Terrobittacus longisetus Tan and Hua, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222930903359628 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03CC4F2D-9966-BA23-FEA3-FAFCBD19F69C |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Terrobittacus longisetus Tan and Hua |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Terrobittacus longisetus Tan and Hua View in CoL , sp. nov.
( Figures 5–7 View Figure 5 View Figure 6 View Figure 7 )
Diagnosis
The new species is unique with the distal portion of male gonocoxites bearing one to three pairs of long convergent bristles; the inner surface of epandrial appendages each bearing more than 10 large, black spines clustered on dorsal angle. It differs from its congeners also by the X-shaped blackish carina of the female subgenitale.
It differs from T. implicatus by its larger size; the pterostigma reddish brown; the fork of M 1+2 (FM 1+2) of wing originating slightly before the level of FR 4+5; and cross-veins r-m and m intercrossing with M 1+2 at FM 1+2.
Etymology
The specific name is derived from the Latin, longisetus (long bristles), referring to the one to three long bristles on each side of the caudal side of male gonocoxites.
Description
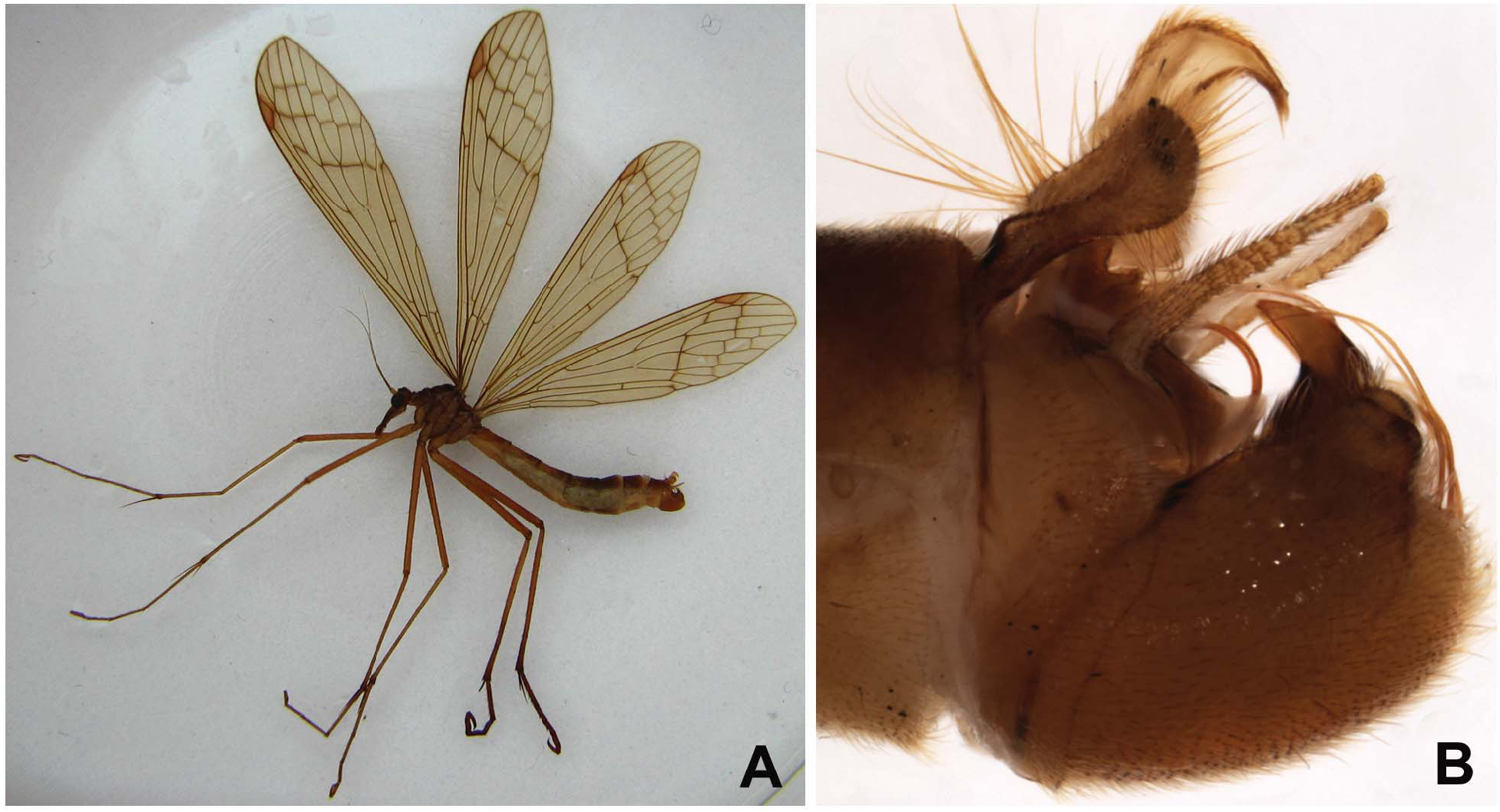
Body yellowish brown. Male body length 13.8–14.6 mm; forewing length 20.3– 20.7 mm, width 4.4–4.7 mm; hindwing length 17.6–17.8 mm, width 3.7–3.9 mm. Female body length 13.7–15.8 mm; forewing length 20.2–21.4 mm, width 4.7– 5.0 mm; hindwing length 17.8–18.6 mm, width 3.9–4.4 mm.
Head. Vertex and frons yellowish brown, with sparse hairs; clypeus and rostrum yellowish brown medially, darker laterally. Maxillary and labial palps yellowish brown; the fifth and fourth segments of maxillary palp about equal length. Antennae filiform; scape and pedicel yellowish brown; flagellum dark brown, with about 18 flagellomeres. Compound eyes black. Ocelli large; ocellar triangle black, with two long setae closely behind the mid ocellus.
Thorax. Pronotum unevenly dark brown; two pairs of setae on its anterior margin. Meso- and metanotum unevenly blackish brown, with pale brown median streak about as wide as scutellum; pleura, coxae and mera light brown. Legs pale brown; hind tarsi and distal hind tibia turning dark brown; tarsomere IV generally with one, but occasionally with two spines on each side.
Wings ( Figure 5A View Figure 5 ). Forewing hyaline with faintly yellowish tinge, without distinct markings; pterostigma conspicuous, reddish brown; a small faint brown fleck at the subdistal part of CuP. Pcv one; Sc ending at level of FR 4+5, far beyond level of FRs; Scv very close to end of Sc, far beyond FRs; Cuv slightly before level of FM; Av absent; 1A terminating at midway of FM and OM; apical cross-veins arranged roughly in three lines each along 1s, 2s and 3s. Hindwing similar to forewing, but Sc ending beyond level of ORs, far before FRs; Scv at midpoint of ORs and FRs.
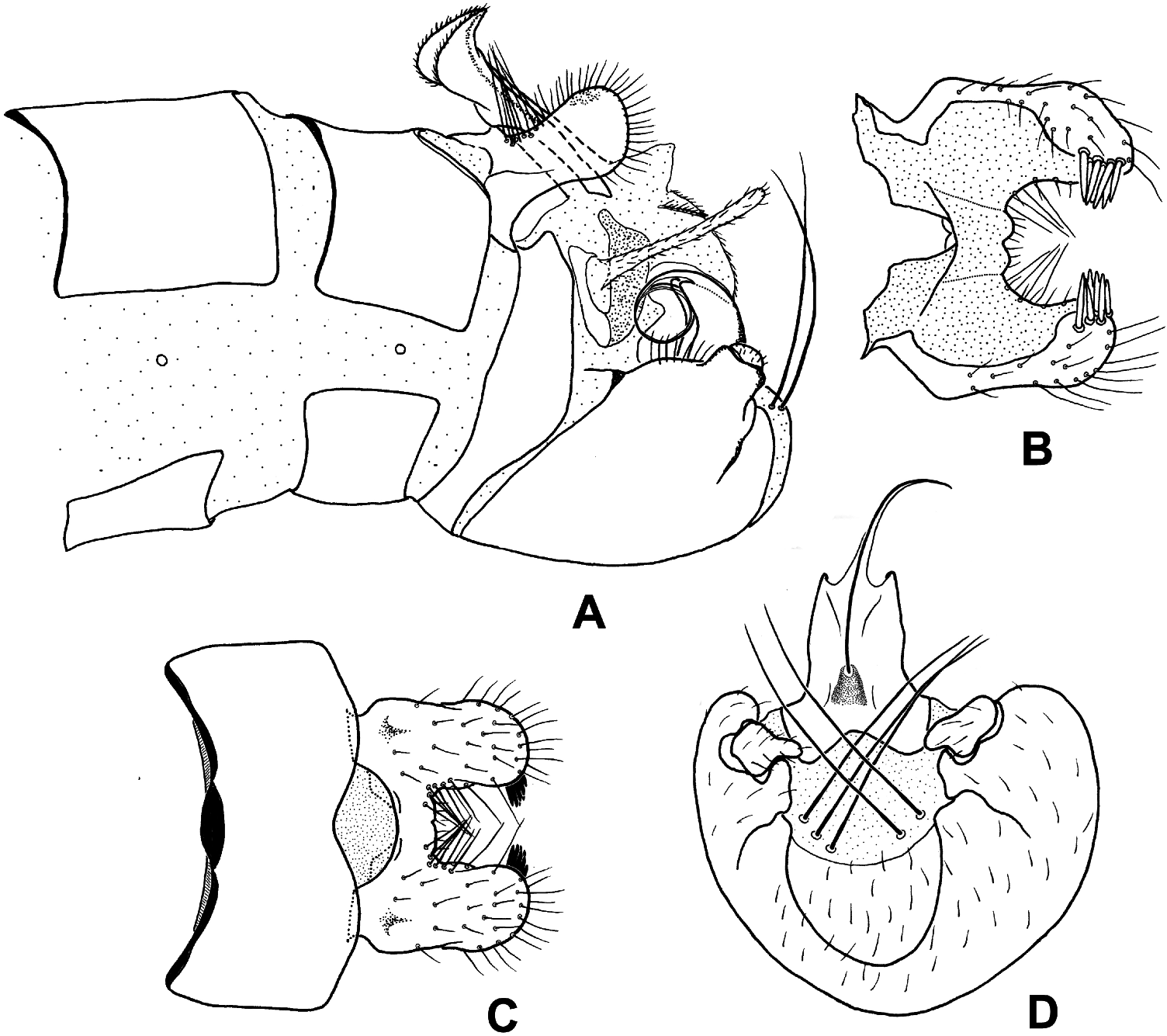
