Megasyringophilus aquilus Skoracki, Lontkowski and Stawarczyk, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.2840.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5294559 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03DC87DB-FF52-FF61-70B5-FF0EFD5EFC8C |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Megasyringophilus aquilus Skoracki, Lontkowski and Stawarczyk, 2010 |
| status |
|
Megasyringophilus aquilus Skoracki, Lontkowski and Stawarczyk, 2010 View in CoL
( Figs. 163–165 View FIGURE 163 View FIGURE 164 View FIGURE 165 )
Megasyringophilus aquilus Skoracki et al., 2010d: 1204 View in CoL , figs. 1–5.
Type host: Aquila rapax (Temminck) (Falconiformes: Accipitridae ). Type locality: South Africa.
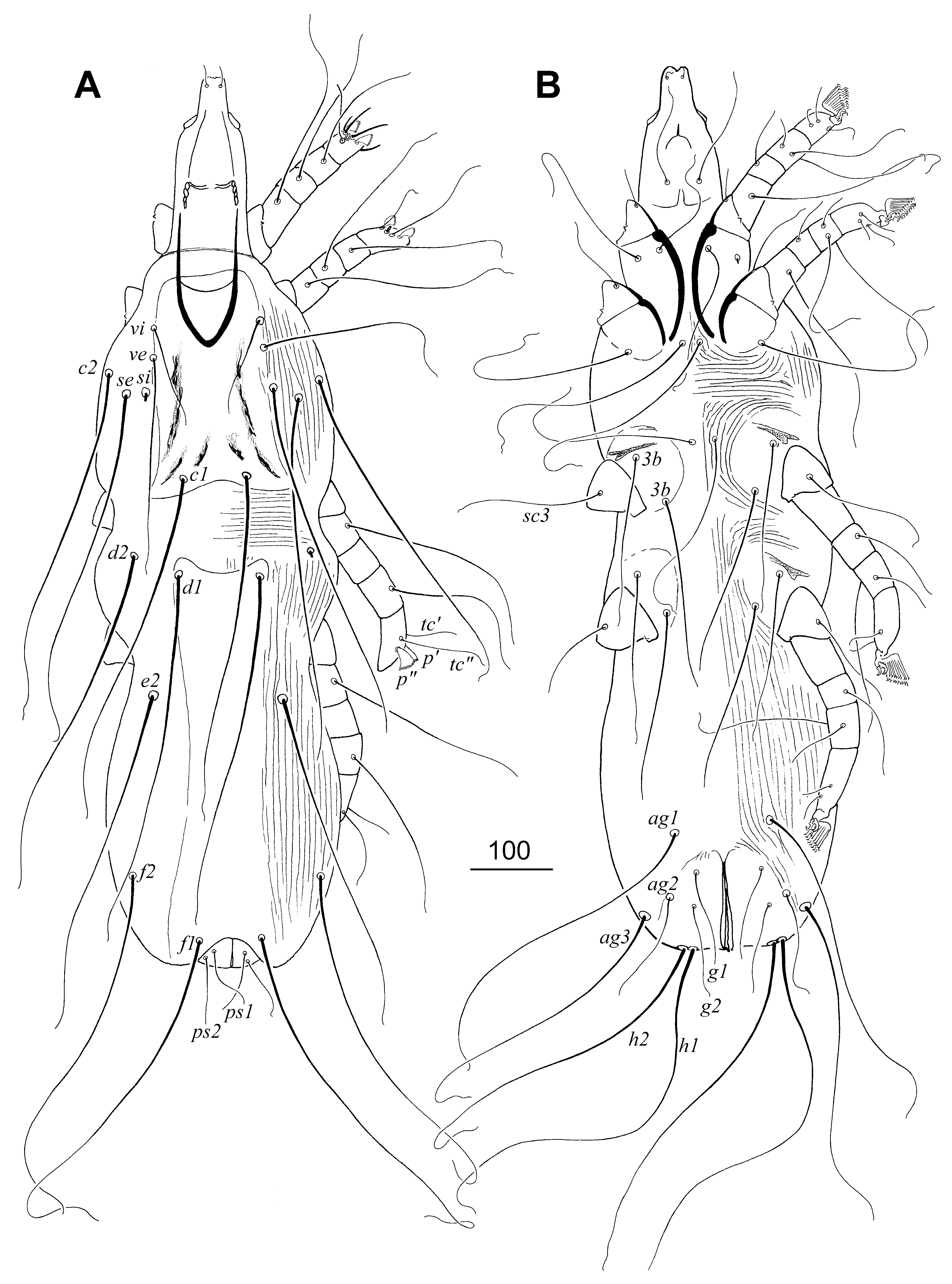
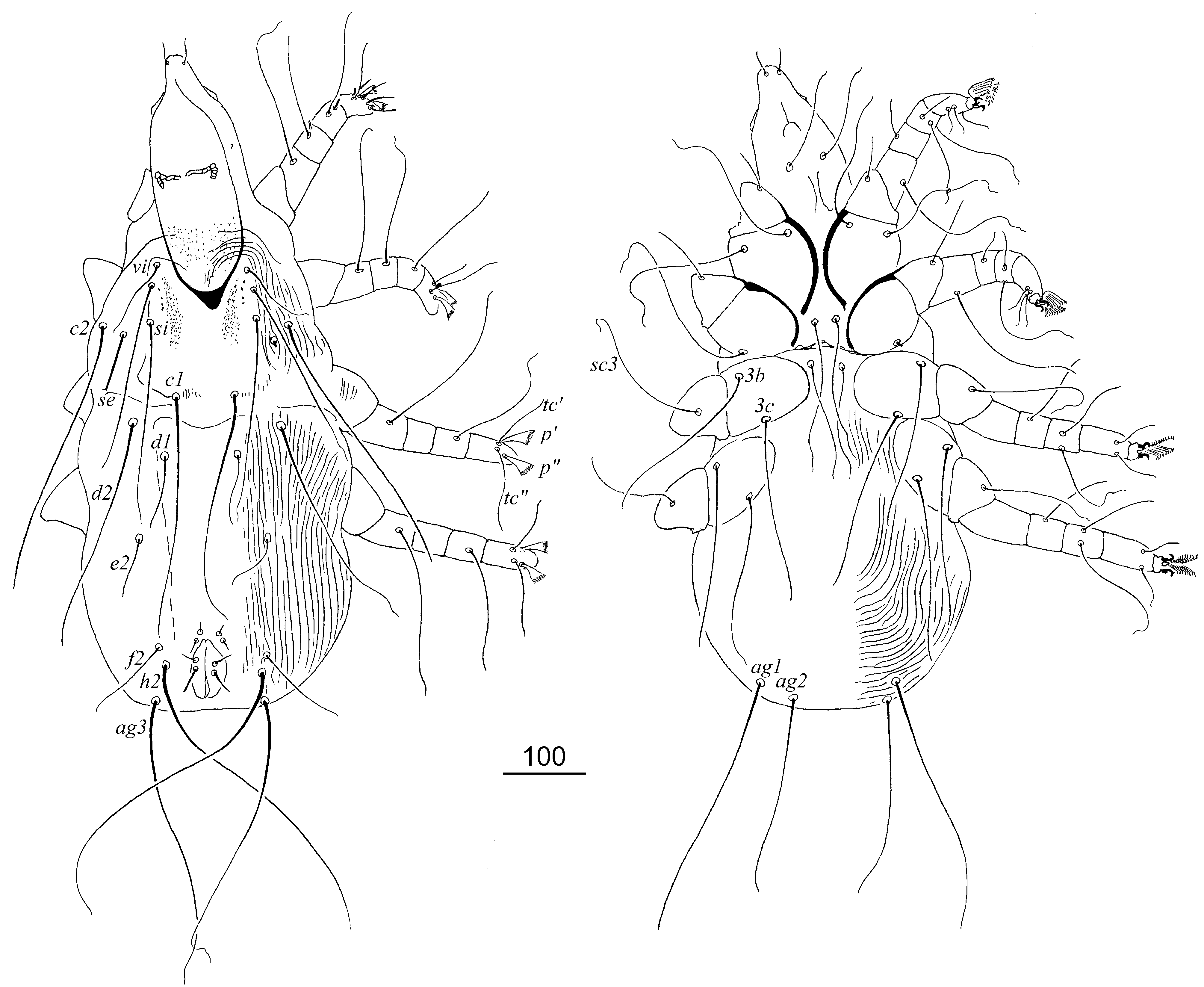
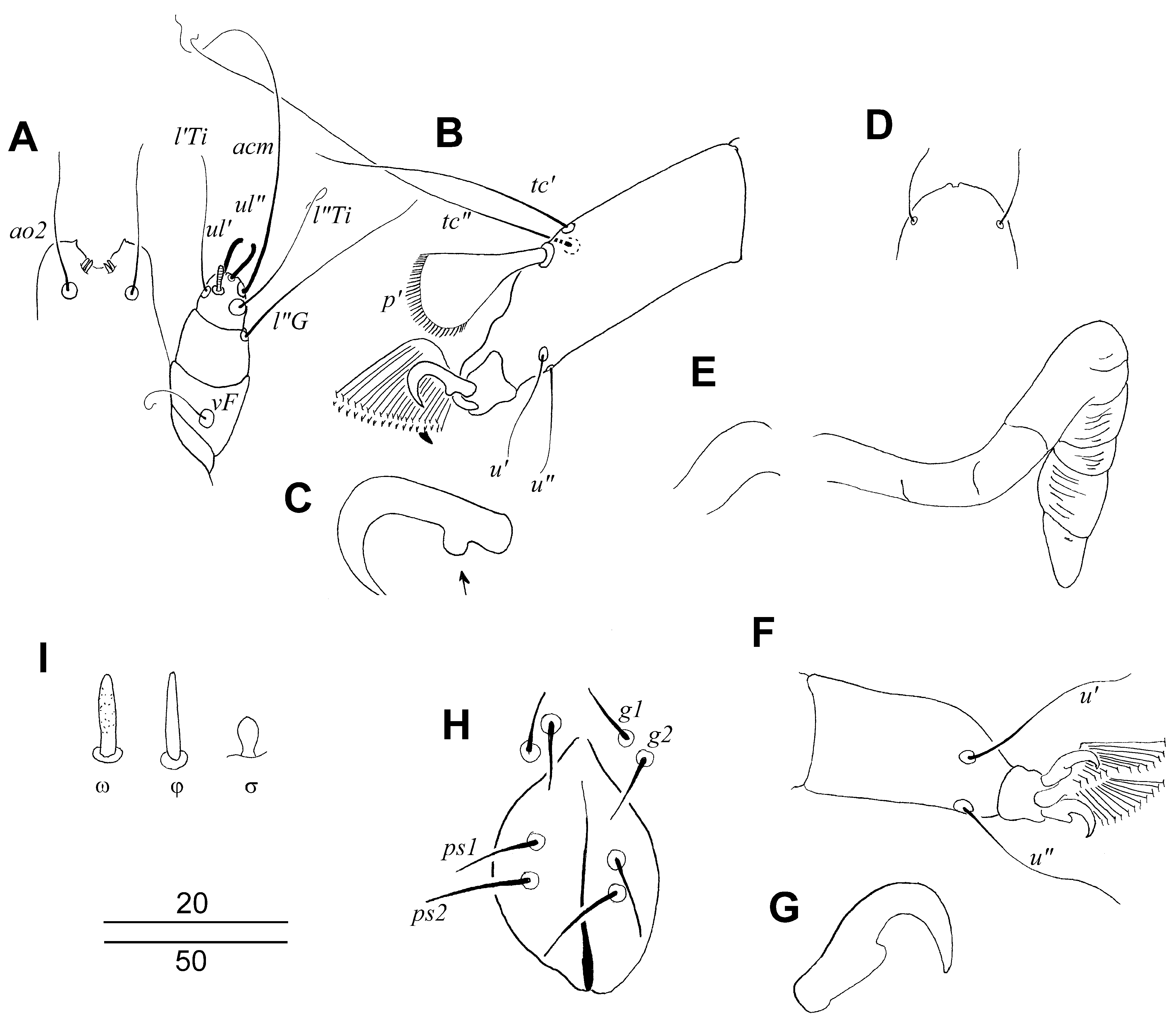
FEMALE (holotype and 6 paratypes). Total body length 1130–1170. Gnathosoma . Infracapitulum apunctate. Hypostomal apex ornamented by 1 pair of small protuberances. Stylophore apunctate, slightly constricted posteriorly, 315–325 long. Movable cheliceral digit, 215–220 long. Each medial branch of peritremes with 2–3 chambers, each lateral branch with 6–8 clearly visible chambers. Idiosoma . Propodonotal shield well sclerotized, with sculptured ornamentation, apunctate, bearing bases of setae vi, ve, si and c1. Length ratio of setae vi: ve: si 1:2:3.5–4. Bases of setae si and c2 situated at same transverse level, bases of setae se situated slightly posterior to them. Hysteronotal shield fused to pygidial shield, apunctate. Setae f2 situated far from level of setae f1. Terminal setae f1, f2, h1 and h2 long. Genital setae g1 and g2 twice as long as pseudanal setae ps1 and ps2. Setae ag1 2.3–2.5 times longer than ag2. All coxal fields apunctate. Setae 3c slightly longer than 3b. Legs. Apodemes I divergent, fusion of apodemes I and II indiscernible. Apodemes III and IV visible. Claws of legs I–IV with basal angle. Tectals setae tc” of legs III and IV twice as long as tc’III–IV. Fan-like setae multiserrate, with ca. 35 short tines. Length ratio of setae l’RI: l’RII: l’RIII: l’RIV 1:3:5:3. Length of setae: vi 130–145, ve 250–285, si 460–520, se 390–485, c1 400– 450, c2 410–475, d1 435–510, d2 420–460, e2 400–450, f1 485, f2 485, h1 460, g1 and g2 130–135, ps1 and ps2 65–70, ag1 340–420, ag2 145–165, ag3 385, tc’III–IV 60–70, tc”III–IV 145, 3b 195–220, 3c 225–250, l’RI 30–35, l’RII 90–105, l’RIII 145–155, l’RIV 90.
MALE (3 specimens from additional host, Aquila pomarina ). Total body length 785–820. Gnathosoma . Infracapitulum apunctate. Hypostomal apex smooth. Stylophore constricted posteriorly, punctate, 305 long. Movable cheliceral digit 250–270 long. Each medial branch of peritremes with 3–4 chambers, each lateral branch with 5–6 clearly visible striated chambers. Idiosoma . Propodonotal shield well sclerotized, punctate, bearing bases of setae vi, ve, si and c1. Length ratio of setae vi: ve: si 1:2.2–2.4:2.3. Bases of setae si and c2 situated at same transverse level, bases of setae se situated slightly posterior to them. Hysteronotal shield fused to pygidial shield, apunctate. Setae d2 3.2 times longer than d1. Setae h2 3.3–3.5 times longer than f2. Length ratio of setae ag1:ag2:ag3 1.7:1:1.7. All coxal fields apunctate. Setae 3b and 3b subequal in length. Setae g1 situated anterior to level of setae g2. Legs. Apodemes I divergent, fusion of apodemes I and II indiscernible. Apodemes III and IV indiscernible. Claws of legs I–IV with basal angle. Tectals setae tc” of legs III and IV 1.8 times longer than tc’III–IV. Fan-like setae multiserrate, with ca. 35 short tines. Length ratio of setae l’RI: l’RII: l’RIII: l’RIV 1:1.5–2:3.2–4:3.2. Lengths of setae: vi 100–120, ve 230–255, si 270, c1 285, c2 330–345, d1 90, d2 285, e2 70, f2 115–125, h2 400–410, ps1 50 ps2 60, ag1 300–340, ag2 190–205, ag3 350–375, tc’III–IV 60–65, tc”III–IV 105–115, 3b 220–230, 3c 220– 230, l’RI 50–60, l’RII 90–100, l’RIII 190–200, l’RIV 160–190.
Type material examined. Aquila rapax (Temminck) (Falconiformes: Accipitridae ): female holotype and 10 female paratypes ( AMU –SYR.265) (bod.); SOUTH AFRICA, 24 June 1940, no other data .
Type material deposition. Holotype deposited in the AMU, paratypes in the AMU and ZISP.
Non-type material examined. Aquila pomarina Brehm (Accipitridae) : 7 females, 10 nymphs ( AMU – SYR.266) (bod.); POLAND, Opolskie, Tulowice, Niemodlin , 21 July 1902. Material deposited in the AMU and ZISP. Host specimen deposited in the MNHW. Accipiter nisus (Linnaeus) (Accipitridae) : 6 females and 5 males ( AVB 07–2010 – 001 ); KAZAKHSTAN, Ongtustik Qazaqstan, Chockpak Ornithological Station , elevation 1134 m. (42°30'45.2"N, 70°35'46.2"E), 20 October 2007, coll. A.V. Bochkov. Material deposited in the ZISP and AMU .
Host range and habitat. In the Palaearctic region this species inhabiting quills of body feathers of two accipitrid birds, Aquila pomarina and Accipiter nisus .
Distribution. Palaearctic: Poland and Kazakhstan.
| ZISP |
Zoological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Megasyringophilus aquilus Skoracki, Lontkowski and Stawarczyk, 2010
| Skoracki, Maciej 2011 |
Megasyringophilus aquilus Skoracki et al., 2010d: 1204
| Skoracki, M. & Lontkowski, J. & Stawarczyk, T. 2010: 1204 |