Stethynium, Enock, 1909
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4773.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B1D8D67C-4FDC-477E-872F-E8BCD4D027FB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3845133 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038A0765-FE83-B826-48D5-F912887CF988 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stethynium |
| status |
|
STETHYNIUM Enock, 1909 View in CoL View at ENA
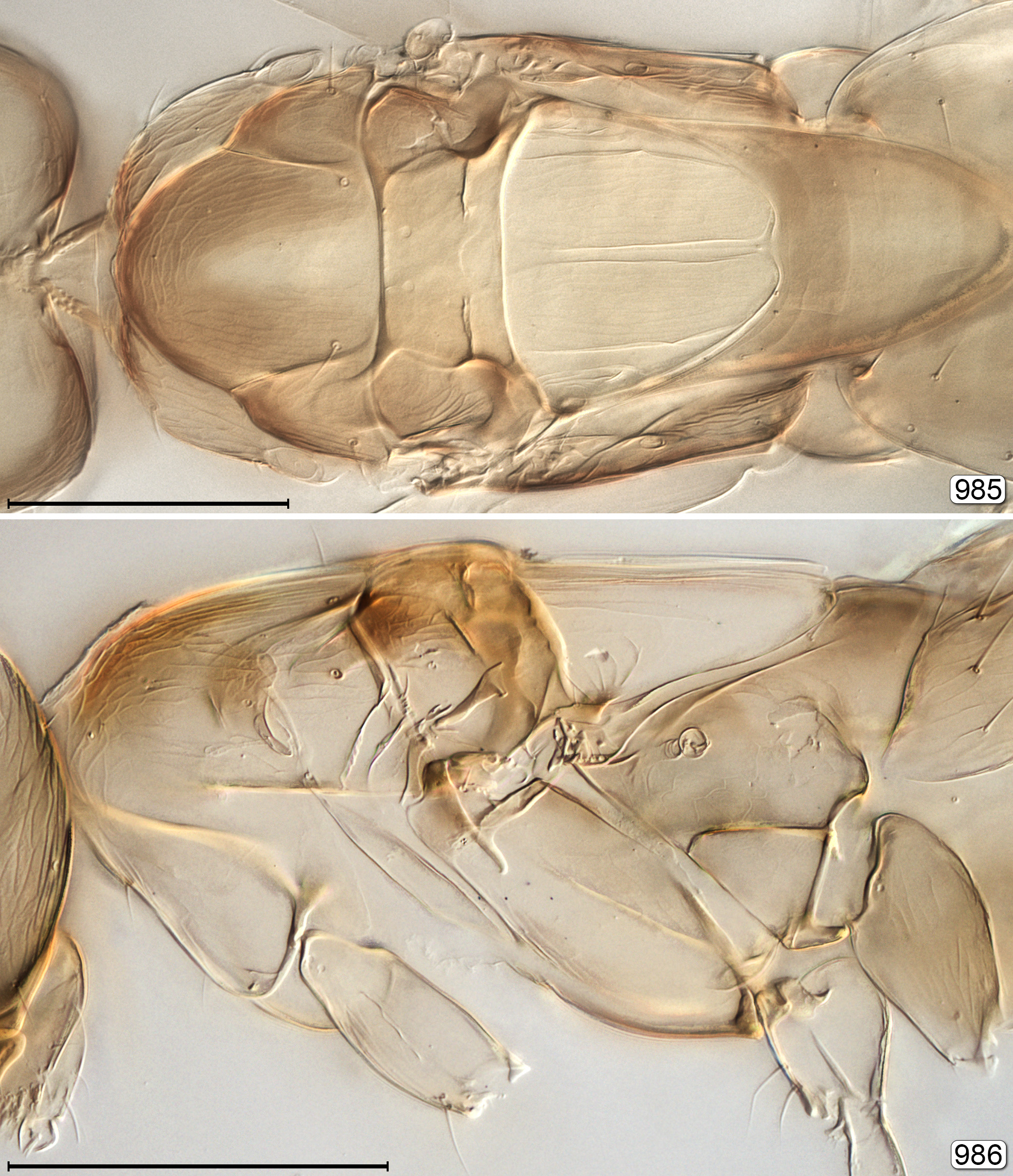
( Figs 979 View FIGURE 979 –1010)
Stethynium Enock, 1909: 452 View in CoL . Type species: Stethynium triclavatum Enock, 1909 View in CoL , by monotypy.
Diagnosis. Body length 525–715 μm. Clava 3-segmented, the sutures between segments strongly oblique ( Fig. 984 View FIGURES 980–984 ); mandible with 4 teeth (Fig. 1000); frenum longitudinally divided, with paramedial plate longer than wide; second phragma with rounded (convex) apex ( Figs 985 View FIGURES 985, 986 , 1001); fore wing with distinct rounded lobe behind venation ( Fig. 987 View FIGURES 987, 988 ). Male with complex asymmetrical genitalia ( Figs 993 View FIGURES 991–994 , 1010).
Discussion. Among the four other genera in the Nearctic with frenum longitudinally divided: Anagrus , Krokella , Platystethynium ( Platypatasson) and Schizophragma , only Krokella also has a 3-segmented clava. Stethynium differs from it by the mandible normal, with 4 equal teeth in both sexes, fore wing more evenly rounded and with a distinct lobe behind apex of venation, and venation shorter.
Nearctic hosts. Unknown. Extralimital hosts are Hemiptera : Cicadellidae , including an important pest in vineyards, Empoasca vitis (Goethe) ( Viggiani 2002) .
Important reference. Huber (1987).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Stethynium
| Huber, John T., Read, Jennifer D. & Triapitsyn, Serguei V. 2020 |
Stethynium
| Enock, F. 1909: 452 |