Abdomen of male. Terga II–VIII yellowish to brown, gradually darker; each with narrow black antecosta ( Figure 5A View Figure 5 ); posterior margin of tergum VIII emarginate in V-shape ( Figure 6C View Figure 6 ). Sex pheromone glands between terga VI–VII and VII–VIII single-lobed. Epandrial appendage pale brown, shorter than half length of gonocoxites, roughly quadrangular in shape in lateral view, with numerous long setae along margins ( Figures 5B View Figure 5 , 6A View Figure 6 ); the setae at base of dorsal margin rather long, stiff, intercrossed apically with setae of opposing side ( Figure 6A,C View Figure 6 ); apical angles blunt, with its inner surface thickened and bearing a cluster of more than 10 large black spines ( Figure 6B,C View Figure 6 ). Dorsal part of tergum X completely absent; a pale yellow lateral narrow plate extending posteroventrad and then curved dorsad around base of cercus ( Figure 6A View Figure 6 ). Upper branch of proctiger yellowish brown, protruding between bases of epandrial appendages, strong sclerotized dorsolaterally, with apex curved into a hook-like rostrum of a parrot; lower branch of proctiger short, broad basally and tapering toward apex ( Figure 6A View Figure 6 ). Cerci rather long, about two-thirds as long as gonocoxites ( Figures 5B View Figure 5 , 6A View Figure 6 ). Gonocoxites yellowish brown, very large in size, posteroventrally rounded with U-shaped unsclerotized median area; on caudal margin of membrane area arise one to three pairs of prominently long convergent bristles (slightly longer than cercus) ( Figure 6D View Figure 6 ); Gonostylus very short, mesally curved with apex bluntly rounded, bearing numerous brown setae ( Figure 6D View Figure 6 ). Aedeagus slender, with greatly coiled elongate penisfilum and two small acute basal lobes ( Figure 6A,D View Figure 6 ).
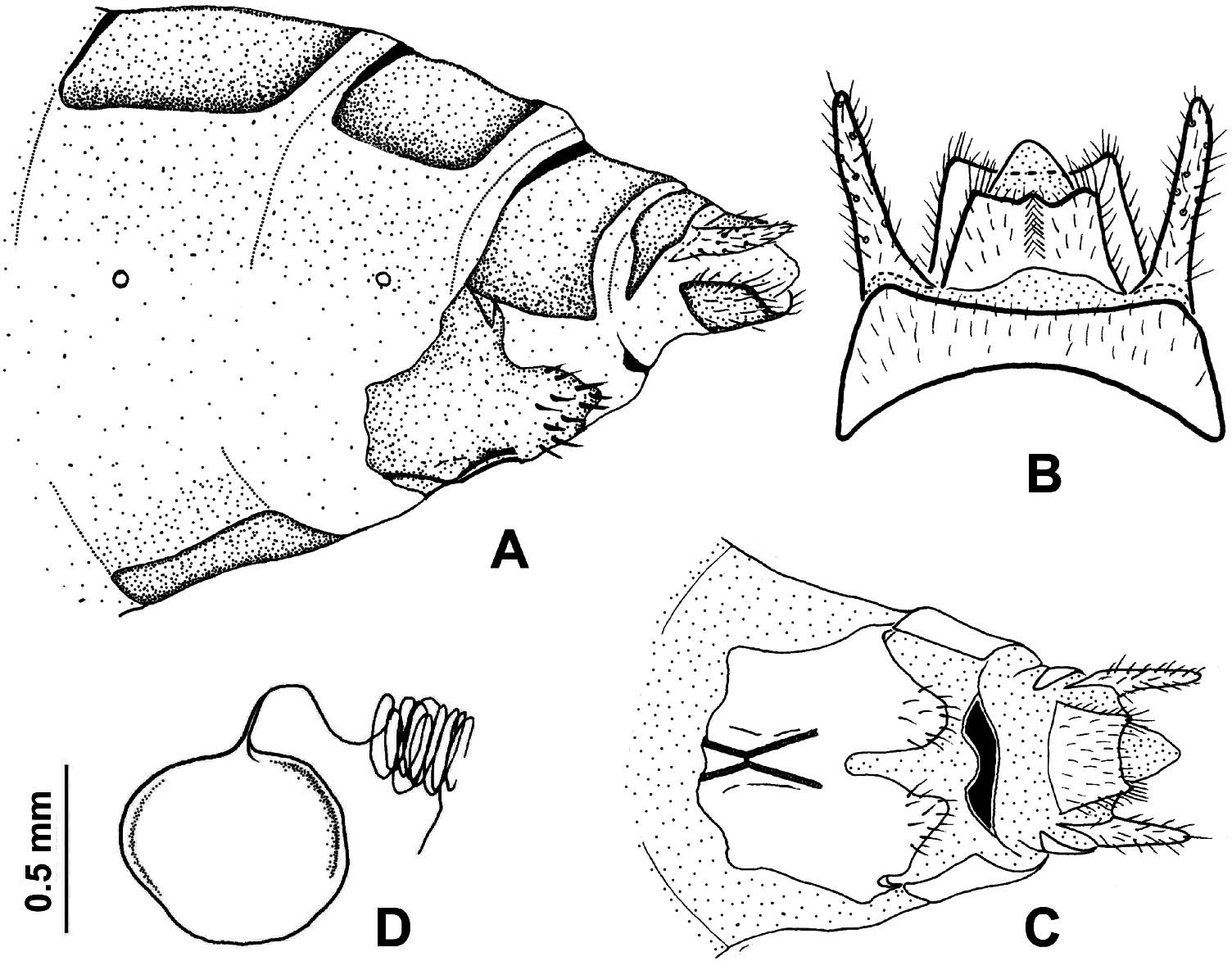
Abdomen of female. Terga II–IX yellowish brown; terga III–IX each with narrow black antecosta. The subgenitale rather small, fused basally, and deeply cleft apically with several black stiff setae; basal half with black, strongly sclerotized carina along midventral line in X-shaped ( Figure 7C View Figure 7 ). Tergum X pale brown, short, not extending ventrad ( Figure 7B,C View Figure 7 ). Supraanale short and broad, almost truncate apically, hairs along its midline intercrossing apically; subanale as long as supraanale, slightly curved cephalad; cerci slender, about twice as long as supraanale ( Figure 7B,C View Figure 7 ). Spermatheca subspherical, 0.6 mm in diameter, with short and very slender rostrum ( Figure 7D View Figure 7 ).
Type specimens
Holotype: male, China: Hunan: Mount Badagongshan, Zhangjiajie , 9 August 2006, coll. Lijun Cai and Huifeng Zhou. Paratypes: 7 males 16 females, same data as holotype, preserved at the Entomological Museum, Northwest A & F University, China ( NWAU) .
| NWAU |
North-West Agricultural University |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |