Dinychus lepus, Kontschán, Jenő & Starý, Josef, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3895.4.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3B26216E-84B7-4B7A-AAD8-B292E9486FA2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5631156 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CE627F-A35E-8766-FF2D-19D7E8FFF9F1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Dinychus lepus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Dinychus lepus sp. nov.
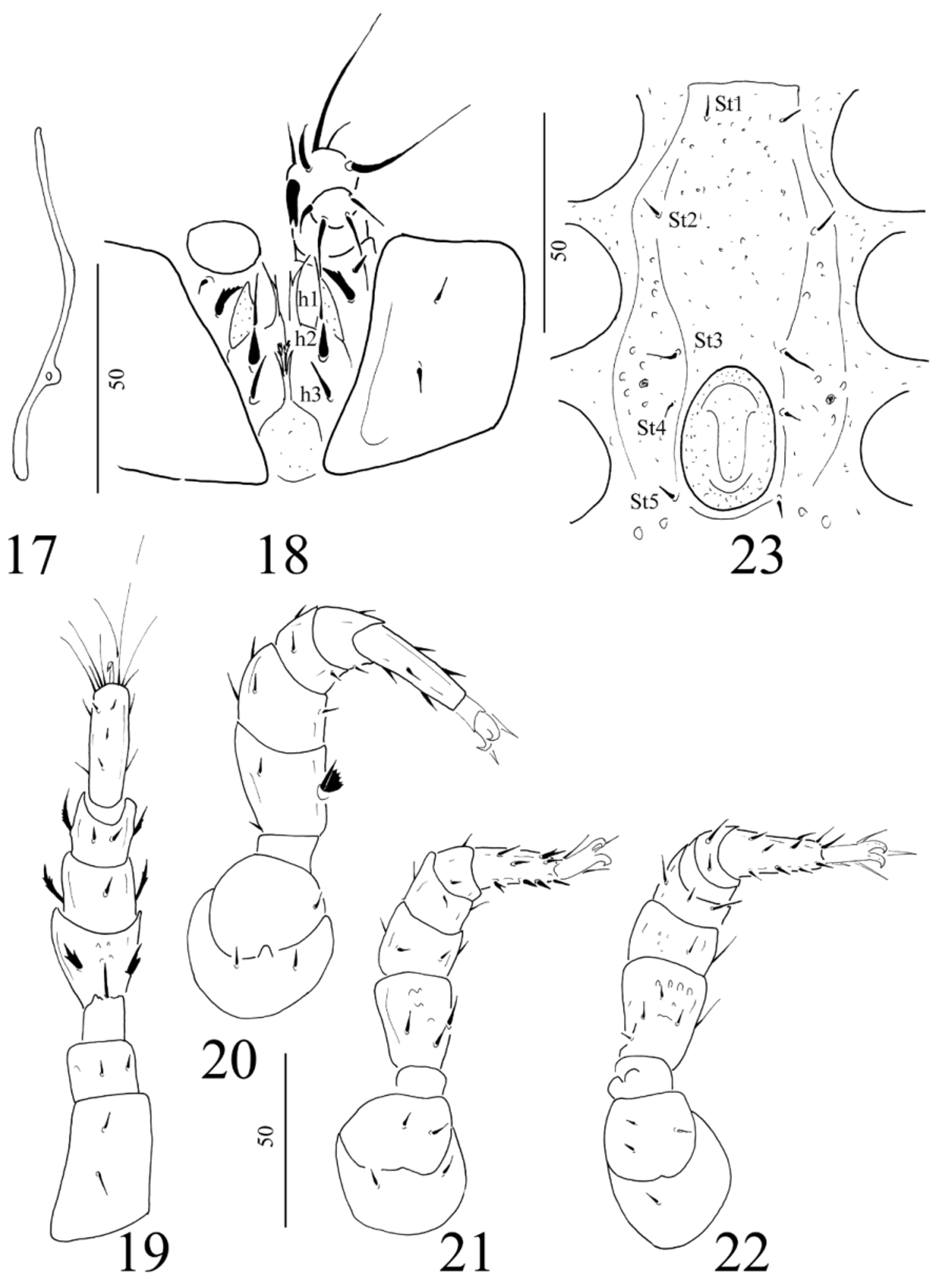
( Figs 12–23 View FIGURES 12 – 16 View FIGURES 17 – 23 )
Material examined. Holotype. Female. Mad-89/8: Madagascar (Prov. Antsiranana [Diego-Suarez], Sous-préf. Antsiranana): Parc National Montagne d’Ambre (= Ambohitra), vers la Petite Cascade, forêt primaire, prélèvement de sol, 980m; 23 November 1989; B. Hauser coll. Paratypes. Five females and seven males. Locality and date same as in holotype ( NHMG).
Description. Female. Length of idiosoma 1080–1100 µm, width 660–670 µm (n=6). Idiosoma oval, dorsally domed.
Dorsal idiosoma ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Dorsal and marginal shields completely separated. Dorsal shield covered by oval pits and bearing short and needle-like setae (ca 6–7 µm), central part of dorsal shield elevated in caudal area and bearing numerous bearing short and needle-like setae (ca 5–6 µm) ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Marginal shield covered by oval pits and bearing numerous short (ca 8–9 µm) and robust setae ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Vertical setae j1 long (ca 15–17 µm), wide and rabbit ear-like ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Posterior platelets bearing one pair of spine-like and three pairs of apically serrate setae (ca 8–9 µm) ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ).
Ventral idiosoma ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 12 – 16 ). Anterior margin of sternal shield serrate. Sternal shield smooth, with some shallow oval pits between St1 and St4, arranged in rows. Sternal setae smooth and needle-like St1-St3 and St5 long (ca 7–9 µm), St4 short (ca 4–5 µm). St1 inserted at anterior margin of coxae II, St2 at posterior margin of coxae II, St3 at posterior margin of coxae III, St4 at central area of coxae IV and St5 situated near to basal edges of genital shield. Ventral shield covered by numerous oval pits in central area and with undulate lines in lateral and caudal parts. Two pairs of ventral setae anterior to anal opening short and needle-like (ca 6–8 µm), setae on lateral area of ventral shields long (ca 15–20 µm), robust and spine-like. Adanal setae smooth, short (ca 4–5 µm) and needle-like, postanal seta absent. Genital shield short, linguliform, situated between coxae IV, apical margin rounded, surface covered by oval pits. Prestigmatid part of peritremes longer than poststigmatid one, mostly straight with a little arch on central part ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 17 – 23 ). Base of tritosternum ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 17 – 23 ) narrow, laciniae divided into two smooth lateral and two apically pilose branches.
Gnathosoma ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 17 – 23 ). Corniculi horn-like; internal malae smooth, narrow, apically bifurcated and longer than corniculi. Hypostomal setae h1 needle-like and long (ca 10–13 µm), and h2 short and robust (ca 6–7 µm), h3 short (ca 9–10 µm) and needle-like, h4 short and antler shaped (ca 8–10 µm). Chelicerae with fixed digit longer than movable digit, both bearing a tooth. Trochanter of palp bearing one long, robust and marginally serrate and one short and needle-like ventral setae, other setae on palp needle-like. Epistome marginally serrate in basal part and pilose in apical part.
Legs ( Figs 19–22 View FIGURES 17 – 23 ). Leg I with a small ambulacral claw, legs bearing both marginally serrate and needle-like setae.
Male. Length of idiosoma 960‒970 µm, width 780‒810 µm (n=7). Sternal shield with smooth surface except around genital opening with some oval pits ( Fig. 23 View FIGURES 17 – 23 ). Sternal setae ca 5–7 µm long. Genital shield oval, placed between coxae IV. Gnathosomal setae h1 wider and bearing two spines on basal part. Other characters as in female.
Etymology. The new species is named after the rabbit ear-like j1 setae (rabbit = lepus in Latin).
Remarks. The new Dinychus species differs from the other previously described species by its wide and rabbit ear-like j1 setae, the shape and the position of the genital shield of the female, and the elevated section of the dorsal shield, which is a new and previously unknown character combination in the genus Dinychus .
| NHMG |
Natural History Museum of Guangxi |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.