Pelomedusa kobe, Petzold & Vargas-Ramírez & Kehlmaier & Vamberger & Branch & Preez & Hofmeyr & Meyer & Schleicher & Široký & Fritz, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3795.5.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:9394634C-9836-4973-868B-BDEE414E4EA8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4915091 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CB02879F-F93B-FFCE-FF74-FA22FA54FE12 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Pelomedusa kobe |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pelomedusa kobe sp. nov.
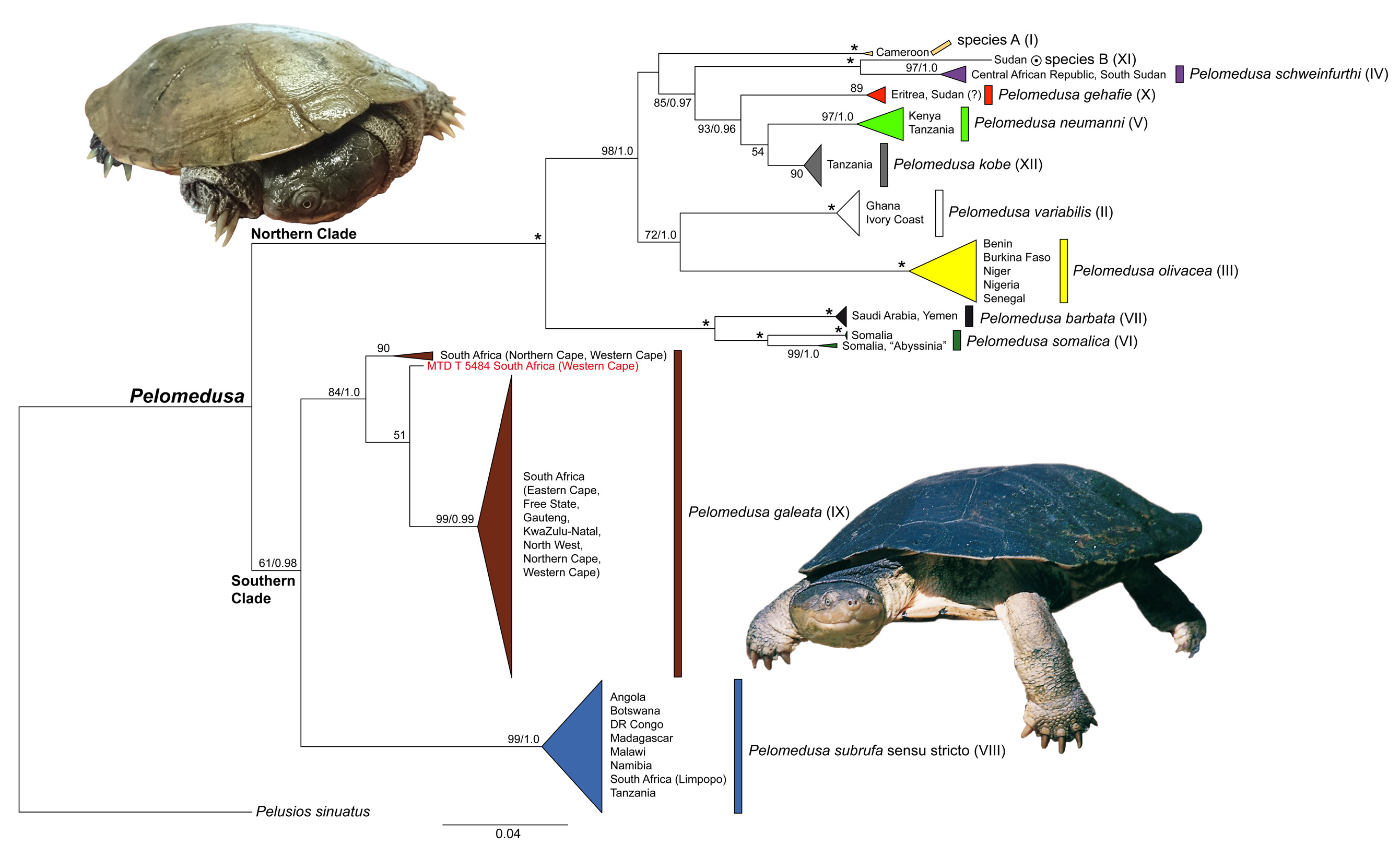
Diagnosis: Medium-sized to, perhaps, large-sized helmeted terrapins with a known maximum straight carapacial length of 15.9 cm. Pectoral scutes rectangular with wide midseam contact or triangular with narrow midseam contact. Normally one large undivided temporal head scale present. Two, rarely three, small barbels under chin. Larger specimens with chestnut carapace and yellow plastron with darker elements along the distal seams; soft parts ventrally lighter than dorsally. Pelomedusa kobe differs from all other Pelomedusa species except P. gehafie , P. subrufa sensu stricto and candidate species B by the presence of guanine (G) instead of adenine (A) at position 223 of the 360-bp-long reference alignment of the 12S rRNA gene (Supporting Information). Pelomedusa kobe differs from these three species by the presence of cytosine (C) instead of thymine (T) at position 188 and from the individual species as shown in Table 5 View TABLE 5 .
Holotype: Zoologische Staatssammlung München ( ZSM 334 View Materials /1978:1, juvenile, Naberera, Manyara, Tanzania, S4°11.66 E36°55.74; leg. J. Popp, 16 July 1960; Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 bottom). GoogleMaps
Description of the holotype: Straight carapacial length 7.5 cm, plastral length 6.5 cm. Pectoral scutes with wide midseam contact. One large undivided temporal scale on each side of head. Two small barbels under chin. Carapace chestnut; plastron yellow with some darker elements concentrated along the seams; gulars, intergular and anals mostly dark. Soft parts dorsally greenish brown, ventrally ochre.
Paratypes: Museum für Naturkunde , Berlin ( ZMB 11741, female, Pumbo creek , Monda / Unguru, Morogoro, Tanzania; ZMB 11742, juvenile, Tabora, Tanzania) ; Zoologische Staatssammlung München ( ZSM 285 View Materials /1937:1–3, male and two juveniles, Tanganyika; ZSM 334 View Materials /1978:2, hatchling, same data as holotype; ZSM 96 View Materials /1960:1–5, two hatchlings and three juveniles, same data as holotype) GoogleMaps .
Derivatio nominis: The species name kobe is the Swahili word for terrapin. It is used as a noun in apposition (ICZN 1999: Art. 31.1).
Distribution: Only known from Tanzania, where it occurs in the Arusha region in close proximity to, or in sympatry with, P. neumanni and P. subrufa .
Remarks: The genetic lineage corresponding to P. kobe was previously unknown. Pelomedusa kobe belongs to the northern species group of Pelomedusa and is related to P. gehafie and P. neumanni ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ).
Pelomedusa kobe most likely reaches a much larger size than c. 16 cm because the largest type specimens still have wide fresh growth rings. One of the paratypes ( ZMB 11742) has the temporal scales on each side of the head divided into two smaller scales, whilst all other types have large undivided temporal scales. Hatchlings of P. kobe have conspicuous light horn-coloured shell margins. The paratype ZSM 96 View Materials /1960:1 has three barbels under the chin .
| ZMB |
Museum für Naturkunde Berlin (Zoological Collections) |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |