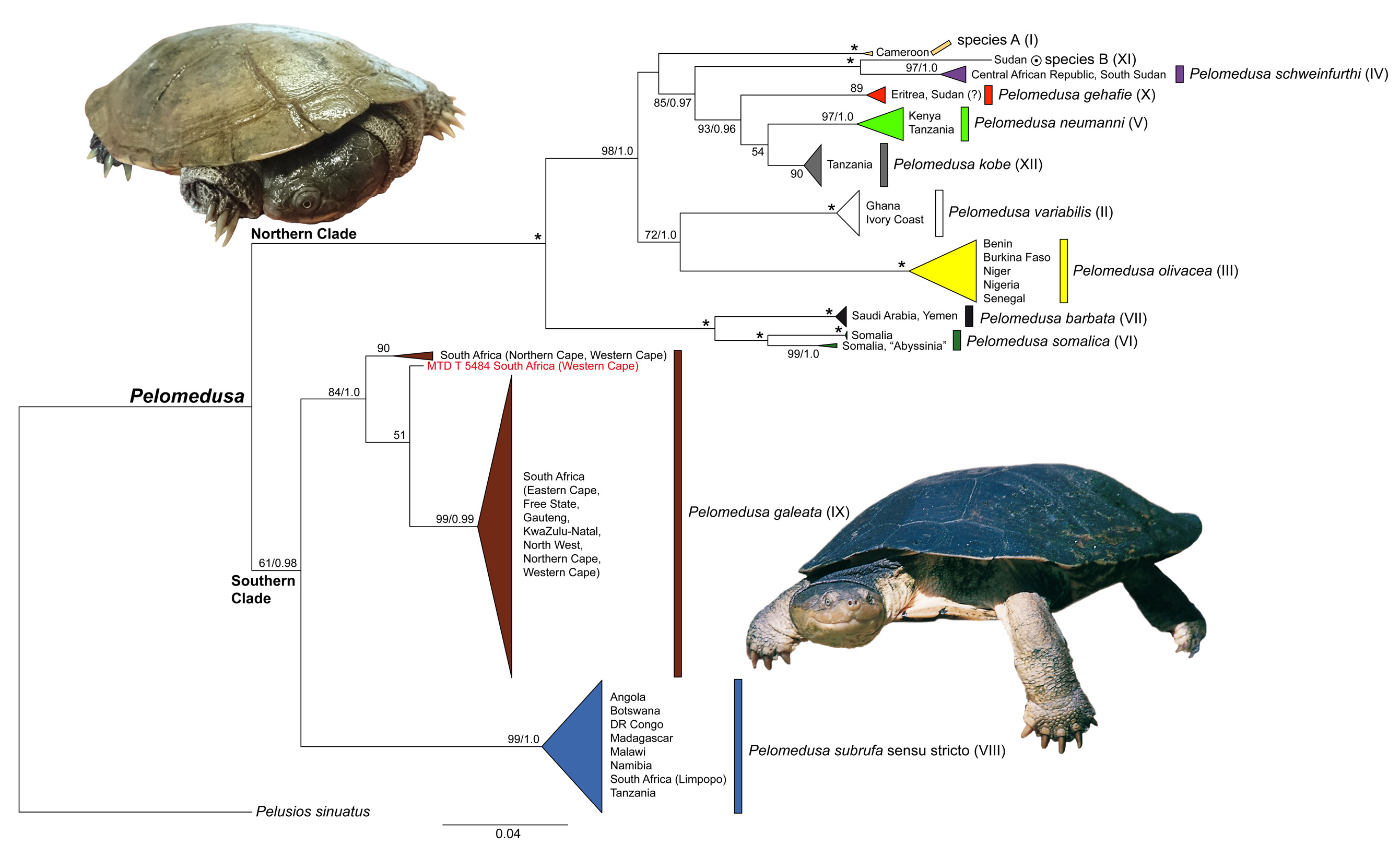
Diagnosis: Medium-sized, light-coloured helmeted terrapins with a known maximum straight carapacial length of 17.8 cm. Pectoral scutes triangular and in adults widely separated from plastral midseam (in hatchlings the tips of the triangular pectorals may meet at the plastral midseam). One large undivided temporal scale on each side of head. Two small barbels under chin. Carapace unpatterned light coloured. Plastron in adults completely yellow. Pelomedusa gehafie differs from all other Pelomedusa species except P. schweinfurthi and P. somalica by the presence of guanine (G) instead of adenine (A) at position 256 of the 360-bp-long reference alignment of the 12S rRNA gene (Supporting Information). Pelomedusa gehafie differs from P. schweinfurthi and P. somalica by the presence of thymine (T) instead of cytosine (C) at positions 125, 267, 287 and 345, by the presence of adenine (A) instead of guanine (G) at position 180, by the presence of guanine (G) instead of adenine (A) at position 223, by the presence of cytosine (C) instead of thymine (T) at position 236, and by the presence of adenine (A) instead of cytosine (C) or thymine (T) at position 268. Furthermore, P. gehafie differs from P. schweinfurthi by the presence of cytosine (C) or guanine (G) instead of adenine (A) at position 147, by the presence of adenine (A) instead of guanine (G) at positions 148 and 297, by the presence of cytosine (C) instead of adenine (A) at positions 166, 191 and 303, by the presence of thymine (T) instead of cytosine (C) at positions 266 and 326, by the presence of cytosine (C) instead of thymine (T) at position 279, by the presence of cytosine (C) instead of a gap at position 298, and by the presence of guanine (G) instead of adenine (A) at position 305. In addition to the above mentioned characters, P. gehafie differs from P. somalica by the presence of adenine (A) instead of thymine (T) at position 94, by the presence of cytosine (C) instead of thymine (T) at positions 95, 122 and 131, by the presence of adenine (A) instead of cytosine (C) at position 123, by the presence of thymine (T) instead of cytosine (C) at position 124, and by the presence of adenine (A) instead of guanine (G) at position 332.
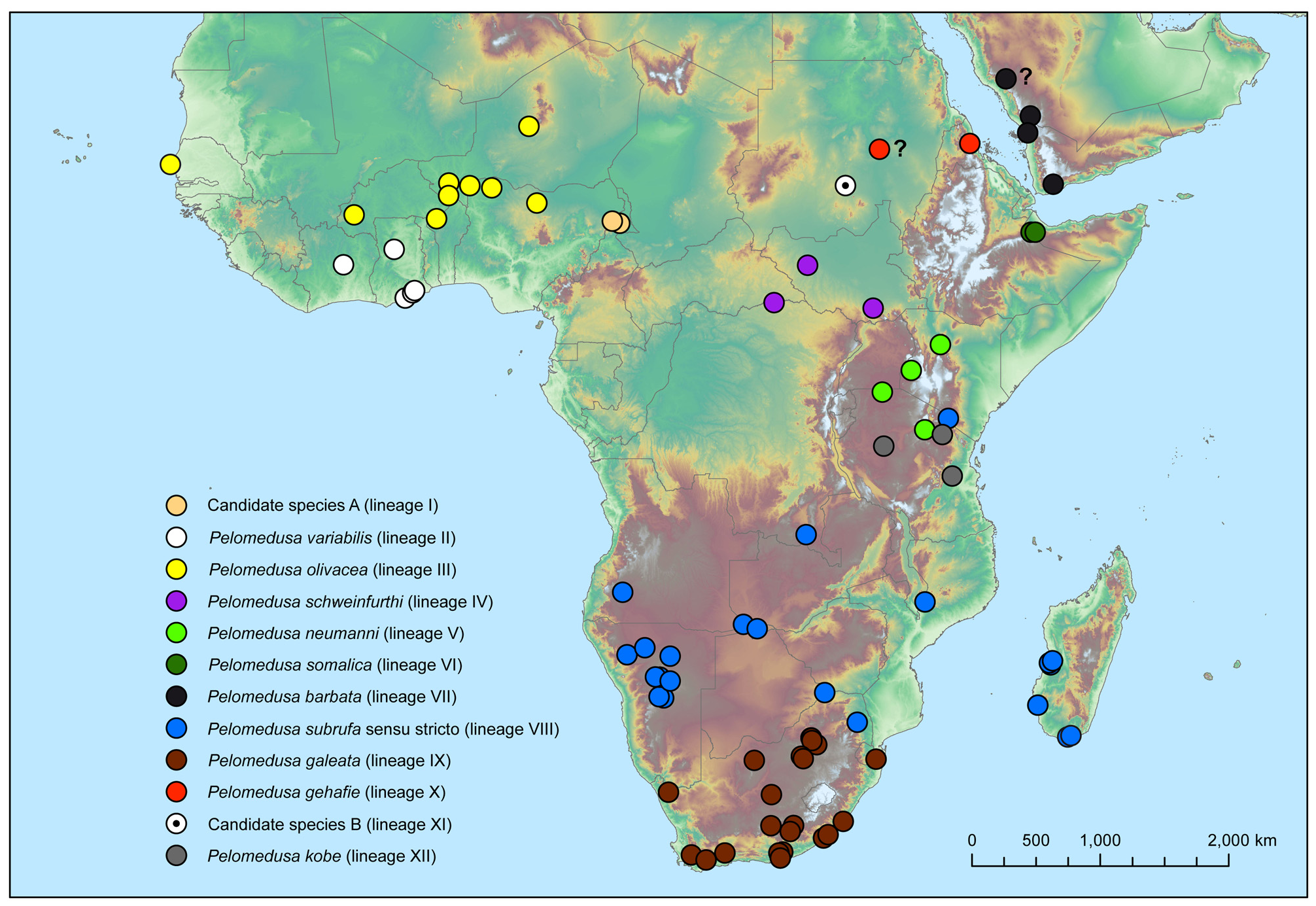
Distribution: Genetically verified specimens of P. gehafie are only known from the type locality in Eritrea and from a second questionable site (Gebel Arary, Naturhistorisches Museum Wien, NMW 24448). The latter locality could to be identified with Jabal Karari, Omdurman near Khartoum, Sudan, because the specimen originates from Joseph Russegger ( 18 November 1802 – 20 June 1863), who is known to have collected near Khartoum. We tentatively identify therefore Gebel Arary with Jabal Karari and show this site in our map ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 ) with a question mark. In the Museum für Naturkunde, Berlin, there is a further genetically verified and morphologically typical specimen originating in “ Abyssinia ” (ZMB 15693, coll. W. Jesse).
Remarks: This is a morphologically distinctive species ( cf. the figures in Fritz et al. 2014 and this study). Pelomedusa gehafie corresponds to mtDNA lineage X of Fritz et al. (2014). It belongs to the northern species group of Pelomedusa , which is well supported in phylogenetic analyses of mtDNA. These reveal that the East African species P. neumanni and P. kobe are closely related to P. gehafie ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). These two species are morphologically easy to tell apart from P. gehafie . Adults of P. gehafie consistently have triangular pectoral scutes not reaching the plastral midseam, whereas the pectorals in the two other species are always in contact in the midline.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Pelomedusa gehafie ( Rüppell, 1835 )
| Petzold, Alice, Vargas-Ramírez, Mario, Kehlmaier, Christian, Vamberger, Melita, Branch, William R., Preez, Louis Du, Hofmeyr, Margaretha D., Meyer, Leon, Schleicher, Alfred, Široký, Pavel & Fritz, Uwe 2014 |
Pelomedusa galeata var. disjuncta
| Vaillant & Grandidier 1910 |