Pseudosteineria sinica, Huang & Li, 2010
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2010.501530 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/039B4C55-FFD4-FFD5-76FA-FD37FE02FEFB |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Pseudosteineria sinica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Pseudosteineria sinica sp. nov.
( Figures 1 View Figure 1 , 2 View Figure 2 )
Type material
Four males and three females were measured and studied. Holotype: 31 on the slide R2008731-2 ; paratype: ♀ 1 on the slide R2008802-7 ; paratypes: three males and two females on the slides R2008731 - 2,3 and R2008802 - 4,6 respectively.
Type locality and habitat
Intertidal sandy sediment at Rizhao coast (119° 34′ E, 35° 26′ N) of the Yellow Sea.
Etymology
This species is named for the country of the type locality, PR China .
Measurements
Also see Table 1.
⎯282 M1162
Holotype 31: 1360 µm; a = 25.7, b = 4.8, c = 6.9, Spic l = 60, Spic r = 48 19 50 53 42
⎯278 V 1176
Paratype
♀ 1: 1365 µm; a = 20.1, b = 4.9, c = 7.3, V % = 663%
20 61 68 46
Description
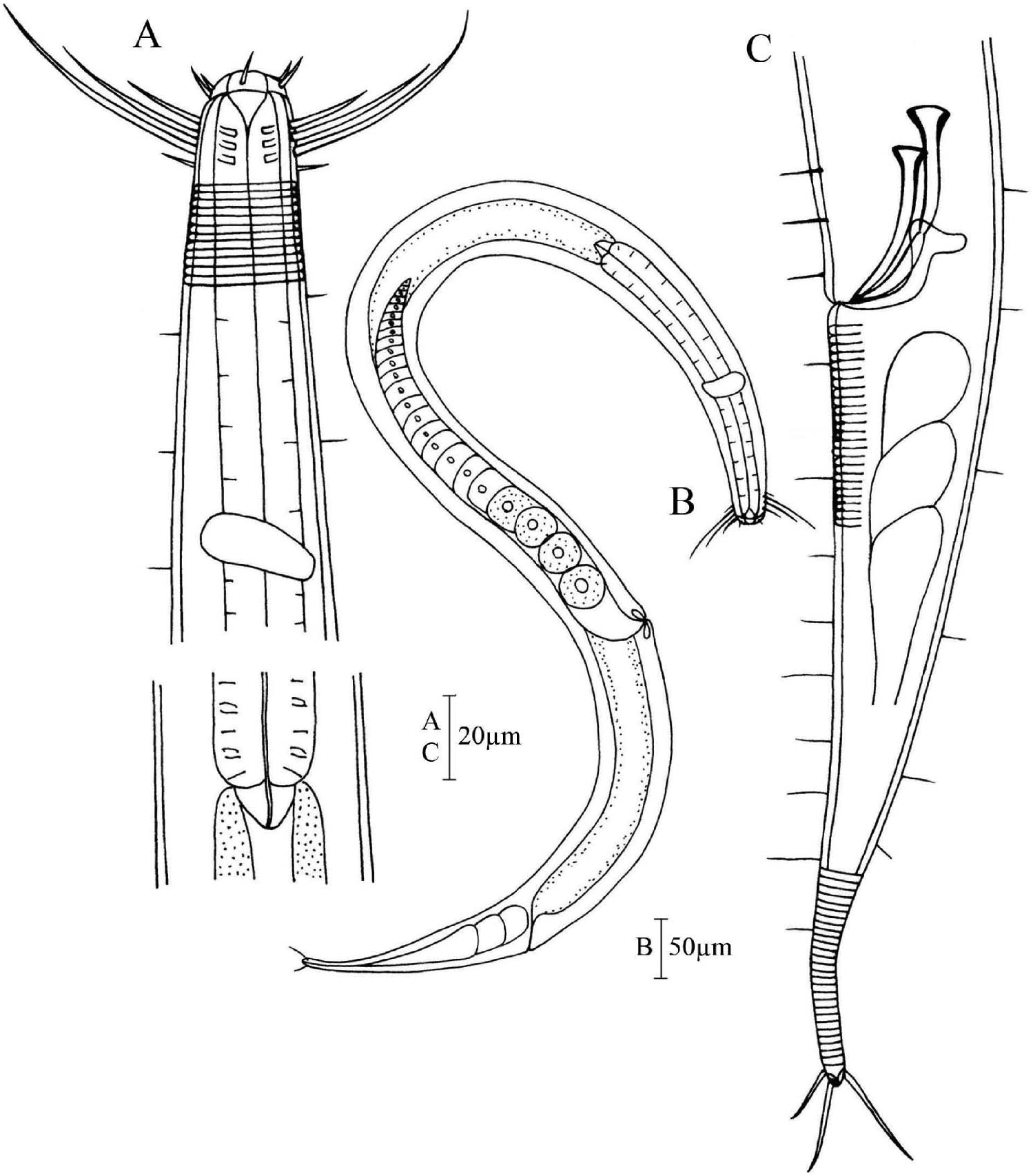
Males. Body spindle-shaped, gradually tapering towards both extremities, more pronounced in tail region ( Figure 1B View Figure 1 ); 1250–1360 µm long and 53–68 µm wide at maximum body diameter. Cuticle with visible annulations, beginning at base of buccal cavity and ending at tail tip.
Buccal cavity with hemispherical cheilostom and conical pharyngostom ( Figures 1A View Figure 1 , 2B View Figure 2 ). Labial region set off. Six lips slightly inflated. Anterior sensilla arranged in two circles: an anterior one with six inner labial papillae and an outer one with 10 sensilla, i.e. six longer (9 µm) outer labial setae and four shorter (5 µm) cephalic setae. Prominent subcephalic setae arranged in eight short longitudinal rows (subdorsal, laterodorsal, lateroventral and subventral on both sides of body) just behind cephalic setae. Each group with 3–4 long setae. Length of subcephalic setae increasing gradually from anterior to posterior seta in every row ( Figure 2A, B View Figure 2 ). Length of shortest about 16 µm, longest about 53 µm. Somatic setae short, scattered over body.
Amphidial fovea not observed. Pharynx cylindrical, about 275 µm long (21% of total body length). Pharyngo-intestinal junction with cardia. Nerve ring at about 105 µm from anterior end (at 38% of pharyngeal length).
Ventral gland not observed.
Tail conico-cylindrical, 162–198 µm (about 4.2 a.b.d.) long, with distal fourth cylindrical part. On conical part of tail, long ventral setae distributed densely. Tail tip bearing three terminal setae, length to 29 µm. Three caudal glands visible.
Spicules paired, unequal in length ( Figure 1C View Figure 1 ). Left spicule longer (average 58 µm), divided into two sections jointed in middle, proximal section with large manubrium ( Figure 2C View Figure 2 ). Right spicule shorter (46 µm), without indentation ( Figure 2D View Figure 2 ). Both spicules curved with proximal capitulum and distal taper tip. Gubernaculum with dorsocaudal apophysis ( Figure 1C View Figure 1 ). Precloacal supplement absent. Anterior testis outstretched and situated to left of intestine; posterior testis reflexed and disposed to right of intestine.
Females. Similar to males in most respects. Body 1185–1570 µm long and 51–69 µm wide at maximum body diameter. A single anterior outstretched ovary, situated to left of intestine. Some round adult eggs presence ( Figure 1B View Figure 1 ). Vulva at about 64% of the body length from the anterior end.
Differential diagnosis
Body spindle-shaped, cuticle distinctly annulated. Amphidial fovea difficult to observe. Spicules unequal in length. Left spicule longer, divided into two sections jointed in the middle. Right spicule shorter, simple, without articulation. Both spicules curved with proximal capitulum; tapered distally. Gubernaculum with dorsocaudal apophysis. Pseudosteineria sinica sp. nov. is similar to Pseudosteineria inaequispiculata (Platonova) Gerlach and Riemann, 1973 in unequal spicules, but the latter has a clearly discernible round amphidial fovea and is without apophysis of gubernaculum. This new species can be easily identified by unequal and articulated spicules from other species in Pseudosteineria .
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |